
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

Isopoda is an order of crustaceans that includes woodlice and their relatives. Isopods live in the sea, in fresh water, or on land. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax.

Calanoida is an order of copepods, a group of arthropods commonly found as zooplankton. The order includes around 46 families with about 1800 species of both marine and freshwater copepods between them.

The Cyclopoida are an order of small crustaceans from the subclass Copepoda. Like many other copepods, members of Cyclopoida are small, planktonic animals living both in the sea and in freshwater habitats. They are capable of rapid movement. Their larval development is metamorphic, and the embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite.

Poecilostomatoida are an suborder of copepods. Although it was previously considered a separate order, recent research showed it to be nested within the Cyclopoida
Attheyella yemanjae is a species of copepod in the family Canthocamptidae. It is only known from the type locality, which is the Campo Úmido da Onça in Brazil's Distrito Federal. It is listed as conservation dependent on the IUCN Red List. The specific epithet yemanjae commemorates Yemanjá, the "beneficent and terrible goddess of the sea and the patroness of those who work on the waters" in Candombé mythology.
Murunducaris is a genus of crustacean in family Parastenocarididae. It contains the following species:
Thermomesochra reducta is a species of copepod in the family Canthocamptidae, and the only species in the genus Thermomesochra. It is listed as Data Deficient on the IUCN Red List.
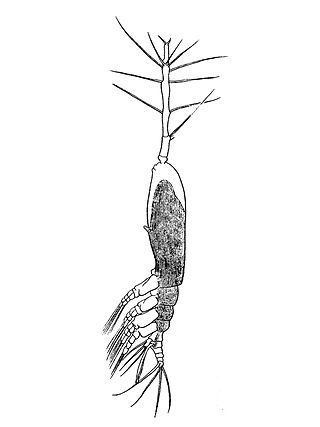
Monstrilloida is an order of copepods with a cosmopolitan distribution in the world's oceans. The order contains a single family, Monstrillidae. The name of the first ever described genus Monstrilla is derived from latin, meaning "tiny monster", because the lack of usual diagnostic features of copepods puzzled early taxonomists.

Canthocamptidae is a family of copepods. Most of the 700 species are confined to fresh water, although there are also marine species. It contains the following genera:

Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish which are preyed on by larger predators for food. Predators include other larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food chain on plankton, often by filter feeding. They include particularly fishes of the order Clupeiformes, but also other small fish, including halfbeaks, silversides, smelt such as capelin and goldband fusiliers.

Gelyella is a genus of freshwater copepods which are "surrounded by mystery". They live in groundwater in karstic areas of southern France and western Switzerland. The two species are the only members of the family Gelyellidae and, although previously placed in the order Harpacticoida, a new order, Gelyelloida, was erected for this family alone.

Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthic creatures, moving over the surface or burrowing in sediments, or living in cracks and crevices in bedrock. A few construct tubes in which they live and some are pelagic, swimming through the water column. There are estimated to be about 3,500 species in the order.
Darcythompsoniidae is a family of copepods, containing four genera. Members of the family have a very wide distribution throughout the tropics, where they live in rotting mangrove leaves. They lack egg sacs and are thought to lay their eggs directly into the leaf litter.
Pennella balaenopterae is a large ectoparasitic copepod specialising in parasitising marine mammals. It is the largest member of the genus Pennella, the other species of which are parasites of larger marine fish.

Crustaceans form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans.
Acartia tonsa is a species of marine copepod in the family Acartiidae.
Mildred Stratton Wilson was an American zoologist, whose work on copepods was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship in 1955.
Pennella exocoeti is a large ectoparasitic copepod, a specialist parasite of flying fish. The adult female copepod clings to the fish's gills or skin and feeds on its body fluids.
Longipedia is a genus of marine copepods of the family Longipediidae, order Canuelloida.












