Desmidiales, commonly called the desmids, are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Desmids consist of single-celled microscopic green algae. Because desmids are highly symmetrical, attractive, and come in a diversity of forms, they are popular subjects for microscopists, both amateur and professional.

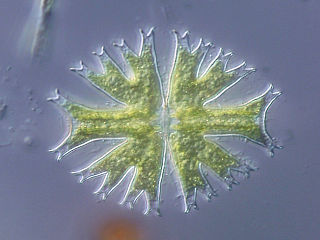
Micrasterias is a unicellular green alga of the order Desmidiales. Its species vary in size reaching up to hundreds of microns.
Actinochloris is a genus of green algae, in the family Actinochloridaceae, with a single species Actinochloris sphaerica. It is a subaerial to terrestrial alga.
Lobocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiosiphonaceae. It contains the single species Lobocharacium coloradoense. It has been isolated from a pond in Colorado, United States.
Treubaria is a genus of green algae, the sole genus in the family Treubariaceae. Treubaria is found in freshwater habitats and has a cosmopolitan distribution.

The Desmidiaceae are one of four families of charophyte green algae in the order Desmidiales (desmids).
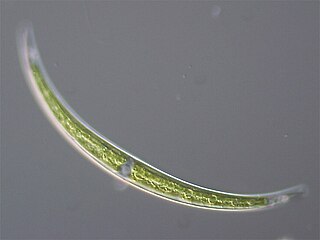
Closterium is a genus of desmid, a group of charophyte green algae. It is placed in the family Closteriaceae. Species of Closterium are a common component of freshwater microalgae flora worldwide.

Cosmarium is a genus of freshwater organisms belonging to the Charophyta, a division of green algae from which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged.

Desmidium is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Desmidiaceae.

Euastrum is a genus of green algae of the Desmidiaceae family. It lives in acidic waters.

Pleurotaenium is a genus of green algae, specifically of the desmids (Desmidiaceae).
Spinoclosterium is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Closteriaceae. It is rare, but widely distributed in freshwater regions throughout the world.

Staurodesmus is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Desmidiaceae.

Triploceras is a genus of desmid in the family Desmidiaceae.
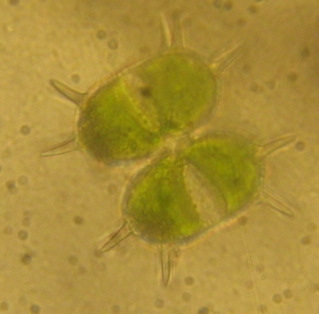
Xanthidium is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Desmidiaceae.

Micrasterias furcata is a species of unicellular desmid which inhabits freshwater areas. M. furcata is round, flattened and lobed in body plan.
Cosmarium tetragonum is a species of green algae in the family Desmidiaceae. It is a freshwater species with a worldwide distribution.

Cosmarium botrytis is a species of green algae in the family Desmidiaceae. It is a freshwater species with a worldwide distribution, and has been recorded from all continents.
Prescottiella is a genus of green algae in the family Desmidiaceae, containing the single species Prescottiella sudanensis. Originally classified as Micrasterias sudanensis in 1958, it was moved into its own genus by Carlos E. M. Bicudo in 1976, due to its asymmetric character. It is named after Gerald Webber Prescott, an American phycologist.

Xanthidium antilopaeum is a species of unicellular desmid in the family Desmidiaceae. It is a common, worldwide species found in acidic waters, particularly the edges of large ponds and lakes.











