
French Naval Aviation is the naval air arm of the French Navy. The long-form official designation is Force maritime de l'aéronautique navale. Born as a fusion of aircraft carrier squadrons and the naval patrol air force, the Aéronavale was created in 1912. The force is under the command of a flag officer officially titled Admiral of Naval Aviation (ALAVIA) with his headquarters at Toulon naval base. It has a strength of around 6,800 military and civilian personnel. It operates from four airbases in Metropolitan France and several detachments in foreign countries or French overseas territories. Carrier-borne pilots of the French Navy do their initial training at Salon-de-Provence Air Base after which they undergo their carrier qualification with the US Navy.

Albert Achard was a French flying ace of the First World War, credited with five aerial victories, one as an observer and four as a pilot. He served as a reserve air force officer in the 1920s and 1930s, and returned to active duty in World War II.

Escadron de Chasse 1/2 Cigognes is a French Air and Space Force fighter squadron currently stationed at BA 116 Luxeuil - Saint-Sauveur Air Base, Haute-Saône, France.

Lieutenant Jean Chaput was a French World War I flying ace credited with 16 aerial victories.
Commandant Jacques Toussaint François Ortoli was a French Corsican patriot who served France in two World Wars. In World War I, he was a flying ace credited with eleven confirmed aerial victories. He returned to his nation's defense during World War II.

Escadrille 3Les Cigognes was a famous French aviation unit during the World War I. It was often referred to as the 'Stork Escadrille N3' due to its insignia. Pilots from Groupe de Combat 12 adopted the name and placed images of storks in different phases of flying on their planes.

Escadrille 12 of the French Air Force was formed in 1912 and known for introducing Nieuport aircraft to the World War I air combat.

Escadrille 26 is a squadron of the French Air Force founded in 1914 and still active today.
Escadrille 15 is one of the oldest units of the French Air Force, which was founded on 22 August 1912 at Reims, France, and is still active.

Escadrille 23 of the French Air Force was formed at Brie on 4 August 1914.

Escadrille 31 of the French Air Force was founded at the beginning of the World War I, on 24 September 1914, at Dijon Air Base. Once equipped with Morane-Saulnier Ns, it was posted to I Armee of the French Army.
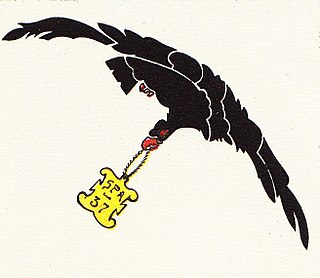
Escadrille 37 of the French Air Force was established at Chateauford, France in January 1915. Its original equipment of Morane-Saulniers led to its original designation of Escadrille MS 37.
Escadrille SPA.48 was a unit of the French Air Force during World War I.

Escadron de Chasse is a French Air and Space Force fighter squadron currently stationed at BA 188 Djibouti Air Base.
Escadrille 38, variously known as Escadrille MS38, Escadrille N38, or Escadrille SPA38, was a French fighter squadron founded on 8 January 1915. Fighting until the 11 November 1918 armistice, they were responsible for downing 98 German aircraft in aerial combat.
Escadrille Spa49 was a squadron of the French Air Services active during World War I, from 1915 - 1918. Credited with 37 aerial victories over German aircraft, it won a unit citation on 8 November 1918.
Escadrille Spa.69 was a French fighter squadron derived from one of its military's oldest aviation units. Active from September 1915 until the 11 November 1918 Armistice, the escadrille campaigned on both the Western and Italian Fronts with X Armee. It was credited with 38 aerial combat victories.
Escadrille Spa.112 was a French air force squadron active for the near-entirety of World War I. After serving until mid-1917 in various iterations of a bombing squadron, they were re-equipped with Nieuport fighters. With their Nieuports, and their subsequent SPADs, they destroyed 28 enemy airplanes by the ceasefire.
Escadrille Spa.68 was a French fighter squadron active from Autumn 1915 until the Armistice that ended World War I. It was equipped with a mixed lot of Nieuports until they were gradually replaced by SPADs in November 1917. The squadron was one of four bundled into Groupe de Combat 20 in February 1918. By war's end, Escadrille Spa.68 was credited with the destruction of 15 enemy aircraft.












