| Siphonostomatoida | |
|---|---|
 | |
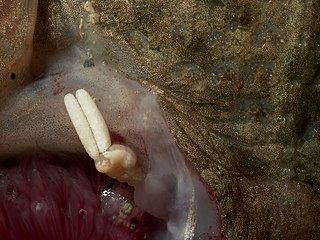
| Lernaeocera branchialis (Pennellidae) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Copepoda |
| Superorder: | Podoplea |
| Order: | Siphonostomatoida Thorell, 1859 |
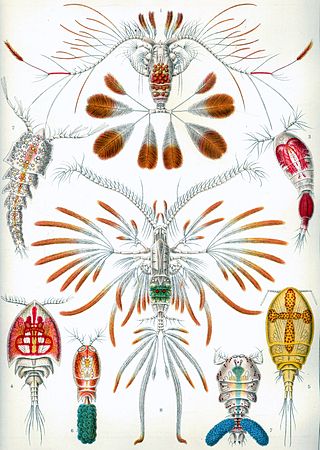
Siphonostomatoida is an order of copepods, containing around 75% of all the copepods that parasitise fishes. [1] Their success has been linked to their possession of siphon-like mandibles and of a "frontal filament" to aid attachment to their hosts. [2] Most are marine, but a few live in fresh water. [3] There are 40 recognised families: [4]
- Archidactylinidae Izawa, 1996
- Artotrogidae Brady, 1880
- Asterocheridae Giesbrecht, 1899
- Brychiopontiidae Humes, 1974
- Caligidae Burmeister, 1835
- Calverocheridae Stock, 1968
- Cancerillidae Giesbrecht, 1897
- Codobidae Boxshall & Ohtsuka, 2001
- Coralliomyzontidae Humes & Stock, 1991
- Dichelesthiidae Milne-Edwards, 1840
- Dichelinidae Boxshall & Ohtsuka, 2001
- Dinopontiidae Murnane, 1967
- Dirivultidae Humes & Dojiri, 1980
- Dissonidae Yamaguti, 1963
- Ecbathyriontidae Humes, 1987
- Entomolepididae Brady, 1899
- Eudactylinidae C. B. Wilson, 1932
- Hatschekiidae Kabata, 1979
- Hyponeoidae Heegaard, 1962
- Kroyeriidae Kabata, 1979
- Lernaeopodidae Milne-Edwards, 1840
- Lernanthropidae Kabata, 1979
- Megapontiidae Heptner, 1968
- Micropontiidae Gooding, 1957
- Nanaspididae Humes & Cressey, 1959
- Nicothoidae Dana, 1852
- Pandaridae Milne Edwards, 1840
- Pennellidae Burmeister, 1835
- Pontoeciellidae Giesbrecht, 1895
- Pseudocycnidae C. B. Wilson, 1922
- Pseudohatschekiidae Tang et al., 2010
- Rataniidae Giesbrecht, 1897
- Samarusidae Lee J. & I.H. Kim, 2018
- Scottomyzontidae Ivanenko et al., 2001
- Sphyriidae C. B. Wilson, 1919
- Sponginticolidae Topsent, 1928
- Spongiocnizontidae Stock & Kleeton, 1964
- Stellicomitidae Humes & Cressey, 1958
- Tanypleuridae Kabata, 1969
- Trebiidae C. B. Wilson, 1905