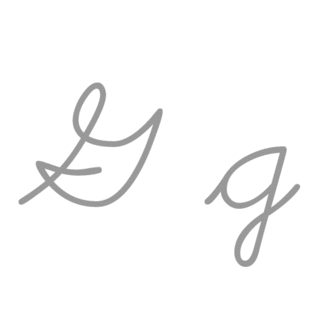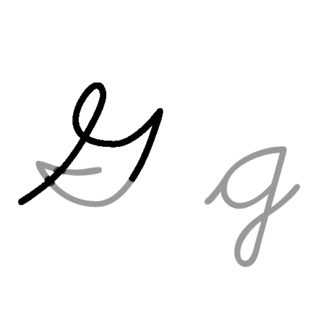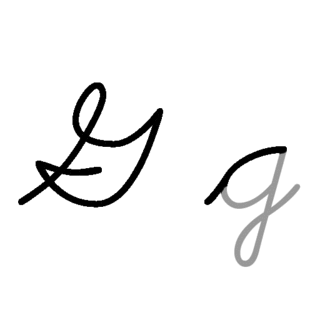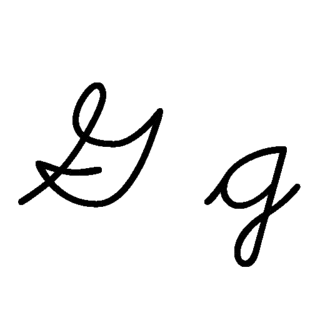In mathematics, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions that produces a third function that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term convolution refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reversed and shifted. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function.
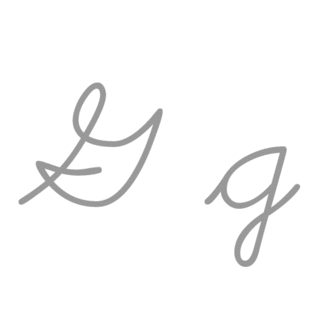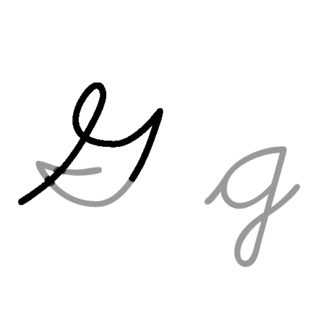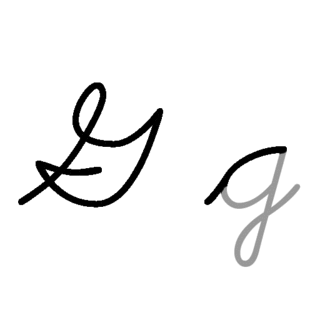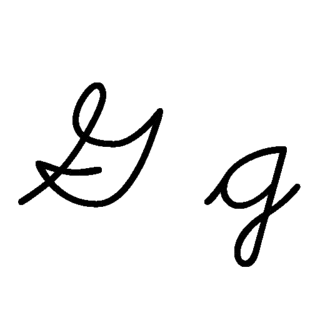
G, or g, is the seventh letter of the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is gee, plural gees.

Gilbert Keith Chesterton was an English writer, philosopher, lay theologian, and literary and art critic. He has been referred to as the "prince of paradox". Of his writing style, Time observed: "Whenever possible Chesterton made his points with popular sayings, proverbs, allegories—first carefully turning them inside out."
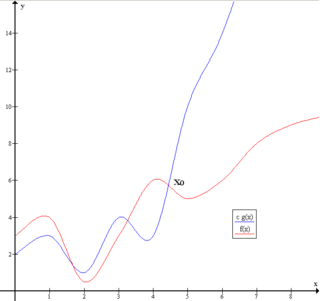
Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a family of notations invented by Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for Ordnung, meaning the order of approximation.

A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions depending on space or time into functions depending on spatial frequency or temporal frequency. That process is also called analysis. An example application would be decomposing the waveform of a musical chord into terms of the intensity of its constituent pitches. The term Fourier transform refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that associates the frequency domain representation to a function of space or time.

Christopher George Latore Wallace, better known by his stage names the Notorious B.I.G., Biggie Smalls, or simply Biggie, was an American rapper and songwriter. Rooted in East Coast hip hop and particularly gangsta rap, he is widely considered one of the greatest rappers of all time. Wallace became known for his distinctive laid-back lyrical delivery, offsetting the lyrics' often grim content. His music was often semi-autobiographical, telling of hardship and criminality, but also of debauchery and celebration.

The Mikoyan MiG-29 is a twin-engine fighter aircraft designed in the Soviet Union. Developed by the Mikoyan design bureau as an air superiority fighter during the 1970s, the MiG-29, along with the larger Sukhoi Su-27, was developed to counter new U.S. fighters such as the McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle and the General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon. The MiG-29 entered service with the Soviet Air Forces in 1982.
The iPhone is a line of smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc. These devices use Apple's iOS mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by then-Apple CEO Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007. Since then, Apple has annually released new iPhone models and iOS updates. As of November 1, 2018, more than 2.2 billion iPhones had been sold.

In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth-generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks which provide connectivity to most current cellphones. 5G networks are predicted to have more than 1.7 billion subscribers worldwide by 2025, according to the GSM Association.

Ephestiodes gilvescentella, the dusky raisin moth, is a moth of the family Pyralidae. It is native to North America, where it has been recorded from California, Arizona, Oklahoma, Utah, Montana, Alberta and British Columbia. It was introduced to Hawaii by commerce.
Ephestiodes erythrella is a moth of the family Pyralidae described by Émile Louis Ragonot in 1887. It is native to North America, where it is found from Texas and Ontario westward, including British Columbia, California and Utah. It is an introduced species in Hawaii.

Ephestiodes infimella is a moth of the family Pyralidae described by Émile Louis Ragonot in 1887. It is native to North America, where it is mostly found in the eastern United States from Maryland to Florida, west to Texas, north to southern Ontario. It is an introduced species in Hawaii.

The Phycitinae are a subfamily of snout moths. Even though the Pyralidae subfamilies are all quite diverse, Phycitinae stand out even by standards of their family: with over 600 genera considered valid and more than 4000 species placed here at present, they unite up more than three-quarters of living snout moth diversity. Together with the closely related Epipaschiinae, they are apparently the most advanced lineage of snout moths.

Ephestiodes is a genus of snout moths. It was described by Émile Louis Ragonot in 1887.
Ephestiodes erasa is a species of snout moth in the genus Ephestiodes. It was described by Carl Heinrich in 1956. It is found in the US states of Florida and Georgia.
Ephestiodes noniella is a species of snout moth in the genus Ephestiodes. It was described by Harrison Gray Dyar Jr. in 1914, and is known from Panama.
Ephestiodes griseus is a species of snout moth in the genus Ephestiodes. It was described by Herbert H. Neunzig in 1990 and is known from the US state of California.