
The fulmars are tubenosed seabirds of the family Procellariidae. The family includes two extant species and two extinct fossil species from the Miocene.

Right whales are three species of large baleen whales of the genus Eubalaena: the North Atlantic right whale, the North Pacific right whale and the Southern right whale. They are classified in the family Balaenidae with the bowhead whale. Right whales have rotund bodies with arching rostrums, V-shaped blowholes and dark gray or black skin. The most distinguishing feature of a right whale is the rough patches of skin on its head, which appear white due to parasitism by whale lice. Right whales are typically 13–17 m (43–56 ft) long and weigh up to 100 short tons or more.

Balaenidae is a family of whales of the parvorder Mysticeti that contains mostly fossil taxa and two living genera: the right whale, and the closely related bowhead whale.

The northern fulmar, fulmar, or Arctic fulmar is a highly abundant seabird found primarily in subarctic regions of the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. There has been one confirmed sighting in the Southern Hemisphere, with a single bird seen south of New Zealand. Fulmars come in one of two color morphs: a light one, with white head and body and gray wings and tail, and a dark one, which is uniformly gray. Though similar in appearance to gulls, fulmars are in fact members of the family Procellariidae, which include petrels and shearwaters.

Arctogadus glacialis, known also with ambiguous common names Arctic cod and polar cod, is an Arctic species of fish in the cod family Gadidae, related to the true cod. Arctogadus glacialis is found in icy water. They grow to about 30 cm long, and are favorite food of narwhals and other arctic whales.
The East Siberian cod also known as the toothed cod, is an Arctic fish closely similar to the Arctic cod Arctogadus glacialis and also related to true cods. It has been differentiated in appearance from the Arctic cod by having pronounced chin barbel. Their sides and back are dark olive and the belly are light grey with dark spots. They may grow up to 60 cm.

Psychroteuthis glacialis, the glacial squid, is the only known species in the monotypic genus Psychroteuthis, in the family Psychroteuthidae. While only one species has been confirmed, two undescribed species also probably exist. The species occurs in coastal waters near Antarctica and South America. It grows to a mantle length of 44 cm (1.44 ft).

Ranunculus glacialis, the glacier buttercup or glacier crowfoot, is a plant of the family Ranunculaceae. It is a 5-10(-20) cm high perennial herb. Often with a single relatively large flower, with 5 petals first white later pink or reddish. The underside of the 5 sepals are densely brown-hairy. The leaves are fleshy, shiny, and deeply loped, forming 3 leaflets. Ranunculus glacialis reported to have a diploid chromosome number of 2n = 16.

Eucobresia nivalis is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Vitrinidae, the glass snails.
Polarella is a dinoflagellate, and is the only extant genus of the Suessiaceae family. The genus was described in 1999 by Marina Montresor, Gabriele Procaccini, and Diane K. Stoecker, and contains only one species, Polarella glacialis. Polarella inhabits channels within ice formations in both the Arctic and Antarctic polar regions, where it plays an important role as a primary producer. Polarella is a thecate dinoflagellate, wherein the cell has an outer covering of cellulose plates, which are arranged in nine latitudinal series. The general morphology of Polarella is similar to that of a typical dinoflagellate. and Polarella has a zygotic life history, wherein it alternates between a motile vegetative phase and a non-motile spiny cyst. While it is thought that the cysts of Polarella have lost their ability to form fossils, the cyst life cycle stage has acted as link to extinct members of the Suessiaceae family.

Clitocybe glacialis is a species of mushroom in the family Tricholomataceae. Formerly known as Lyophyllum montanum, this is a snowbank mushroom, always associated with melting snow along snowbanks and thus glacialis. Originally described by Alexander H. Smith in 1957, this North American species is typically found growing under conifers on mountains.

Epacris glacialis, commonly known as reddish bog-heath, is a species of flowering plant in the family Ericaceae and is endemic to south-eastern continental Australia. It is a prostrate to low-lying shrub with crowded, rhombus-shaped to broadly egg-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, and tube-shaped, white flowers in small clusters near the ends of the branches.

Semi-slugs, also spelled semislugs, are land gastropods whose shells are too small for them to retract into, but not quite vestigial. The shell of some semi-slugs may not be easily visible on casual inspection, because the shell may be covered over with the mantle.

Eucobresia is a genus of air-breathing land snails or semi-slugs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Vitrinidae, the glass snails.

Galiteuthis glacialis is a species of glass squid from the Antarctic Convergence. It is in the cranchiidae family and subfamily taoniinae. They are endemic to the Antarctic and are found in the Southern Ocean, around the Weddell Sea and South Shetland Islands. Galiteuthis glacialis are one of the most plentiful and widely dispersed species of Antarctic squid. These squids are found in the mesopelagic and bathypelagic layers of the open ocean and demonstrate vertical migration. They can reach a maximum mantle length of 500 mm (0.5m).

Marthasterias is a genus of starfish in the family Asteriidae. It is monotypic and the only species in the genus is Marthasterias glacialis, commonly known as the spiny starfish. It is native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean.
Cirroctopus glacialis is an octopus located in the Palmer Archipelago of Antarctica. Its shell is v-shaped, and it has a distinctive pigmentation pattern on its web's oral face. C. glacialis is thought to be demersal, like other members of the genus Cirroctopus. These octopuses are found between 333 and 914 meters deep. Their population is currently unknown.

Leucorrhinia glacialis, the crimson-ringed whiteface, is a species of skimmer in the dragonfly family Libellulidae. It is found in North America.
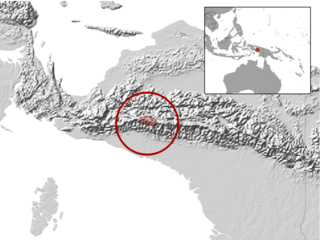
Nubeoscincus glacialis is a species of skink found in Indonesia.
















