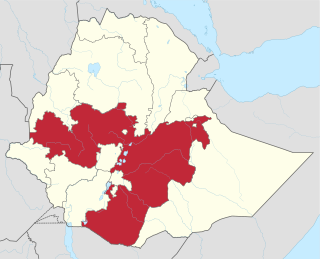
Oromia is a regional state in Ethiopia and the homeland of the Oromo people. Under Article 49 of Ethiopian Constitution, the capital of Oromia is Addis Ababa, also called Finfinne. The provision of the article maintains special interest of Oromia by utilizing social services and natural resources of Addis Ababa.
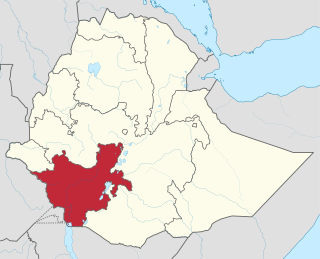
The Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region was a regional state in southwestern Ethiopia. It was formed from the merger of five kililoch, called Regions 7 to 11, following the regional council elections on 21 June 1992. Its government was based in Hawassa.
Dilla is a market town and separate woreda in southern Ethiopia. The administrative center of the Gedeo Zone in the former Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples Region (SNNPR) now it is South Ethiopia Regional State (SER), it is located on the main road from Addis Ababa to Nairobi. The town has a longitude and latitude of 6°24′30″N38°18′30″E, with an elevation of 1570 meters above sea level. It was part of Wenago woreda and is currently surrounded by Dilla Zuria woreda.

Amaro Zone (Kore) is a zone in the south-west Ethiopian Regional State of Ethiopia, and the people are called Kore, and their language is Korigna. The Amaro Kore people are the descendants of the Christian missioners of the north Ethiopian sematic peoples of Gonder, who were moved gradually through the northern shewa (menze) to the central and south-western Ethiopian lands of Damot (wolayta), Dawuro, Gamo Gofa, and surrounding areas of the region with their Christian traditions and heritages around the eleventh, twelfth, and thirteenth centuries. As the native of kore nation Theologian Jebdu kassahun evidentially assured and narrated, that was a time of ST. Abune Gebremenfes kidus, st.tekle Haymanot, and emperor Yikuno Amlak, who were preached and expanded Christianity to central and south western Ethiopian lands. Amaro is one of the areas in which members of Kore nations widely live in. Amaro Kore people got zonal status in August 2023 A.D upon the formation of the South west Ethiopia Regional State. In 2011 A.D, the Segen Area Peoples Zone was established, which includes Amaro woreda and the three former special woredas surrounding it. Located in the Great Rift Valley, Amaro kore peoples land is bordered on the south by Burji Zone, on the southwest by Konso Zone, on the west by Dirashe Zone, on the northwest by Gamo Zone and Lake Chamo, and on the north by Lake Abaya and in east and northeast by Oromia Region. It is divided into 35 kebeles. The administrative center of the woreda is Kelle, and Jijola woreda, Derba Menena woreda, and Kereda are other growing municipals of the zone. The highest peak in the zone is Mount Dello, which is part of the Kore mountains, the highest in Jemjem plateau and the second from the region. Much of the western part of this zone lies inside the Nechisar National Park. The major crops grown in Amaro are enset, teff, maize, wheat, barley, navy beans, and coffee. Amaro has 39 kilometers of all-weather roads and 16 kilometers of dry-weather roads, for an average road density of 36 kilometers per 1000 square kilometers. The Central Statistical Agency (CSA) reported that 1,082 tons of coffee were produced in the year ending in 2005, based on inspection records from the Ethiopian Coffee and Tea authority. This represented 0.48% of the Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples' Region (SNNPR)'s output and 1.08% of Ethiopia's total output.

Burji Zone is one of the zones in the South Ethiopia Regional State of Ethiopia. In August 2023 Burji special Woreda got zonal status upon the formation of South Ethiopia Region. In 2011, the Segen Area Peoples Zone was established, which includes Burji woreda and the 3 former special woredas surrounding it. It is named for the Burji people, who have their homeland in this zone. Burji is bordered on the east and south by the Oromia Region, on the west by the Konso Zone, and on the north by the Amaro Zone. The administrative center of Burji is Soyama.

Konso is a zone in the South Ethiopia Regional State, Ethiopia. It was formerly a woreda. Prior to 2011, Konso was not part of any Zone in the Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples' Region (SNNPR) and was therefore considered a special woreda, an administrative subdivision which is similar to an autonomous area. In 2011, the Segen Area Peoples Zone was established, which includes Konso special woreda and the 3 former woredas surrounding it. This special woreda is named after the Konso people. Located in the Great Rift Valley, Konso is bordered on the south by the Oromia Region, on the west by the South Omo Zone, on the northwest by Alle special woreda, on the north by Dirashe special woreda, on the northeast by Amaro special woreda, and on the east by Burji special woreda. The Sagan River, which flows south then west to join the Weito, defines part of the woreda's boundary with Burji and the entire length of the boundary with the Oromia Region. The administrative center is Karati; other towns in Konso include Fasha and Sagen. After protesting by residents to become a zone for several years, Konso became a zone in November 2018.

The Oromo Liberation Front is an Oromo nationalist political party formed in 1973 to promote self-determination for the Oromo people inhabiting today's Oromia Region and Oromia Zone in the Amhara Region of Ethiopia. The OLF has offices in Addis Ababa, Washington, D.C., and Berlin, from which it operates radio stations that broadcast in Amharic and Oromo.
Wenago is one of the woredas in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of Ethiopia. Part of the Gedeo Zone, Wenago is bordered on the southwest by Yirgachefe, on the northwest by the Oromia Region, on the northeast by Dila Zuria, and on the southeast by Bule. Towns in Wenago include Wenago. Dila Zuria woreda and Dila town were separated from Wenago.
Abaya is a woreda in the Oromia Region, Ethiopia. It is part of former Gelana Abaya woreda what was divided for Abaya and Gelana woredas. Part of the Borena Zone, Gelana Abaya was bordered on the south by Hagere Mariam, and on the west, north and east by the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples Region (SNNPR). Lake Abaya, on the western border, is divided between this woreda and the SNNPR. However, the Guji Oromo who live in Nechisar National Park are claimed to be administratively part of this woreda, in a kebele called "Irgansaa".

The Oromo conflict is a protracted conflict between the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF) and the Ethiopian government. The Oromo Liberation Front formed to fight the Ethiopian Empire to liberate the Oromo people and establish an independent state of Oromia. The conflict began in 1973, when Oromo nationalists established the OLF and its armed wing, the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA). These groups formed in response to prejudice against the Oromo people during the Haile Selassie and Derg era, when their language was banned from public administration, courts, church and schools, and the stereotype of Oromo people as a hindrance to expanding Ethiopian national identity.
The ongoing Ethiopian civil conflict began with the 2018 dissolution of the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (ERPDF), an ethnic federalist, dominant party political coalition. After the 20-year border conflict between Ethiopia and Eritrea, a decade of internal tensions, two years of protests, and a state of emergency, Hailemariam Desalegn resigned on 15 February 2018 as prime minister and EPRDF chairman, and there were hopes of peace under his successor Abiy Ahmed. However, war broke out in the Tigray Region, with resurgent regional and ethnic factional attacks throughout Ethiopia. The civil wars caused substantial human rights violations, war crimes, and extrajudicial killings.
The Gambela Massacre was a three-day-long massacre in the city of Gambela targeting Anuak people in December of 2003. The massacre perpetrated by the ENDF and "highlander" militias after an ambush of ARRA employees. Calls from International community made to condemn and stop the various forms of attacks against the Anuak people- i.e. Ethiopia to take immediate action and to comply to the International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (“ICERD”). The calls included actions against: 1) Racial Discrimination, 2) State obligation to protect and ensure economic development, economic, social, and cultural rights, 3) Freedom of movement, 4)The right to equal treatment in the justice system, 5) Protection Against Violence, and 6) Access to Remedies and Justice for Crimes of Racial Discrimination.

The OLA insurgency is an armed conflict between the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA), which split from the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF) in 2018, and the Ethiopian government, continuing in the context of the long-term Oromo conflict, typically dated to have started with the formation of the Oromo Liberation Front in 1973.

Since the 1990s, the Amhara people of Ethiopia have been subject to ethnic violence, including massacres by Tigrayan, Oromo and Gumuz ethnic groups among others, which some have characterized as a genocide. Large-scale killings and grave human rights violations followed the implementation of the ethnic-federalist system in the country. In most of the cases, the mass murders were silent with perpetrators from various ethno-militant groups—from TPLF/TDF, OLF–OLA, and Gumuz armed groups.
The 1995 Ethiopian Federal Constitution formalizes an ethnic federalism law aimed at undermining long-standing ethnic imperial rule, reducing ethnic tensions, promoting regional autonomy, and upholding unqualified rights to self-determination and secession in a state with more than 80 different ethnic groups. But the constitution is divisive, both among Ethiopian nationalists who believe it undermines centralized authority and fuels interethnic conflict, and among ethnic federalists who fear that the development of its vague components could lead to authoritarian centralization or even the maintenance of minority ethnic hegemony. Parliamentary elections since 1995 have taken place every five years since enactment. All but one of these have resulted in government by members of the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) political coalition, under three prime ministers. The EPRDF was under the effective control of the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF), which represents a small ethnic minority. In 2019 the EPRDF, under Abiy, was dissolved and he inaugurated the pan-ethnic Prosperity Party which won the 2021 Ethiopian Election, returning him as prime minister. But both political entities were different kinds of responses to the ongoing tension between constitutional ethnic federalism and the Ethiopian state's authority. Over the same period, and all administrations, a range of major conflicts with ethnic roots have occurred or continued, and the press and availability of information have been controlled. There has also been dramatic economic growth and liberalization, which has itself been attributed to, and used to justify, authoritarian state policy.
Events in the year 2023 in Ethiopia.
The conflict in Konso is part of a series of ethnic-based violence in Ethiopia. UN OCHA reported that its Early warning department of SNNPR categorized Konso as a priority hot spot area. Repeated conflict and the issue of adverse weather exacerbated the existing humanitarian crisis in the Zone. Interpersonal ethnic violence are deepening into serious human rights violations and suffering, with the ethnic federalism system that drew formal administrative divisions with regional boundaries falling along ethnic lines.
The 2022 North Shewaclashes were a series of clashes that broke out between ethnic Amhara Fano militiamen, the Oromo Liberation Army, and the Ethiopian National Defence Forces in the North Shewa zone in the Oromia region and the Oromia Zone in the Amhara region, which resulted in dozens of people killed and thousands displaced.







