
Vilonia is a city in Faulkner County, Arkansas, United States. Its population was 4,288 in 2020 and estimated at4,429 in 2021, up from 3,815 at the 2010 census and 2,106 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Central Arkansas region.

A tornado warning is a public warning that is issued by weather forecasting agencies to an area in the direct path of a tornado, or a thunderstorm capable of producing one, and advises individuals in that area to take cover. Modern weather surveillance technology such as Doppler weather radar can detect rotation in a thunderstorm, allowing for early warning before a tornado develops. They are also commonly issued based on reported visual sighting of a tornado, funnel cloud, or wall cloud, typically from weather spotters or the public, but also law enforcement or local emergency management. When radar is unavailable or insufficient, such ground truth is crucial. In particular, a tornado can develop in a gap of radar coverage, of which there are several known in the United States.

A severe thunderstorm watch is a statement issued by weather forecasting agencies to advise the public that atmospheric conditions in a given region may lead to the development of severe thunderstorms within the region over several hours. The criteria for issuing a watch varies from country to country and may also include torrential rainfall and tornadoes. A watch may also be issued several hours ahead of the arrival of a mature and organized complex of storms, such as a mesoscale convective system.

The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the purposes of protection, safety, and general information. It is a part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) branch of the Department of Commerce, and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland, within the Washington metropolitan area. The agency was known as the United States Weather Bureau from 1890 until it adopted its current name in 1970.

The Storm Prediction Center (SPC) is a US government agency that is part of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), operating under the control of the National Weather Service (NWS), which in turn is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) of the United States Department of Commerce (DoC).
The National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL) is a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) weather research laboratory under the Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research. It is one of seven NOAA Research Laboratories (RLs).
This article describes severe weather terminology used by the National Weather Service (NWS) in the United States. The NWS, a government agency operating as an arm of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) branch.It defines precise meanings for nearly all of its weather terms.
A tornado emergency is an enhanced version of a tornado warning, which is used by the National Weather Service (NWS) in the United States during imminent, significant tornado occurrences in highly populated areas. Although it is not a new warning type from the NWS, issued instead within a severe weather statement or in the initial tornado warning, a tornado emergency generally means that significant, widespread damage is expected to occur and a high likelihood of numerous fatalities is expected with a large, strong to violent tornado.

The tornado outbreak of October 17–19, 2007 was a widespread tornado outbreak that took place across much of the eastern half of North America starting on October 17, 2007, and continuing into the early hours of October 19. The outbreak was also responsible for five deaths; three in Michigan and two in Missouri, plus many injuries. At least 64 tornadoes were confirmed including 16 on October 17 across six states including Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi and Missouri with wind damage reported in Oklahoma, Kansas, Illinois, Iowa, Arkansas and Mississippi. On October 18, at least 48 tornadoes were confirmed across eight states including Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Tennessee, Kentucky, Illinois, Indiana and Michigan, plus widespread straight line wind damage. Until 2010, this event held the record for largest tornado outbreak ever recorded in the month of October according to NOAA.

The Tornado outbreak of November 23–24, 2001 was a fall tornado outbreak which affected portions of the southern United States from Arkansas to Alabama on November 23–24, 2001, with additional tornadoes recorded in Louisiana, Kentucky, Missouri, Indiana and Georgia. Recorded as one of the most intense November outbreaks ever across that area, tornadoes from the event killed at least 13 across three states including 4 in Alabama, four in Arkansas and five in Mississippi.
The March 1997 tornado outbreak was a major tornado outbreak that struck portions of the central and southern United States on March 1–2, 1997. Affecting areas mostly from Arkansas to Kentucky, the outbreak produced 58 tornadoes, including three violent (F4) tornadoes, and killed at least 27 people, including 25 in Arkansas alone and one death each in Mississippi and Tennessee. This was Arkansas' deadliest tornado outbreak since May 15, 1968, when 34 were killed in Jonesboro. Severe flooding also occurred across the Ohio and Tennessee Valleys, resulting in 16 Ohio counties and 44 Kentucky counties being declared disaster areas. The flash floods and damaging wind elsewhere caused 34 deaths across six states including 19 in Kentucky, five in Ohio, five in Tennessee, two in Texas and three in West Virginia. Damage estimates were about $1 billion while 75,000 homes were damaged.

The 2008 Super Tuesday tornado outbreak was a deadly tornado outbreak which affected the Southern United States and the lower Ohio Valley on February 5 and 6, 2008. The event began on Super Tuesday, while 24 states in the United States were holding primary elections and caucuses to select the presidential candidates for the upcoming presidential election. Missouri, Illinois, Arkansas, Alabama, and Tennessee were among the affected regions in which primaries were being held. Some voting locations were forced to close early due to the approaching severe weather.
In National Weather Service (NWS) terminology, a Hazardous Weather Outlook is a weather statement issued to provide information of potential severe weather events within the next seven days. The outlook may include information about potential severe thunderstorms, heavy rain or flooding, winter weather, extremes temperatures.

The 2011 Super Outbreak was the largest, costliest, and one of the deadliest tornado outbreaks ever recorded, taking place in the Southern, Midwestern, and Northeastern United States from April 25 to 28, 2011, leaving catastrophic destruction in its wake. Over 175 tornadoes struck Alabama, Mississippi, and Tennessee, which were the most severely damaged states. Other destructive tornadoes occurred in Arkansas, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, New York, and Virginia, with storms also affecting other states in the Southern and Eastern United States. In total, 360 tornadoes were confirmed by NOAA's National Weather Service (NWS) and Government of Canada's Environment Canada in 21 states from Texas to New York to southern Canada. Widespread and destructive tornadoes occurred on each day of the outbreak. April 27 was the most active day, with a record 216 tornadoes touching down that day from midnight to midnight CDT. Four of the tornadoes were rated EF5, which is the highest ranking on the Enhanced Fujita scale; typically these tornadoes are recorded no more than once a year.
Bowman is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Craighead County, Arkansas, United States. It was first listed as a CDP in the 2020 census with a population of 75.
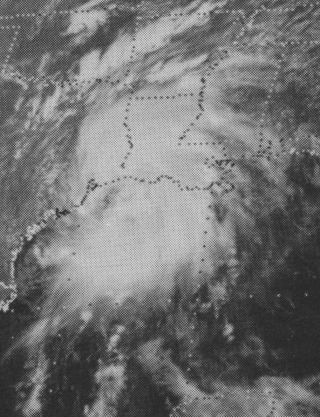
Tropical Storm Debra was the second of two tropical storms to hit the United States in the 1978 Atlantic hurricane season. The fourth named storm of the season, Debra developed from the interaction between a high-altitude cold low and a lower tropical wave in the Gulf of Mexico. Forming on August 25, it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Debra based on data from a Hurricane Hunter aircraft. As Debra approached the coast, it attained peak winds of 60 mph (95 km/h). The storm made landfall on the coast of Louisiana, east of the Texas border. Two deaths were caused by the storm. Debra weakened as it moved inland and ultimately dissipated on August 29 over Arkansas.

This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2020. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Bangladesh, and eastern India, but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina, Australia and New Zealand. Tornadic events are often accompanied by other forms of severe weather, including strong thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail.

A localized, but destructive and deadly tornado outbreak impacted Tennessee, Alabama, and Georgia on Leap Day in 1952. Thanks in part to unseasonably strong jet stream winds and a strong cold front, eight tornadoes left trails of damage and casualties. The tornado to cause the most casualties was an F1 tornado in Belfast, Tennessee, which killed three people and injured 166. A violent F4 tornado moved through Fayetteville, Tennessee, destroying most of the town and killing two and injuring 150 others. On the north side of Fort Payne, Alabama, an F3 tornado caused major damage and injured 12 people. In all, the outbreak killed five, injured 336, and caused $3.1 million (1952 USD) in damage. Four more fatalities and 14 more injuries occurred from other non-tornadic events as well.

A significant early spring tornado outbreak occurred during the afternoon and evening hours of March 5, 2022 in the Midwest, primarily in the state of Iowa, before transitioning to a damaging wind event across northern parts of Illinois and Indiana. Multiple tornadoes were reported, several of which were produced by a dominant supercell thunderstorm in central Iowa. One long-track, low-end EF4 tornado caused major damage near the towns of Winterset and Norwalk, resulting in six fatalities. Multiple other supercells spawned along an area of moderate destabilization in northern Missouri, prompting further tornado warnings in southern Iowa, as they entered a highly favorable environment for maturing. Large hail and damaging wind gusts accompanied the storms, which continued their passage across the Midwestern states into overnight. More tornadic weather was confirmed in Arkansas and Missouri the next day and into the early morning of March 7. In addition to that, straight line winds killed one person near Hazel, Kentucky when a semi trailer was blown over on US 641. Another non-tornadic fatality occurred in western New York as the storm approached.















