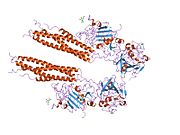
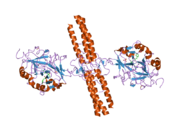Fibrinogen is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood clot. Fibrin clots function primarily to occlude blood vessels to stop bleeding. Fibrin also binds and reduces the activity of thrombin. This activity, sometimes referred to as antithrombin I, limits clotting. Fibrin also mediates blood platelet and endothelial cell spreading, tissue fibroblast proliferation, capillary tube formation, and angiogenesis and thereby promotes revascularization and wound healing.

CD11c, also known as Integrin, alpha X (ITGAX), is a gene that encodes for CD11c.
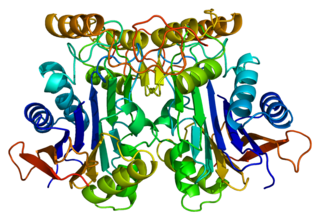
N(4)-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparaginase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AGA gene.

β2-glycoprotein 1, also known as beta-2 glycoprotein 1 and Apolipoprotein H (Apo-H), is a 38 kDa multifunctional plasma protein that in humans is encoded by the APOH gene. One of its functions is to bind cardiolipin. When bound, the structure of cardiolipin and β2-GP1 both undergo large changes in structure. Within the structure of Apo-H is a stretch of positively charged amino acids, Lys-Asn-Lys-Glu-Lys-Lys, are involved in phospholipid binding.

Integrin beta-3 (β3) or CD61 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITGB3 gene. CD61 is a cluster of differentiation found on thrombocytes.

Hemoglobin subunit alpha, Hemoglobin, alpha 1, is a hemoglobin protein that in humans is encoded by the HBA1 gene.

Integrin alpha-IIb is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITGA2B gene. ITGA2B, also known as CD41, encodes integrin alpha chain 2b. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. Alpha chain 2b undergoes post-translational cleavage to yield disulfide-linked light and heavy chains that join with beta 3 to form a fibrinogen receptor expressed in platelets that plays a crucial role in coagulation. Mutations that interfere with this role result in thrombasthenia. At least 38 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. In addition to adhesion, integrins are known to participate in cell-surface mediated signalling.

Fibrinogen gamma chain, also known as fibrinogen gamma gene (FGG), is a human gene found on chromosome 3.
An Error has occurred retrieving Wikidata item for infobox Coagulation factor XIII B chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the F13B gene.

Fibrinogen alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGA gene.

Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 also known as S1PR3 is a human gene which encodes a G protein-coupled receptor which binds the lipid signaling molecule sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). Hence this receptor is also known as S1P3.
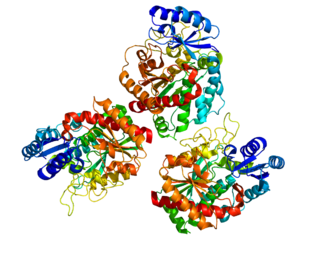
Carboxypeptidase B2 (CPB2), also known as carboxypeptidase U (CPU), plasma carboxypeptidase B (pCPB) or thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI), is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the gene CPB2.

alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein also known as fetuin-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AHSG gene. Fetuin-A belongs to the fetuin class of plasma binding proteins and is more abundant in fetal than adult blood.

Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL6A1 gene.

Glycoprotein Ib (platelet), beta polypeptide (GP1BB) also known as CD42c, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP1BB gene.

Glycoprotein IX (platelet) (GP9) also known as CD42a (Cluster of Differentiation 42a), is a human gene.

Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITIH1 gene.

Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITIH2 gene.

Glycoprotein V (platelet) (GP5) also known as CD42d (Cluster of Differentiation 42d), is a human gene.

Hyaluronan synthase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HAS1 gene.