The New Zealand lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found off New Zealand. Some taxonomic authorities consider it to be conspecific with the southern lanternshark.

Etmopterus is a genus of lantern sharks in the squaliform family Etmopteridae. They are found in deep sea ecosystems of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

The cylindrical lanternshark or Carter Gilbert's lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found along the Caribbean coast of Colombia in South America, at depths of between 285 and 355 m. Its maximum length is 21 cm.

The Hawaiian lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found around the Hawaiian Islands, between latitudes 23°N and 19°N, at depths between 400 and 910 m. Its maximum length is at least 46 cm.

The dense-scale lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the southeast Pacific off Peru and Chile.

The fringefin lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the western central Atlantic from Texas to Florida, northern Gulf of Mexico, and Mexico.

The slendertail lanternshark or Moller's lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the western Indian Ocean between latitudes 34°N and 46°S at depths between 250 and 860 m. It can grow up to 46 cm in length.

The Caribbean lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the eastern and western Atlantic at depths between 180 and 720 m. Its length is up to 50 cm.

The smalleye lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the southeast Pacific off Peru and Chile, at depths between 630 and 1,100 m. Its length is up to 61 cm.

The African lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the eastern Atlantic between latitudes 12°N and 18°S, at depths between 300 and 1,000 m. Its length is up to 30 cm.

The great lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the northeast and northwest Atlantic. Its name was given as at the time of its discovery, it was thought to be bioluminescent, but this has been challenged.
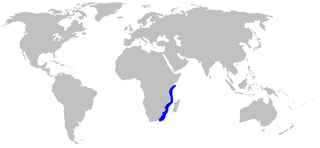
The thorny lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the western Indian Ocean between latitudes 0° and 31°S, at depths between 200 and 500 m. Its length is up to 27 cm.

The splendid lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the western Pacific at depths between 120 and 210 m. Its length is up to 30 cm.

The brown lanternshark or bristled lanternshark is a little-known species of deep-sea dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae. It is found off Japan and New Zealand, and possibly also South Africa and Australia, typically deeper than 300 m (980 ft). This species can be distinguished from other lanternsharks by its coloration, which is a uniform dark gray or brown without the ventral surface being much darker and clearly delineated from the rest of the body. The brown lanternshark feeds on small bony fishes, cephalopods, and crustaceans. Reproduction is ovoviviparous, with females giving birth to 9–18 young. An unusually high proportion of individuals in Suruga Bay are hermaphrodites, with both male and female characteristics.

The tailspot lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found around New Caledonia, at depths of between 640 and 800 m. Its length is up to 31 cm.

Etmopterus dislineatus, sometimes called the lined lanternshark, is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the central Coral Sea at depths of between 590 and 800 m. Its length is up to 45 cm.

The blackmouth lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found off Western Australia and the Arafura Sea, at depths between 430 and 550 m. Its length is up to 26 cm.

The false lanternshark or false pygmy shark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the western Pacific from the Norfolk Ridge and Lord Howe Ridge off New Caledonia.

The West Indian lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the western central Atlantic, at depths between 400 and 800 m. Its length is up to 31 cm (12 in).

Etmopterus burgessi, sometimes known as the broad-snout lanternshark, is a lanternshark of the family Etmopteridae in the order Squaliformes. It is found only around Taiwan.




















