
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word laser is an anacronym that originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow.

An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from the cavity is suppressed. Optical amplifiers are important in optical communication and laser physics. They are used as optical repeaters in the long distance fiber-optic cables which carry much of the world's telecommunication links.
Mode locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example, in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be "phase-locked" or "mode-locked".
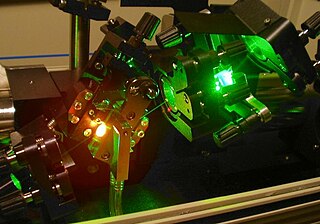
Titanium-sapphire lasers (also known as Ti:sapphire lasers, Ti:Al2O3 lasers or Ti:sapphs) are tunable lasers which emit red and near-infrared light in the range from 650 to 1100 nanometers. These lasers are mainly used in scientific research because of their tunability and their ability to generate ultrashort pulses thanks to its broad light emission spectrum. Lasers based on Ti:sapphire were first constructed and invented in June 1982 by Peter Moulton at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory.

Kerr-lens mode-locking (KLM) is a method of mode-locking lasers via the nonlinear optical Kerr effect. This method allows the generation of pulses of light with a duration as short as a few femtoseconds.
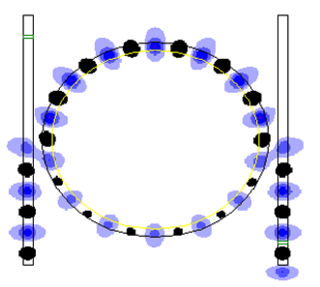
An optical ring resonator is a set of waveguides in which at least one is a closed loop coupled to some sort of light input and output. The concepts behind optical ring resonators are the same as those behind whispering galleries except that they use light and obey the properties behind constructive interference and total internal reflection. When light of the resonant wavelength is passed through the loop from the input waveguide, the light builds up in intensity over multiple round-trips owing to constructive interference and is output to the output bus waveguide which serves as a detector waveguide. Because only a select few wavelengths will be at resonance within the loop, the optical ring resonator functions as a filter. Additionally, as implied earlier, two or more ring waveguides can be coupled to each other to form an add/drop optical filter.
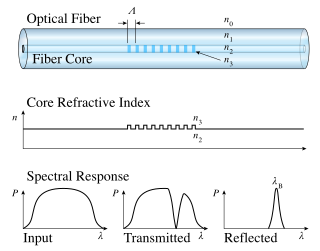
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical filter to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector.
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber waveguides, transparent dielectric waveguides made of plastic and glass, liquid light guides, and liquid waveguides.
A fiber laser is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, thulium and holmium. They are related to doped fiber amplifiers, which provide light amplification without lasing.
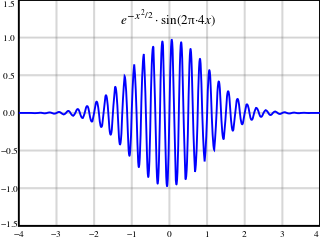
A frequency comb or spectral comb is a spectrum made of discrete and regularly spaced spectral lines. In optics, a frequency comb can be generated by certain laser sources.

Silicon photonics is the study and application of photonic systems which use silicon as an optical medium. The silicon is usually patterned with sub-micrometre precision, into microphotonic components. These operate in the infrared, most commonly at the 1.55 micrometre wavelength used by most fiber optic telecommunication systems. The silicon typically lies on top of a layer of silica in what is known as silicon on insulator (SOI).

In optics, a supercontinuum is formed when a collection of nonlinear processes act together upon a pump beam in order to cause severe spectral broadening of the original pump beam, for example using a microstructured optical fiber. The result is a smooth spectral continuum. There is no consensus on how much broadening constitutes a supercontinuum; however researchers have published work claiming as little as 60 nm of broadening as a supercontinuum. There is also no agreement on the spectral flatness required to define the bandwidth of the source, with authors using anything from 5 dB to 40 dB or more. In addition the term supercontinuum itself did not gain widespread acceptance until this century, with many authors using alternative phrases to describe their continua during the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s.

Coherent addition of lasers is a method of power scaling. It allows increasing the output power and brightness of single-transversal mode laser.
EKSPLA is a laser and laser electronics manufacturing company based in Vilnius, Lithuania. EKSPLA is known for their lasers and laser systems, as well as other photonics components. The company is supplying their products for scientific, OEM and industrial applications.
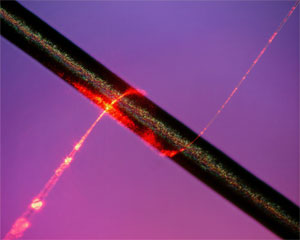
A subwavelength-diameter optical fibre is an optical fibre whose diameter is less than the wavelength of the light being propagated through it. An SDF usually consists of long thick parts at both ends, transition regions (tapers) where the fibre diameter gradually decreases down to the subwavelength value, and a subwavelength-diameter waist, which is the main acting part. Due to such a strong geometrical confinement, the guided electromagnetic field in an SDF is restricted to a single mode called fundamental. In usual optical fibres, light both excites and feels shear and longitudinal bulk elastic waves, giving rise to forward-guided acoustic wave Brillouin scattering and backward-stimulated Brillouin scattering. In a subwavelength-diameter optical fibre, the situation changes dramatically.
The Mamyshev 2R regenerator is an all-optical regenerator used in optical communications. In 1998, Pavel V. Mamyshev of Bell Labs proposed and patented the use of the self-phase modulation (SPM) for single channel optical pulse reshaping and re-amplification. More recent applications target the field of ultrashort high peak-power pulse generation.
Pulsed operation of lasers refers to any laser not classified as continuous wave, so that the optical power appears in pulses of some duration at some repetition rate. This encompasses a wide range of technologies addressing a number of different motivations. Some lasers are pulsed simply because they cannot be run in continuous mode.
Govind P. Agrawal is an Indian American physicist and a fellow of Optica, Life Fellow of the IEEE, and Distinguished Fellow of the Optical Society of India. He is the recipient of James C. Wyant Professorship of Optics at the Institute of Optics and a professor of physics at the University of Rochester. He is also a Distinguished scientist at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) in the University of Rochester. Agrawal has authored and co-authored several highly cited books in the fields of non-linear fiber optics, optical communications, and semiconductor lasers.

A tapered double-clad fiber (T-DCF) is a double-clad optical fiber which is formed using a specialised fiber drawing process, in which temperature and pulling forces are controlled to form a taper along the length of the fiber. By using pre-clad fiber preforms both the fiber core and the inner and outer cladding layers vary in diameter and thickness along the full length of the fiber. This tapering of the fiber enables the combination of the characteristics of conventional 8–10 μm diameter double-clad single-mode fibers to propagate light in fundamental mode with those of larger diameter (50–100 μm) double-clad multi-mode fibers used for optical amplification and lasing. The result is improved maintenance of pulse fidelity compared to conventional consistent diameter fiber amplifiers. By virtue of the large cladding diameter T-DCF can be pumped by optical sources with very poor brightness factor such as laser diode bars or even VECSELs matrices, significantly reducing the cost of fiber lasers/amplifiers.
Semiconductor saturable-absorber mirrors (SESAMs) are a type of saturable absorber used in mode locking lasers.











