Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.

Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors on other cells. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, a family of transmembrane proteins that are cytokines, chemical messengers of the immune system. Excessive production of TNF plays a critical role in several inflammatory diseases, and TNF-blocking drugs are often employed to treat these diseases.
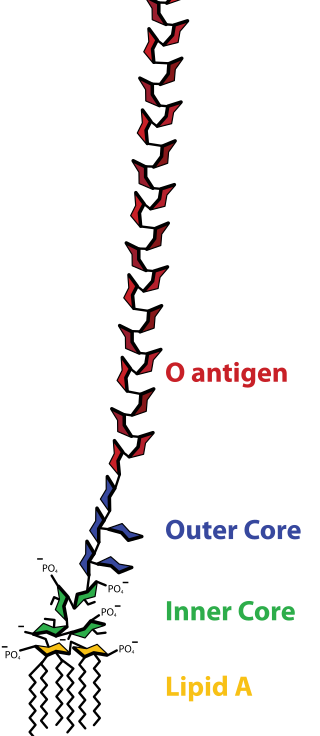
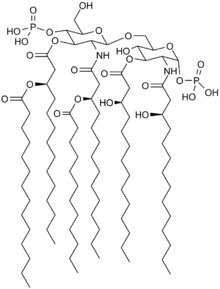
Lipopolysaccharide, now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli and Salmonella with a common structural architecture. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of three parts: an outer core polysaccharide termed the O-antigen, an inner core oligosaccharide and Lipid A, all covalently linked. In current terminology, the term endotoxin is often used synonymously with LPS, although there are a few endotoxins that are not related to LPS, such as the so-called delta endotoxin proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis.

Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) defines septic shock as a subset of sepsis in which particularly profound circulatory, cellular, and metabolic abnormalities are associated with a greater risk of mortality than with sepsis alone. Patients with septic shock can be clinically identified by requiring a vasopressor to maintain a mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg or greater and having serum lactate level greater than 2 mmol/L (>18 mg/dL) in the absence of hypovolemia. This combination is associated with hospital mortality rates greater than 40%.

Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-spanning receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes. Once these microbes have reached physical barriers such as the skin or intestinal tract mucosa, they are recognized by TLRs, which activate immune cell responses. The TLRs include TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, TLR10, TLR11, TLR12, and TLR13. Humans lack genes for TLR11, TLR12 and TLR13 and mice lack a functional gene for TLR10. The receptors TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, and TLR10 are located on the cell membrane, whereas TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are located in intracellular vesicles.
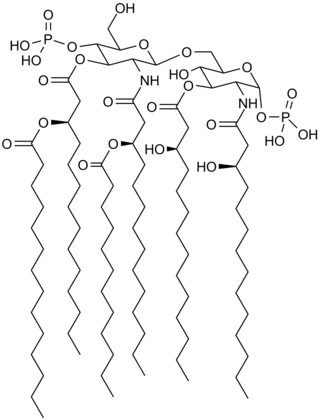
Lipid A is a lipid component of an endotoxin held responsible for the toxicity of gram-negative bacteria. It is the innermost of the three regions of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS), also called endotoxin molecule, and its hydrophobic nature allows it to anchor the LPS to the outer membrane. While its toxic effects can be damaging, the sensing of lipid A by the immune system may also be critical for the onset of immune responses to gram-negative infection, and for the subsequent successful fight against the infection.
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma, so TNF inhibitors may be used in their treatment. The important side effects of TNF inhibitors include lymphomas, infections, congestive heart failure, demyelinating disease, a lupus-like syndrome, induction of auto-antibodies, injection site reactions, and systemic side effects.

Toll-like receptor 2 also known as TLR2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR2 gene. TLR2 has also been designated as CD282. TLR2 is one of the toll-like receptors and plays a role in the immune system. TLR2 is a membrane protein, a receptor, which is expressed on the surface of certain cells and recognizes foreign substances and passes on appropriate signals to the cells of the immune system.
Inhibitors of apoptosis are a group of proteins that mainly act on the intrinsic pathway that block programmed cell death, which can frequently lead to cancer or other effects for the cell if mutated or improperly regulated. Many of these inhibitors act to block caspases, a family of cysteine proteases that play an integral role in apoptosis. Some of these inhibitors include the Bcl-2 family, viral inhibitor crmA, and IAP's.

Toll-like receptor 7, also known as TLR7, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR7 gene. Orthologs are found in mammals and birds. It is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family and detects single stranded RNA.

Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), also designated as CD284, is a key activator of the innate immune response and plays a central role in the fight against bacterial infections. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein of approximately 95 kDa that is encoded by the TLR4 gene.

Toll-like receptor 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR9 gene. TLR9 has also been designated as CD289. It is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family. TLR9 is an important receptor expressed in immune system cells including dendritic cells, macrophages, natural killer cells, and other antigen presenting cells. TLR9 is expressed on endosomes internalized from the plasma membrane, binds DNA, and triggers signaling cascades that lead to a pro-inflammatory cytokine response. Cancer, infection, and tissue damage can all modulate TLR9 expression and activation. TLR9 is also an important factor in autoimmune diseases, and there is active research into synthetic TLR9 agonists and antagonists that help regulate autoimmune inflammation.

Prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 (DP2 or CRTH2) is a human protein encoded by the PTGDR2 gene. DP2 has also been designated as CD294 (cluster of differentiation 294). It is a member of the class of prostaglandin receptors which bind with and respond to various prostaglandins. DP2 along with prostaglandin DP1 receptor are receptors for prostglandin D2 (PGD2). Activation of DP2 by PGD2 or other cognate receptor ligands has been associated with certain physiological and pathological responses, particularly those associated with allergy and inflammation, in animal models and certain human diseases.

Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 (TREM1) is an immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily transmembrane protein that, in humans, is encoded by the TREM1 gene. TREM1 is constitutively expressed on the surface of peripheral blood monocytes and neutrophils, and upregulated by toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands; activation of TREM1 amplifies immune responses.

Single Ig IL-1-related receptor (SIGIRR), also called Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor 8 (TIR8) or Interleukin-1 receptor 8 (IL-1R8), is transmembrane protein encoded by gene SIGIRR, which modulate inflammation, immune response, and tumorigenesis of colonic epithelial cells.
CCR5 receptor antagonists are a class of small molecules that antagonize the CCR5 receptor. The C-C motif chemokine receptor CCR5 is involved in the process by which HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, enters cells. Hence antagonists of this receptor are entry inhibitors and have potential therapeutic applications in the treatment of HIV infections.

The Interleukin-1 family is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults.
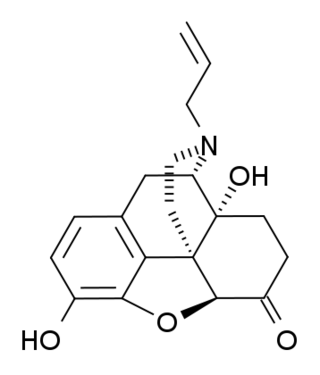
(+)-Naloxone (dextro-naloxone) is a drug which is the opposite enantiomer of the opioid antagonist drug (−)-naloxone. Unlike (−)-naloxone, (+)-naloxone has no significant affinity for opioid receptors, but instead has been discovered to act as a selective antagonist of Toll-like receptor 4. This receptor is involved in immune system responses, and activation of TLR4 induces glial activation and release of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and Interleukin-1.
Murine caspase-11, and its human homologs caspase-4 and caspase-5, are mammalian intracellular receptor proteases activated by TLR4 and TLR3 signaling during the innate immune response. Caspase-11, also termed the non-canonical inflammasome, is activated by TLR3/TLR4-TRIF signaling and directly binds cytosolic lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a major structural element of Gram-negative bacterial cell walls. Activation of caspase-11 by LPS is known to cause the activation of other caspase proteins, leading to septic shock, pyroptosis, and often organismal death.
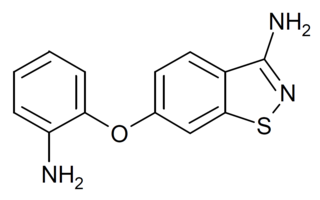
M62812 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). In animal studies it blocks TLR4-mediated cytokine release and has antiinflammatory effects, showing efficacy in animal models of arthritis and septic shock.