In Greek mythology and Roman mythology, Erebus, or Erebos, is the personification of darkness and one of the primordial deities. Hesiod's Theogony identifies him as one of the first five beings in existence, born of Chaos.

Servius was a late fourth-century and early fifth-century grammarian. He earned a contemporary reputation as the most learned man of his generation in Italy; he authored a set of commentaries on the works of Virgil. These works, In tria Virgilii Opera Expositio, constituted the first incunable to be printed at Florence, by Bernardo Cennini, in 1471.
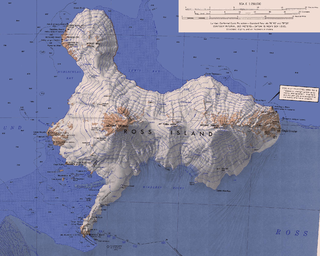
Ross Island is an island formed by four volcanoes in the Ross Sea near the continent of Antarctica, off the coast of Victoria Land in McMurdo Sound. Ross Island lies within the boundaries of Ross Dependency, an area of Antarctica claimed by New Zealand.

Mount Erebus is the second-highest volcano in Antarctica, the highest active volcano in Antarctica, and the southernmost active volcano on Earth. It is the sixth-highest ultra mountain on the continent. With a summit elevation of 3,794 metres (12,448 ft), it is located in the Ross Dependency on Ross Island, which is also home to three inactive volcanoes: Mount Terror, Mount Bird, and Mount Terra Nova.

The Siberian stonechat or Asian stonechat is a recently validated species of the Old World flycatcher family (Muscicapidae). Like the other thrush-like flycatchers, it was often placed in the Turdidae in the past. It breeds in the East Palearctic including in easternmost Europe and winters in the Old World tropics.

HMS Erebus was a Hecla-class bomb vessel constructed by the Royal Navy in Pembroke dockyard, Wales, in 1826. The vessel was the second in the Royal Navy named after Erebus, the personification of darkness in Greek mythology.

Rabanus Maurus Magnentius, also known as Hrabanus or Rhabanus, was a Frankish Benedictine monk, theologian, poet, encyclopedist and military writer who became archbishop of Mainz in East Francia. He was the author of the encyclopaedia De rerum naturis. He also wrote treatises on education and grammar and commentaries on the Bible. He was one of the most prominent teachers and writers of the Carolingian age, and was called "Praeceptor Germaniae", or "the teacher of Germany". In the most recent edition of the Roman Martyrology, his feast is given as 4 February and he is qualified as a Saint ('sanctus').

The Mount Erebus disaster occurred on 28 November 1979 when Air New Zealand Flight 901 (TE-901) flew into Mount Erebus on Ross Island, Antarctica, killing all 237 passengers and 20 crew on board. Air New Zealand had been operating scheduled Antarctic sightseeing flights since 1977. This flight was supposed to leave Auckland Airport in the morning and spend a few hours flying over the Antarctic continent, before returning to Auckland in the evening via Christchurch.

The Erebus class of warships was a class of 20th century Royal Navy monitors armed with a main battery of two 15-inch /42 Mk 1 guns in a single turret. It consisted of two vessels, Erebus and Terror, named after the two ships lost in the Franklin Expedition. Both were launched in 1916 and saw active service in World War I off the Belgian coast. After being placed in reserve between the wars, they served in World War II, with Terror being lost in 1941 and Erebus surviving to be scrapped in 1946.

Maurus was the first disciple of Benedict of Nursia (512–584). He is mentioned in Gregory the Great's biography of the latter as the first oblate, offered to the monastery by his noble Roman parents as a young boy to be brought up in the monastic life.

HMS Terror was a specialised warship and a newly developed bomb vessel constructed for the Royal Navy in 1813. She participated in several battles of the War of 1812, including the Battle of Baltimore with the bombardment of Fort McHenry. She was converted into a polar exploration ship two decades later, and participated in George Back's Arctic expedition of 1836–1837, the successful Ross expedition to the Antarctic of 1839 to 1843, and Sir John Franklin's ill-fated attempt to force the Northwest Passage in 1845, during which she was lost with all hands along with HMS Erebus.

Beuron Archabbey is a major house of the Benedictine Order located at Beuron in the upper Danube valley in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.

The Lower Erebus Hut (LEH) is a permanent field facility located on Mount Erebus on Ross Island, Antarctica. The hut served as the seasonal base of the Mount Erebus Volcano Observatory (MEVO), run by New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology (NMT). The installation comprises two huts, one kitchen and recreation building and one working and storage building.

The Erebus Ice Tongue is a mountain outlet glacier and the seaward extension of Erebus Glacier from Ross Island. It projects 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) into McMurdo Sound from the Ross Island coastline near Cape Evans, Antarctica. The glacier tongue varies in thickness from 50 metres (160 ft) at the snout to 300 metres (980 ft) at the point where it is grounded on the shoreline. Explorers from Robert F. Scott's Discovery Expedition (1901–1904) named and charted the ice tongue.

Erebus is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae.

Erebus Montes is a group of mountains in the Diacria quadrangle of Mars, located at 35.66° North and 185.02° West. It is 811 km across and was named after an albedo feature at 26N, 182W.

Erebus crepuscularis is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. It is found in Indonesia, New Guinea, Taiwan and the Australian states of Queensland and New South Wales.
Erebus Glacier is a glacier draining the lower southern slopes of Mount Erebus, Ross Island, Antarctica. It flows west to Erebus Bay where it forms the floating Erebus Glacier Tongue. It was named in association with Mount Erebus by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott.

Mount Terra Nova is a snow-covered inactive volcanic mountain, 2,130 m (6,990 ft), between Mount Erebus and Mount Terror on Ross Island. It was first mapped by the Discovery expedition in 1901–04, and named for Terra Nova, the relief ship for this expedition and the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13.















