Related Research Articles

Sir Roy George Douglas Allen, CBE, FBA was an English economist, mathematician and statistician, also member of the International Statistical Institute.
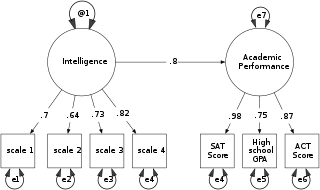
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a diverse set of methods used by scientists doing both observational and experimental research. SEM is used mostly in the social and behavioral sciences but it is also used in epidemiology, business, and other fields. A definition of SEM is difficult without reference to technical language, but a good starting place is the name itself.
Multilevel models are statistical models of parameters that vary at more than one level. An example could be a model of student performance that contains measures for individual students as well as measures for classrooms within which the students are grouped. These models can be seen as generalizations of linear models, although they can also extend to non-linear models. These models became much more popular after sufficient computing power and software became available.
A mixed model, mixed-effects model or mixed error-component model is a statistical model containing both fixed effects and random effects. These models are useful in a wide variety of disciplines in the physical, biological and social sciences. They are particularly useful in settings where repeated measurements are made on the same statistical units, or where measurements are made on clusters of related statistical units. Mixed models are often preferred over traditional analysis of variance regression models because of their flexibility in dealing with missing values and uneven spacing of repeated measurements. The Mixed model analysis allows measurements to be explicitly modeled in a wider variety of correlation and variance-covariance structures.
Latent growth modeling is a statistical technique used in the structural equation modeling (SEM) framework to estimate growth trajectories. It is a longitudinal analysis technique to estimate growth over a period of time. It is widely used in the field of psychology, behavioral science, education and social science. It is also called latent growth curve analysis. The latent growth model was derived from theories of SEM. General purpose SEM software, such as OpenMx, lavaan, AMOS, Mplus, LISREL, or EQS among others may be used to estimate growth trajectories.
Sir David Forbes Hendry, FBA CStat is a British econometrician, currently a professor of economics and from 2001 to 2007 was head of the economics department at the University of Oxford. He is also a professorial fellow at Nuffield College, Oxford.
Stephen Webb Raudenbush is the Lewis-Sebring Professor of Sociology and Chairman of the Committee on Education at the University of Chicago. He is best known for his development and application of hierarchical linear models (HLM) in the field of education but he has also published on other subjects such as health and crime. Hierarchical linear models, which go by many other names, are used to study many natural processes. To use an example from education, a three level hierarchical model might account for the fact that students are nested in classrooms which are nested in schools. With the right data one could go further and note that schools are nested in districts which are nested in states. Repeated measures of the same individuals can be studied with these models as observations nested in people.
Sylvia Therese Richardson is a French/British Bayesian statistician and is currently Professor of Biostatistics and Director of the MRC Biostatistics Unit at the University of Cambridge. In 2021 she became the president of the Royal Statistical Society for the 2021–22 year.
Harvey Goldstein was a British statistician known for his contributions to multilevel modelling methodology, statistical software, social statistics, and for applying this to educational assessment and league tables.

James Durbin FBA was a British statistician and econometrician, known particularly for his work on time series analysis and serial correlation.

David John Bartholomew was a British statistician who was president of the Royal Statistical Society between 1993 and 1995. He was professor of statistics at the London School of Economics between 1973 and 1996.
John Denis Sargan, FBA was a British econometrician who specialized in the analysis of economic time-series.
One application of multilevel modeling (MLM) is the analysis of repeated measures data. Multilevel modeling for repeated measures data is most often discussed in the context of modeling change over time ; however, it may also be used for repeated measures data in which time is not a factor.
Sophia Rabe-Hesketh is a statistician who works as a professor in the Department of Educational Statistics and Biostatistics at the University of California, Berkeley. Her research involves the development of generalized linear mixed models of data that incorporate latent variables to handle hidden data.
Julia Mary Black is the strategic director of innovation and a professor of law at the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE). She was the interim director of the LSE, a post she held from September 2016 until September 2017, at which time Minouche Shafik took over the directorship. She is the president of the British Academy, the UK's national academy for the humanities and social sciences, and became the academy's second female president in July 2021 for a four-year term.
Patrick James Curran is an American psychologist and statistician. He is a professor of quantitative psychology at the University of North Carolina, where he is also a faculty member at the Center for Developmental Science.
Daniel John Bauer is an American statistician, professor, and director of the quantitative psychology program at the University of North Carolina, where he is also on the faculty at the Center for Developmental Science. He is known for rigorous methodological work on latent variable models and is a proponent of integrative data analysis, a meta-analytic technique that pools raw data across multiple independent studies.

Kelvyn Jones, is a British professor (Emeritus) of human quantitative geography at the University of Bristol. He focuses on the quantitative modelling of social science data with complex structure through the application of multilevel models; especially in relation to change and health outcomes. Uniquely he is an elected Fellow of the British Academy, the Academy of the Social Sciences and the Learned Society of Wales.

Ellen Louise "E.L." Hamaker is a Dutch-American psychologist, and statistician. Since 2018 she has been a full professor at Utrecht University, holding the chair Longitudinal Data Analysis at the Department of Methodology and Statistics. Her work focuses on the development of statistical models for the analysis of intensive longitudinal data in psychology, mainly within the frameworks of structural equation modeling and time series analysis.
Brinley Thomas, CBE, FBA was a Welsh economist. He was Professor of Economics and Social Sciences at University College, Cardiff, from 1946 to 1973.
References
- ↑ "Steele, Prof. Fiona Alison", Who's Who (online edition, Oxford University Press, December 2017). Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- 1 2 "Professor Fiona Steele", London School of Economics. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- 1 2 3 "Professor Fiona Steele", British Academy. 2 May 2018.
- ↑ The London Gazette, supplement 59647 (31 December 2010), p. 12.
- ↑ "No. 63714". The London Gazette (Supplement). 1 June 2022. p. B10.