
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.
Tetraphyllidea is a large tapeworm order that contains some 60 genera and about 800 described species. Tetraphyllideans are remarkable for their scolex morphologies, which are the most varied and morphologically complex amongst all tapeworm orders.

The banded houndshark is a species of houndshark in the family Triakidae, common in the northwestern Pacific Ocean from the southern Russian Far East to Taiwan. Found on or near the bottom, it favors shallow coastal habitats with sandy or vegetated bottoms, and also enters brackish water. This shark reaches 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length. It has a short, rounded snout and mostly narrow fins; the pectoral fins are broad and triangular, and the trailing margin of the first dorsal fin is almost vertical. It is gray above and lighter below; younger sharks have darker saddles and dots, which fade with age.

The sand devil or Atlantic angel shark is a species of angelshark, family Squatinidae, native to the northwestern Atlantic Ocean. It occurs off the eastern United States, in the northern Gulf of Mexico, and possibly in parts of the Caribbean Sea. This bottom-dwelling shark is found in shallow inshore waters in summer and fall, and deep offshore waters in winter and spring. The sand devil's flattened body and enlarged pectoral and pelvic fins give it a ray-like appearance. There is a band of enlarged thorns running along the middle of its back. It is gray or brown in color, with scattered small dark spots. This species reaches 1.2–1.5 m (3.9–4.9 ft) in length.
Abergasilus amplexus is a species of parasitic copepod endemic to euryhaline habitats in New Zealand. It is the only known species in the genus Abergasilus.
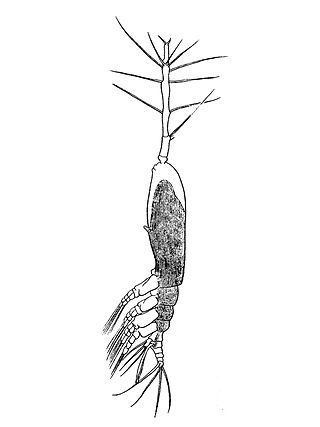
Monstrilloida is an order of copepods with a cosmopolitan distribution in the world's oceans. The order contains a single family, Monstrillidae. The name of the first ever described genus Monstrilla is derived from latin, meaning "tiny monster", because the lack of usual diagnostic features of copepods puzzled early taxonomists.
Shiinoidae is a family of parasitic copepods.
Syndinium is a cosmopolitan genus of parasitic dinoflagellates that infest and kill marine planktonic species of copepods and radiolarians. Syndinium belongs to order Syndiniales, a candidate for the uncultured group I and II marine alveolates. The lifecycle of Syndinium is not well understood beyond the parasitic and zoospore stages.
Stygotantulus is a genus of crustacean with the sole species Stygotantulus stocki. It lives as an ectoparasite on harpacticoid copepods of the families Tisbidae and Canuellidae. It is the smallest arthropod in the world, at a length of less than 0.1 millimetres (0.004 in). The specific name stocki commemorates Jan Hendrik Stock, a Dutch carcinologist. Another contender for the world's smallest arthropod is Tantulacus dieteri, with a total body length of only 85 micrometres (0.0033 in).

Lernaeocera branchialis, sometimes called cod worm, is a parasite of marine fish, found mainly in the North Atlantic. It is a marine copepod which starts life as a small pelagic crustacean larva. It is among the largest of copepods, ranging in size from 2 to 3 millimetres when it matures as a copepodid larva to more than 40 mm as a sessile adult.
Hydrichthys is a genus of colonial marine hydrozoans formerly placed in the family Hydrichthyidae but is now included in the family Pandeidae. The polyps of members of this genus are parasitic. The polyp attaches itself to a fish, and in one species exhibits hyperparasitism by attaching itself to a copepod, itself the parasite of a fish.
Hamaticolax is a genus of parasitic copepods belonging to the family Bomolochidae. Its members can only be distinguished from the closely related genus Acantholochus by the presence of an accessory process on the claw of the maxillipeds. It includes the following species:
Nicothoe tumulosa is a species of copepod parasitic on the gills of the glypheoid lobster Neoglyphea inopinata. It was described as a new species in 1976 by Roger F. Cressey. It can be differentiated from related species by the setal formula, and the trunk's covering of small bumps, which give the species its name.
Ellobiopsis is a genus of unicellular, ectoparasitic eukaryotes causing disease in crustaceans. This genus is widespread and has been found infecting copepods from both marine and freshwater ecosystems. parasitism has been seen to interfere with fertility in both sexes of copepods.

Eudactylinidae is a family of copepods, most of which live as parasites on the gills of elasmobranch fishes; two genera lives on the gills of teleost fishes.

Eudactylina is a genus of copepods. They parasitise elasmobranch fishes.
Peniculisa is a genus of marine parasitic copepods in the family Pennellidae.
Cardiodectes bellottii is a species of copepods in the family Pennellidae. It is a parasite of fish. It is found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans as well as the Mediterranean Sea; specimens from the Pacific were formerly treated as a separate species, Cardiodectes medusaeus.
Blastodinium is a diverse genus of dinoflagellates and important parasites of planktonic copepods. They exist in either a parasitic stage, a trophont stage, and a dinospore stage. Although morphologically and functionally diverse, as parasites they live exclusively in the intestinal tract of copeods.
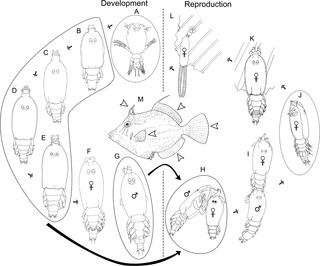
Peniculus minuticaudae is a species of parasitic pennellid copepod. It is known from the northeast Pacific Ocean. It was originally described in 1956, redescribed in 2012, and its complete life cycle has been elucidated on the cultured threadsail filefish, Stephanolepis cirrhifer in 2013.








