
Epeolus cruciger, the red-thighed epeolus, is a species of cuckoo bee from the family Apidae. It is endemic to Europe where its main host is the common colletes, although other species of Colletes mining bees have been recorded as hosts.

Epeolus is a genus of cuckoo bees of the tribe Epeolini, the subfamily Nomadinae part of the honey bee family Apidae. They are often known as variegated cuckoo-bees.

Epeolus scutellaris is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Epeolus pusillus, the cuckoo bee, is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Epeolus mesillae is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae.

Triepeolus verbesinae is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Epeolus canadensis is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in North America.
Triepeolus loomisorum is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Epeolus lectoides, the cuckoo bee, is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in North America.

Xenoglossa is a genus of large squash bees in the family Apidae. There are about 11 described species in Xenoglossa.

Epeolus compactus is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Triepeolus simplex is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in North America.

Triepeolus remigatus is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Epeolus carolinus is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in North America.

Epeolus zonatus is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in North America.

Epeolus glabratus is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in North America.
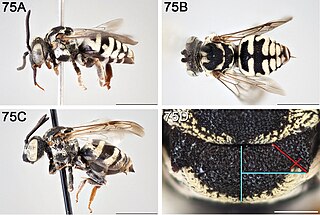
Epeolus olympiellus is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in North America.

Epeolus autumnalis, the cuckoo bee, is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in North America.

Epeolus bifasciatus, the cuckoo bee, is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in Central America and North America.
Triepeolus intrepidus is a species of cuckoo bee in the family Apidae. It is found in Central America and North America.


















