
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit.

Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs of northern temperate regions that belong to the family Cupressaceae. The word cypress is derived from Old French cipres, which was imported from Latin cypressus, the latinisation of the Greek κυπάρισσος (kyparissos).

The Eriocaulaceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in the order Poales, commonly known as the pipewort family. The family is large, with about 1207 known species described in seven genera. They are widely distributed, with the centers of diversity for the group occurring in tropical regions, particularly the Americas. Very few species extend to temperate regions, with only 16 species in the United States, mostly in the southern states from California to Florida, only two species in Canada, and only one species in Europe. They tend to be associated with wet soils, many growing in shallow water. This is also reported from the southern part of India and the regions of Western Ghats hot spots.

Eriocaulon is a genus of about 400 species commonly known as pipeworts, of monocotyledonous flowering plants in the family Eriocaulaceae. The genus is widely distributed, with the centers of diversity for the group occurring in tropical regions, particularly southern Asia and the Americas. A few species extend to temperate regions, with ca. 10 species in the United States, mostly in the southern states from California to Florida, and only two species in Canada; China has 35 species, also mostly southern. Only one species occurs in Europe, where it is confined to the Atlantic Ocean coasts of Scotland and Ireland; this species also occurs in eastern North America and is thought to be a relatively recent natural colonist in Europe. In the Americas, Eriocaulon is the only genus in its family that occurs north of Florida. They tend to be associated with wet soils, many growing in shallow water, in wetlands, or in wet savannas like flatwoods. In wet soils, their abundance appears to be related to water levels, fire frequency, and competition from other plants such as grasses. Experiments have shown that they are weak competitors compared to many other wetland plant species. Some species can persist as buried seeds during unfavorable conditions. The scientific name is derived from Ancient Greek εριον, erion, meaning 'wool', and καυλός, caulos, meaning 'stalk'.

Madayi. is a Grama panchayat near Pazhayangadi in Kannur district, Kerala. a Bhagavathy shrine, Madayi Kavu where devotees worship Bhadrakali, is located here. The Goddess is one of the family deity of the Chirakkal Royal family, and the temple is known for the Koyikalasham. The temple was one of the few to survive desecration by the armies of Tippu Sultan, which devotees attribute to the grace of the Goddess. The Kolathiri Rajahs were the administrators of the temple, however recently the administration was transferred to the Malabar Devaswom Board. Nearby is the Vadukunnu Temple dedicated to Shiva. The temple was razed by followers of Tippu Sultan in the 18th century, but the temple has been rebuilt and is a vibrant centre of religion in the region.
The red-finned blue-eye is a tiny, critically endangered species of fish in the Pseudomugilidae family and the only species in its genus. The species was first recorded in 1990. It is endemic to central Queensland in Australia, where it is restricted to springs in Bush Heritage's Edgbaston Reserve.

Eriocaulon decangulare, commonly known as ten-angled pipewort, hat pin and bog button, is a monocotyledonous plant native to the eastern United States, Mexico and Nicaragua. The plant's distribution is quite irregular, with several disjunct populations and a discontinuous primary range. Most of its habitat in the United States runs along the Atlantic Coastal Plain, but some populations also occur in more mountainous regions. It is found in areas of relatively low elevation and the plant does not occur higher than 300 metres above sea level. This pipewort is found in peat and sand that is moist to wet and associated with savannahs, bogs, low pinelands, ditches and the banks of cypress domes.
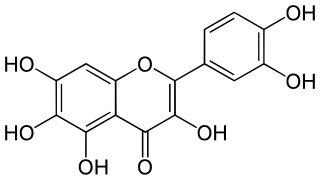
Quercetagetin is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in the genus Eriocaulon.

Patuletin is an O-methylated flavonol. It can be found in the genus Eriocaulon.

Eriocaulon parkeri is a species of flowering plant in the pipewort family known by the common names Parker's pipewort and estuary pipewort. It is native to eastern North America, where its distribution spans the coast from Quebec to North Carolina. It is extirpated from New York and Pennsylvania, however.

Madayipara is a flat topped hillock located in the Madayi, of Kannur district of Kerala state in the Southern India. It is overlooking Payangadi town on the northern bank of Kuppam river.

Eriocaulon scariosum, commonly named common, rough or pale pipewort, is a species of tufted grass-like herbaceous plants, constituting part of the plant family Eriocaulaceae. Common pipewort plants grow naturally in wetlands, bogs and drainage areas, from central and eastern Victoria, through eastern New South Wales, including the Australian Capital Territory, to eastern and north Queensland, Australia.
Eriocaulon koernickianum, common names dwarf pipewort or gulf pipewort, is a plant species native to Oklahoma, Arkansas, Georgia and Texas. It occurs in moist, sandy acidic soils in seeps and bogs.
Eriocaulon bolei is a critically endangered monocotyledonous plant only recorded in Satara district in the state of Maharashtra, India. It is a herb which grows up to 10–20 cm in height and seen in running water.
Eriocaulon ratnagiricum is a critically endangered monocotyledonous plant only recorded near Ratnagiri in the state of Maharashtra, India. It is a small annual which grows on the edges of temporary pools on lateritic plateaus.
Eriocaulon santapaui is a critically endangered monocotyledonous plant endemic to the Western Ghats around Khandala and Pune in the state of Maharashtra, India.

Eriocaulon sharmae is a critically endangered monocotyledonous plant endemic to Amboli and Sindhudurg in the state of Maharashtra, India.
Eriocaulon sivarajanii is a critically endangered monocotyledonous plant endemic to Kozhikode in the state of Kerala, India.

Eriocaulon australasicum is an endangered monocotyledonous plant in the Eriocaulaceae family found in Australia, in Victoria, South Australia and New South Wales.












