
This article details features of the Opera web browser.

This article details features of the Opera web browser.
Opera 7, released 28 January 2003
Opera 11, released 16 December 2010
Some of the default mouse gestures include:
Opera 5.10, released April 2001
Around April 2019, Opera removed this functionality in its desktop browsers and it's no longer supported on desktop. The fate of it on its mobile browsers is uncertain.
Opera's original privacy feature, Private Tabs, allowed users to open a private browsing session in a tab in the current window, instead of a separate window. It would not record browsing history, use the web cache, or stored passwords, and would forget any information accessed in the Tab when it is closed. This feature was replaced by Private Windows in Opera 15. Opera 10.50 (Tabs) / Opera 15 (Windows)
This tool is directly tied to NetCraft and Phishtank, thereby serving as a phishing filter as well as real-time fraud protection.
The user can select the desired search engine via a list or by using keywords in the address field. Example: Opera has a pre-set keyword for using the Google search engine: "g". Therefore, if a user types "g Wikipedia" directly into the address field, Opera performs a Google search for "Wikipedia". Other keywords are included, including "b" for Bing, "y" for Yahoo! Search, and "w" for Wikipedia. Users can also customize their own keywords. Opera 4, released 28 June 2000
Opera 49

Users are able to save all the tabs in a window as a Speed Dial group, manage the saved links, and open them all later if wished. Opera 9.2, released 11 April 2007 [11]
Furthermore, other browsers including, but not limited to; Google Chrome, Safari, and Internet Explorer have or previously had a near identical feature. Although not necessarily branded as Speed Dial, it may be informally referred to as Speed Dial in non-Opera browsers or with 3rd party browser extensions that add the feature, considering that the feature first debuted in Opera browsers. [12]
Opera 11, released 16 December 2010
Opera 4, released 28 June 2000

Many notable features, there were available in older versions of the Opera web browser, were removed when Opera switched from its legacy layout engine, Presto, to the Chromium-based Blink engine. Presto was introduced in 2003 (Opera 7) and was used until Opera 12.18, in 2016. [14] [15] [16] [17]
g , yt and w prior to the search string launches a search using Google, YouTube and Wikipedia respectively.Opera 9, released 20 June 2006
Opera stores its content-blocking URL list in a file called urlfilter.ini. Several internet sites provide a regularly updated urlfilter.ini already loaded with the web's most common advertisements so users can block ads using the built-in feature. The users are able to sync the content blocker list using Opera Link.
Skins: Opera supports customized user-interface skins, allowing users to change the style and size of toolbars, buttons and menus. A drag and drop functionality allows the user to easily place links and buttons on toolbars. The user is able to install custom skins, ranging from color changes to OS mimics to animated GIF images. [19]
Toolbars: Opera provides toolbars that display different menus and buttons. For example, the "start" toolbar is a drop-down toolbar which can be enabled to provide access to history and bookmarks when the user focuses the address field. Additionally a "view" toolbar includes multiple shortcuts to control the page exhibition and a find in page tool, a "navigation" toolbar can show commands to navigate through webpages, etc.
Dragonfly is written using standard web technology and the Scope protocol, and source is available under the Apache License 2.0. Opera Dragonfly is compatible with Opera products using Presto 2.1 and later. The first stable version of Opera Dragonfly was released on 5 May 2011. Opera 9.5, released 2008
Opera 9.5, released 12 June 2008
Opera 6, released 18 December 2001
It is possible to control all main functions of the browser using only the keyboard, and the default keyboard shortcuts can be modified. Opera also supports the use of access keys to allow a computer user to immediately jump to a specific part of a web page via the keyboard.
Opera Link servers left users with only a month to backup their bookmarks one by one, before the feature was discontinued in 2015. [24] User data synchronization support was set to return in a later release, though users on Symbian, J2ME and BlackBerry would not have access to it. Opera 9.50, released 12 June 2008. 14 December 2015
This feature was replaced by Private Windows in Opera 15. Opera 10.50 Opera 15
Since version 32 this feature can only be achieved with a combination of Speed Dial and Bookmarks, or more elegantly by installing a session-manager extension. [25] [26] Opera 4, released 28 June 2000 Opera 32, released September 2015
Not loading of tabs until they're selected after a session restore (lazy loading) - introduced in version 21 (along with delayed loading), [27] [28] removed in version 46. [29] [30]
Opera 8, released 19 April 2005
Common compatibility problems are caused by websites not following standards or using methods for detecting the browser being used. To cope with outdated detection methods or poorly built websites, Opera enables users to change the information that is sent to websites to identify what kind of browser is being used—known as the user-agent. In previous years, Opera came preconfigured to partially "cloak" itself as Internet Explorer, but still included the word "Opera" in the user-agent information allowing the browser to be counted in web browser statistics. As websites modernized themselves and Opera 9 became more compatible with IE code, Opera began to use its own identification by default.
Later versions of Opera offered a limited method of cloaking allowing selection from a pre-defined range of options including Mozilla and Internet Explorer. If needed, Opera can mask completely as Internet Explorer or Mozilla, leaving out the reference to Opera in the UA string and JavaScript objects. Some sites test only for objects that are not present in Opera.
The version 8 of Opera introduced a further provision for dealing with faulty coding, by providing a set of scripts in BrowserJS that rewrites known broken pages as they are being opened. The closely related UserJS (similar to Mozilla's Greasemonkey), allows users to run their own code at various times in the processing of a page. These techniques have allowed many popular but incompatible sites to be used fully with Opera. [34]
Opera periodically updates itself with the latest version of BrowserJS and override_downloaded.ini files to keep more sites working correctly in the browser, respectively, they serve to patch websites which would otherwise have issues to run on Opera and to cloak the UA string by default for some website domains.
A web browser is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. By 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people had used a browser. The most-used browser is Google Chrome, with a 67% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%.

A bookmarklet is a bookmark stored in a web browser that contains JavaScript commands that add new features to the browser. They are stored as the URL of a bookmark in a web browser or as a hyperlink on a web page. Bookmarklets are usually small snippets of JavaScript executed when user clicks on them. When clicked, bookmarklets can perform a wide variety of operations, such as running a search query from selected text or extracting data from a table.
iCab is a web browser for MacOS and Classic Mac OS by Alexander Clauss, derived from Crystal Atari Browser (CAB) for Atari TOS compatible computers. It was one of the few browsers still updated for the classic Mac OS prior to that version being discontinued after version 3.0.5 in 2008; Classilla was the last browser that was maintained for that OS but it was discontinued in 2021.

Safari is a web browser developed by Apple. It is built into several of Apple's operating systems, including macOS, iOS, iPadOS and visionOS, and uses Apple's open-source browser engine WebKit, which was derived from KHTML.
The taskbar is a graphical user interface element that has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95, displaying and facilitating switching between running programs. The taskbar and the associated Start Menu were created and named in 1993 by Daniel Oran, a program manager at Microsoft who had previously collaborated on great ape language research with the behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner at Harvard.

Pop-up ads or pop-ups are forms of online advertising on the World Wide Web. A pop-up is a graphical user interface (GUI) display area, usually a small window, that suddenly appears in the foreground of the visual interface. The pop-up window containing an advertisement is usually generated by JavaScript that uses cross-site scripting (XSS), sometimes with a secondary payload that uses Adobe Flash. They can also be generated by other vulnerabilities/security holes in browser security.

Maxthon is a freeware web browser, created by JeffChen in Singapore. It is available for Windows, macOS, Linux, and as Maxthon Mobile for Android, iOS, and Windows Phone 8. Since version 6, Maxthon is based on Chromium.
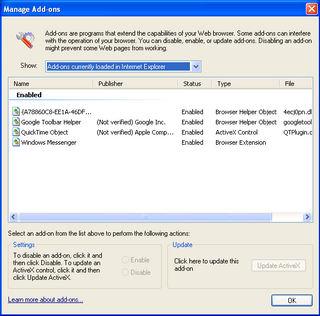
A Browser Helper Object (BHO) is a DLL module designed as a plugin for the Microsoft Internet Explorer web browser to provide added functionality. BHOs were introduced in October 1997 with the release of version 4 of Internet Explorer. Most BHOs are loaded once by each new instance of Internet Explorer. However, in the case of Windows Explorer, a new instance is launched for each window.
This is a comparison of both historical and current web browsers based on developer, engine, platform(s), releases, license, and cost.

Netscape Browser is the eighth major release of the Netscape series of web browsers, now all discontinued. It was published by AOL, but developed by Mercurial Communications, and originally released for Windows on May 19, 2005.
The Windows shell is the graphical user interface for the Microsoft Windows operating system. Its readily identifiable elements consist of the desktop, the taskbar, the Start menu, the task switcher and the AutoPlay feature. On some versions of Windows, it also includes Flip 3D and the charms. In Windows 10, the Windows Shell Experience Host interface drives visuals like the Start Menu, Action Center, Taskbar, and Task View/Timeline. However, the Windows shell also implements a shell namespace that enables computer programs running on Windows to access the computer's resources via the hierarchy of shell objects. "Desktop" is the top object of the hierarchy; below it there are a number of files and folders stored on the disk, as well as a number of special folders whose contents are either virtual or dynamically created. Recycle Bin, Libraries, Control Panel, This PC and Network are examples of such shell objects.

The history of the Opera web browser began in 1994 when it was started as a research project at Telenor, the largest Norwegian telecommunications company. In 1995, the project branched out into a separate company named Opera Software ASA, with the first publicly available version released in 1996. Opera has undergone extensive changes and improvements, and introduced notable features such as Speed Dial.
A browser toolbar is a toolbar that resides within a browser's window. All major web browsers provide support to browser toolbar development as a way to extend the browser's GUI and functionality. Browser toolbars are considered to be a particular kind of browser extensions that present a toolbar. Browser toolbars are specific to each browser, which means that a toolbar working on a browser does not work on another one. All browser toolbars must be installed in the corresponding browser before they can be used and require updates when new versions are released.
IE7Pro is an add-on for Internet Explorer 6, 7, and 8 that aims to enhance the feature set provided by the browser. IE7Pro adds features such as tab enhancement, an ad blocker and flash blocker, mouse gestures, inline search, privacy enhancements, online bookmark service, Greasemonkey-like user script support, and plug-in support. IE7Pro is available in several languages – this is made possible by user translations.
Opera is a multi-platform web browser developed by its namesake company Opera. The current edition of the browser is based on Chromium. Opera is available on Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. Two mobile versions are still active, called Opera Mobile and Opera Mini. Opera also has a news aggregator app called Opera News with Aria, an AI-based search engine.
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google. It was first released in 2008 for Microsoft Windows, built with free software components from Apple WebKit and Mozilla Firefox. Versions were later released for Linux, macOS, iOS, iPadOS, and also for Android, where it is the default browser. The browser is also the main component of ChromeOS, where it serves as the platform for web applications.
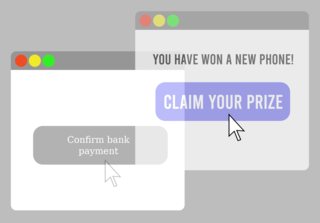
Clickjacking is a malicious technique of tricking a user into clicking on something different from what the user perceives, thus potentially revealing confidential information or allowing others to take control of their computer while clicking on seemingly innocuous objects, including web pages.
Firefox was created by Dave Hyatt and Blake Ross as an experimental branch of the Mozilla browser, first released as Firefox 1.0 on November 9, 2004. Starting with version 5.0, a rapid release cycle was put into effect, resulting in a new major version release every six weeks. This was gradually accelerated further in late 2019, so that new major releases occur on four-week cycles starting in 2020.

Vivaldi is a freeware, cross-platform web browser with a built-in email client developed by Vivaldi Technologies, a company founded by Tatsuki Tomita and Jon Stephenson von Tetzchner, who was the co-founder and CEO of Opera Software. Vivaldi was initially released on 27 January 2015.