
Botflies, also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, are a family of flies technically known as the Oestridae. Their larvae are internal parasites of mammals, some species growing in the host's flesh and others within the gut. Dermatobia hominis is the only species of botfly known to parasitize humans routinely, though other species of flies cause myiasis in humans.

The Fanniidae are a small group of true flies largely confined to the Holarctic and temperate Neotropical realms; there are 11 Afrotropical species, 29 Oriental, and 14 Australasian.
Evelyn Cecil Muschamp d’Assis Fonseca was a British dipterist. He was responsible for formally naming a number of fly species, including:

The lesser house fly or little house fly, Fannia canicularis, is somewhat smaller than the common housefly. It is best known for its habit of entering buildings and flying in jagged patterns in the middle of a room. It is slender, and the median vein in the wing is straight. Larvae feed on all manner of decaying organic matter, including carrion.
Entomological evidence is legal evidence in the form of insects or related artifacts and is a field of study in forensic entomology. Such evidence is used particularly in medicolegal and medicocriminal applications due to the consistency of insects and arthropods in detecting decomposition quickly. Insect evidence is customarily used to determine post mortem interval (PMI), but can also be used as evidence of neglect or abuse. It can indicate how long a person was abused/neglected as well as provide important insights into the amount of bodily care given to the neglected or abused person.

Fannia is a very large genus of approximately 288 species of flies. The genus was originally described by the French entomologist Jean-Baptiste Robineau-Desvoidy in 1830. A number of species were formerly placed in the genus Musca.
Fannia pusio, known as the chicken dung fly is a fly species of the family Fanniidae including over 260 species of flies worldwide. Originally native to Central and North America, its distribution is now largely global, having been introduced with livestock. As its common name implies it can be very abundant at poultry facilities, resulting in considerable nuisance by their huge numbers. But the larvae will also feed on a wide variety of food, including rotting vegetable matter, excrement, fungi and carrion.
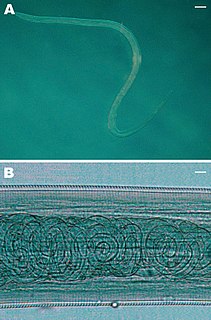
Thelazia is a genus of nematode worms which parasitize the eyes and associated tissues of various bird and mammal hosts, including humans. They are often called "eyeworms", and infestation with Thelazia species is referred to as "thelaziasis". Adults are usually found in the eyelids, tear glands, tear ducts, or the so-called "third eyelid". Occasionally, they are found in the eyeball itself, either under the conjunctiva or in the vitreous cavity of the eyeball. All species of Thelazia for which the life cycle has been studied are transmitted by species of Diptera (flies) which do not bite, but which feed on tears.

Thelaziasis is the term for infestation with parasitic nematodes of the genus Thelazia. The adults of all Thelazia species discovered so far inhabit the eyes and associated tissues of various mammal and bird hosts, including humans. Thelazia nematodes are often referred to as "eyeworms".

Fannia scalaris, also known as the latrine fly, is a fly species in the Fanniidae family. This species is smaller and more slender than the house fly, Musca domestica, and is similar in appearance to the lesser house fly, Fannia canicularis. The life cycle of this species can be as long as one month. These flies are globally distributed in urban areas as they are drawn to unsanitary environments. F. scalaris is a major cause of myiasis, the infestation of a body cavity by fly maggots. The adults infest bodies that have decomposed, making the species an important part of forensic entomology. The larvae of this fly have adapted protuberances, or feathered appendages, that allow them to survive in such a moist environment. Entomologists continue to research the effects that F. scalaris may have medically, forensically, and on the environment around them.

Fannia armata is a fly species in the Fanniidae family. This species is smaller and more slender than the house fly, Musca domestica, and is similar in appearance to the lesser house fly, Fannia canicularis. It is found in the Palearctic. For identification see

Fannia lepida is a fly species in the Fanniidae family. This species is smaller and more slender than the house fly, Musca domestica, and is similar in appearance to the lesser house fly, Fannia canicularis. It is found in the Palearctic. For identification see

Fannia lucidula is a fly species in the Fanniidae family. This species is smaller and more slender than the house fly, Musca domestica, and is similar in appearance to the lesser house fly, Fannia canicularis.

Fannia lustrator is a fly species in the Fanniidae family. This species is smaller and more slender than the house fly, Musca domestica, and is similar in appearance to the lesser house fly, Fannia canicularis. It is found in the Palearctic.

Fannia sociella is a fly species in the Fanniidae family. This species is smaller and more slender than the house fly, Musca domestica, and is similar in appearance to the lesser house fly, Fannia canicularis. It is found in the Palearctic. For identification see

Fannia ornata is a species of fly in the family Fanniidae. This species is smaller and more slender than the house fly, Musca domestica, and is similar in appearance to the lesser house fly, Fannia canicularis.
F. carbonaria may refer to:

Fannia mollissima is a species of fly in the family Fanniidae. It is found in the Palearctic. For identification see

Fannia rondanii is a species of fly in the family Fanniidae. It is found in the Palearctic. For identification see
Fannia pellucida is a species of fly in the family Fanniidae.














