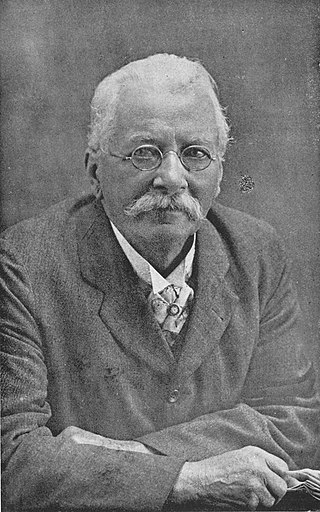Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

Captain Frederick Wollaston Hutton was an English-New Zealand scientist who applied the theory of natural selection to explain the origins and nature of the natural history of New Zealand. An army officer in early life, he then had an academic career in geology and biology. He became one of the most able and prolific nineteenth century naturalists of New Zealand.
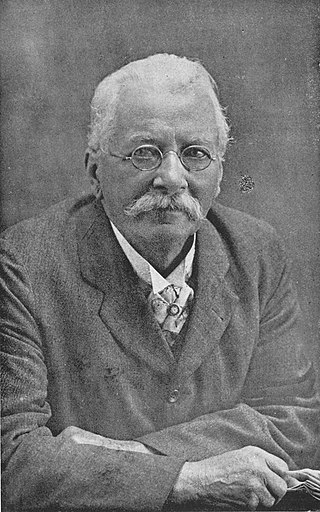
Henry Suter was a Swiss-born New Zealand zoologist, naturalist, palaeontologist, and malacologist.

Xymene is a genus of predatory sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Muricidae, the rock snails, found in New Zealand.

Microvoluta is a genus of very small sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Volutomitridae.

Linopyrga is a small genus of very small sea snails, pyramidellid gastropod mollusks or micromollusks. This genus is currently placed in the subfamily Chrysallidinae of the family Odostomiidae.

Austromitra is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Costellariidae.

Chaetocoelopa littoralis, commonly known as the hairy kelp fly, is a fly of the family Coelopidae. It is endemic to New Zealand and is widely distributed around the coastline, including offshore islands. These flies are black in appearance and show large variation in size, with males tending to be larger and more robust and 'hairy' than females.

The Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG) is a taxonomic database which attempts to cover published genus names for all domains of life from 1758 in zoology up to the present, arranged in a single, internally consistent taxonomic hierarchy, for the benefit of Biodiversity Informatics initiatives plus general users of biodiversity (taxonomic) information. In addition to containing over 490,000 published genus name instances as at March 2020, the database holds over 1.7 million species names, although this component of the data is not maintained in as current or complete state as the genus-level holdings. IRMNG can be queried online for access to the latest version of the dataset and is also made available as periodic snapshots or data dumps for import/upload into other systems as desired.

Exsul singularis, the bat-winged fly, is a species of fly that is endemic to New Zealand, first described by Frederick Hutton in 1901. The males have enormously expanded wings. The species is found in the south-western South Island and occurs mostly in high-altitude meadows near streams. It preys on soft-bodied flying insects and is believed to uses its wings to increase its body temperature to offset the cool temperatures of its alpine habitat.
Trieres is a genus of beetles belonging to the family Elateridae.

Lamprinodes is a genus of beetles belonging to the family Staphylinidae.
Haemonais is a genus of annelids belonging to the family Naididae.

Pantopsalis listeri is a species of harvestman in the family Neopilionidae.
Odontionopa is a genus of leaf beetles in the subfamily Eumolpinae. It is distributed in Africa.
Heterosquilla is a genus of shrimps belonging to the family Tetrasquillidae.
Gastroblastea is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the family Campanulariidae.
Asteliaphasma is a genus of phasmids belonging to the family Diapheromeridae.
Phialucium is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the monotypic family Phialuciidae.
Kiwilichus is a genus of feather mites in Kiwilichidae, a monotypic family of mites that is endemic to New Zealand. Kiwi (Apteryx) are the host birds of the two species. Kiwilichus cryptosikyus is known to be hosted by southern brown kiwi and great spotted kiwi, and Kiwilichus delosikyus by southern brown kiwi.