Ambrosia beetles are beetles of the weevil subfamilies Scolytinae and Platypodinae, which live in nutritional symbiosis with ambrosia fungi. The beetles excavate tunnels in dead or stressed trees in which they cultivate fungal gardens, their sole source of nutrition. After landing on a suitable tree, an ambrosia beetle excavates a tunnel in which it releases spores of its fungal symbiont. The fungus penetrates the plant's xylem tissue, extracts nutrients from it, and concentrates the nutrients on and near the surface of the beetle gallery. Ambrosia fungi are typically poor wood degraders, and instead utilize less demanding nutrients. The majority of ambrosia beetles colonize xylem of recently dead trees, but some attack stressed trees that are still alive, and a few species attack healthy trees. Species differ in their preference for different parts of trees, different stages of deterioration, and in the shape of their tunnels ("galleries"). However, the majority of ambrosia beetles are not specialized to any taxonomic group of hosts, unlike most phytophagous organisms including the closely related bark beetles. One species of ambrosia beetle, Austroplatypus incompertus exhibits eusociality, one of the few organisms outside of Hymenoptera and Isoptera to do so.

The deathwatch beetle is a species of woodboring beetle that sometimes infests the structural timbers of old buildings. The adult beetle is brown and measures on average 7 mm (0.3 in) long. Eggs are laid in dark crevices in old wood inside buildings, trees, and inside tunnels left behind by previous larvae. The larvae bore into the timber, feeding for up to ten years before pupating, and later emerging from the wood as adult beetles. Timber that has been damp and is affected by fungal decay is soft enough for the larvae to chew through. They obtain sufficient nourishment by using a number of enzymes present in their gut to digest the cellulose and hemicellulose in the wood.

Frass refers loosely to the more or less solid excreta of insects, and to certain other related matter.

The Lymexylidae, also known as ship-timber beetles, are a family of wood-boring beetles. Lymexylidae belong to the suborder Polyphaga and are the sole member of the superfamily Lymexyloidea.

The term mycangium is used in biology for special structures on the body of an animal that are adapted for the transport of symbiotic fungi. This is seen in many xylophagous insects, which apparently derive much of their nutrition from the digestion of various fungi that are growing amidst the wood fibers. In some cases, as in ambrosia beetles, the fungi are the sole food, and the excavations in the wood are simply to make a suitable microenvironment for the fungus to grow. In other cases, wood tissue is the main food, and fungi weaken the defense response from the host plant.
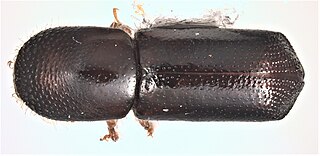
Xyleborus glabratus is a type of ambrosia beetle invasive to the United States. It has been documented as the primary vector of Raffaelea lauricola, the fungus that causes laurel wilt, a disease that can kill several North American tree species in the family Lauraceae, including redbay, sassafras, and avocado.

Platypodinae is a weevil subfamily in the family Curculionidae. They are important early decomposers of dead woody plant material in wet tropics; all but two species are ambrosia beetles that cultivate fungi in tunnels excavated in dead wood as the sole food for their larvae. They are sometimes known as pinhole borers.
Austroplatypus incompertus is a species of ambrosia beetle belonging to the true weevil family, native to Australia, with a verified distribution in New South Wales and Victoria. It forms colonies in the heartwood of Eucalyptus trees and is the first beetle to be recognized as a eusocial insect. Austroplatypus incompertus is considered eusocial because groups contain a single fertilized female that is protected and taken care of by a small number of unfertilized females that also do much of the work. These beetles appear to be the oldest farming creatures, having domesticated fungi nearly 90 million years ago. The species likely passed on cultivated fungi to other weevils.

The European spruce bark beetle, is a species of beetle in the weevil subfamily Scolytinae, the bark beetles, and is found from Europe to Asia Minor and some parts of Africa.

Hylastes ater is a species of beetle in the family Curculionidae, the true weevils. It is a bark beetle, a member of the subfamily Scolytinae. Its common name is the black pine bark beetle. It is native to Europe and parts of Asia, including China and Korea. It is known as an introduced species in many other regions, including Australia, New Zealand, the Americas, and South Africa. It is a pest of pines and other trees, and it is widespread in areas where pine trees are cultivated. The species "is an important threat to the biosecurity of all forested countries."

Ips is a genus of beetles in the family Curculionidae, the true weevils. They are bark beetles, members of the subfamily Scolytinae. Species are distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere. Some are known as introduced species in Australia and Africa. Many species are pests of forest trees, especially pines and spruces. They are known commonly as engraver beetles, ips engraver beetles, and pine engravers.

Platypus apicalis, known by its common name the New Zealand pinhole boring beetle, is a wood boring beetle endemic to New Zealand and found throughout the North and South Island in a range of environments.

Euwallacea fornicatus is a species complex consisting of three cryptic species of ambrosia beetles, known as an invasive species in California, Israel and South Africa. As the rest of the ambrosia beetles, E. fornicatus larvae and adults feed on a symbiotic fungus carried in a specific structure called mycangium. In E. fornicatus, the mycangium is located in the mandible. The combination of massive numbers of beetles with the symbiotic fungus kill trees, even though the fungus alone is a weak pathogen.

Xylosandrus compactus is a species of ambrosia beetle. Common names for this beetle include black twig borer, black coffee borer, black coffee twig borer and tea stem borer. The adult beetle is dark brown or black and inconspicuous; it bores into a twig of a host plant and lays its eggs, and the larvae create further tunnels through the plant tissues. These beetles are agricultural pests that damage the shoots of such crops as coffee, tea, cocoa and avocado.

Platypus cylindrus, commonly known as the oak pinhole borer, is a species of ambrosia beetle in the weevil family Scolytinae. The adults and larvae burrow under the bark of mature oak trees. It is native to Europe.

Xylosandrus crassiusculus, known generally as the Asian ambrosia beetle or granulate ambrosia beetle, is a species of tropical bark beetle in the family Curculionidae. It is native to Asia and has spread to Africa, Europe, Australasia and the Americas. The adult beetle is reddish-brown and some 2 to 3 mm long.
Xyloterinus is a genus of typical bark beetles in the family Curculionidae. This is a monotypic genus and the one described species is Xyloterinus politus. It is native to North America where it infests both hardwood and softwood trees, as well as stacks of logs.
Platypus quercivorus, the oak ambrosia beetle, is a species of weevil and pest of broad-leaved trees. This species is most commonly known for vectoring the fungus responsible for excessive oak dieback in Japan since the 1980s. It is found in Japan, India, Indonesia, New Guinea, and Taiwan.

The lemon tree borer, also known as the whistling beetle or the singing beetle, is a longhorn beetle endemic to New Zealand. Its larvae are generalist feeders, boring into the wood of a wide variety of trees, native and introduced. When citrus orchards were first established in New Zealand, this beetle started inflicting serious damage, and so gained the name "lemon tree borer". Four species within the genus Oemona have been identified, suggesting that more species could be found. When disturbed by predators or humans, the adult beetle stridulates creating a "rasp" or "squeak" sound by rubbing its thorax and head together against an area of thin ridges. Māori would eat a liquid called "pia manuka", which was produced by manuka trees when its wood was damaged by the larva. When Captain Cook first arrived in NZ, his naturalists, Banks and Solander, collected a lemon tree borer in their first collection between 1769-1771. This oldest collected specimen can be found in the British Museum. A few years after the first collection, the species would be first described by the Danish naturalist Fabricius in 1775.

Cnestus mutilatus, commonly known as the camphor shot borer, camphor shoot borer, or sweetgum ambrosia beetle, is a species of ambrosia beetle in the subfamily Scolytinae of the weevil family Curculionidae. It is native to Asia, but has been established as an invasive species in the United States since 1999.














