The derivative is a fundamental tool of calculus that quantifies the sensitivity of change of a function's output with respect to its input. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the instantaneous rate of change, the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. The process of finding a derivative is called differentiation.
In mathematics, a field is a set on which addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are defined and behave as the corresponding operations on rational and real numbers. A field is thus a fundamental algebraic structure which is widely used in algebra, number theory, and many other areas of mathematics.

In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn . The sequence commonly starts from 0 and 1, although some authors start the sequence from 1 and 1 or sometimes from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the sequence begins

The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is an American single-engine supersonic multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful all-weather multirole aircraft with over 4,600 built since 1976. Although no longer purchased by the U.S. Air Force, improved versions are being built for export. In 1993, General Dynamics sold its aircraft manufacturing business to the Lockheed Corporation, which became part of Lockheed Martin after a 1995 merger with Martin Marietta.

The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy. Proving highly adaptable, it entered service with the Navy in 1961 before it was adopted by the United States Marine Corps and the United States Air Force, and by the mid-1960s it had become a major part of their air arms. Phantom production ran from 1958 to 1981 with a total of 5,195 aircraft built, making it the most produced American supersonic military aircraft in history, and cementing its position as a signature combat aircraft of the Cold War.

The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is an American family of single-seat, single-engine, stealth multirole combat aircraft designed for air superiority and strike missions; it also has electronic warfare and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities. Lockheed Martin is the prime F-35 contractor with principal partners Northrop Grumman and BAE Systems. The aircraft has three main variants: the conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) F-35A, the short take-off and vertical-landing (STOVL) F-35B, and the carrier-based (CV/CATOBAR) F-35C.
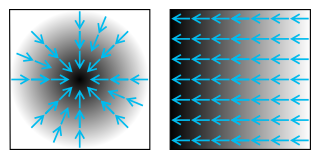
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function of several variables is the vector field whose value at a point gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The gradient transforms like a vector under change of basis of the space of variables of . If the gradient of a function is non-zero at a point , the direction of the gradient is the direction in which the function increases most quickly from , and the magnitude of the gradient is the rate of increase in that direction, the greatest absolute directional derivative. Further, a point where the gradient is the zero vector is known as a stationary point. The gradient thus plays a fundamental role in optimization theory, where it is used to minimize a function by gradient descent. In coordinate-free terms, the gradient of a function may be defined by:

In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a sum, which is used to calculate areas, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental operations of calculus, the other being differentiation. Integration was initially used to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under a curve, or determining displacement from velocity. Usage of integration expanded to a wide variety of scientific fields thereafter.
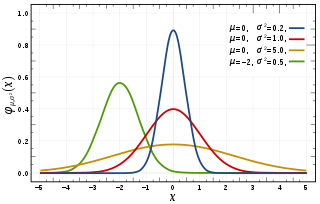
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is The parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution, while the parameter is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is . A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate.

In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events.
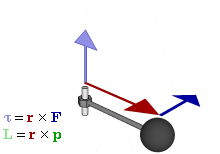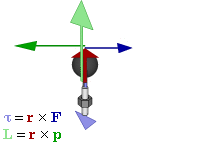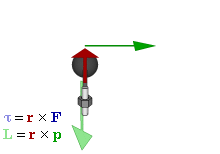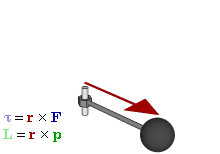
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force. The symbol for torque is typically , the lowercase Greek letter tau. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by M. Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis. A force of three newtons applied two metres from the fulcrum, for example, exerts the same torque as a force of one newton applied six metres from the fulcrum.

In mathematics, the Taylor series or Taylor expansion of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor series are named after Brook Taylor, who introduced them in 1715. A Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series when 0 is the point where the derivatives are considered, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the 18th century.

The uncertainty principle, also known as Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. It states that there is a limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as position and momentum, can be simultaneously known. In other words, the more accurately one property is measured, the less accurately the other property can be known.
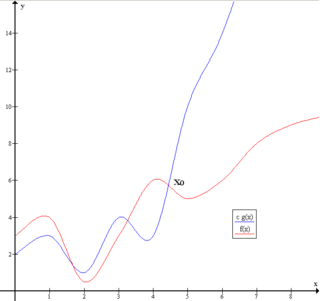
Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a family of notations invented by German mathematicians Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for Ordnung, meaning the order of approximation.

In physics, engineering and mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that takes a function as input and outputs another function that describes the extent to which various frequencies are present in the original function. The output of the transform is a complex-valued function of frequency. The term Fourier transform refers to both this complex-valued function and the mathematical operation. When a distinction needs to be made, the output of the operation is sometimes called the frequency domain representation of the original function. The Fourier transform is analogous to decomposing the sound of a musical chord into the intensities of its constituent pitches.

The Lockheed Martin/Boeing F-22 Raptor is an American twin-engine all-weather stealth fighter aircraft developed and produced for the United States Air Force (USAF). As a product of the USAF's Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) program the aircraft was designed as an air superiority fighter, but also incorporates ground attack, electronic warfare, and signals intelligence capabilities. The prime contractor, Lockheed Martin, built most of the F-22's airframe and weapons systems and conducted final assembly, while program partner Boeing provided the wings, aft fuselage, avionics integration, and training systems.
A mathematical symbol is a figure or a combination of figures that is used to represent a mathematical object, an action on mathematical objects, a relation between mathematical objects, or for structuring the other symbols that occur in a formula. As formulas are entirely constituted with symbols of various types, many symbols are needed for expressing all mathematics.
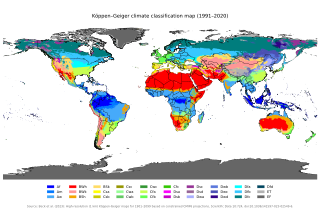
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, German climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system in 1954 and 1961, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification.
ATC code B01Antithrombotic agents is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup B01 is part of the anatomical group B Blood and blood forming organs.

The garden strawberry is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus Fragaria in the rose family, Rosaceae, collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely appreciated for its characteristic aroma, bright red color, juicy texture, and sweetness. It is consumed in large quantities, either fresh or in such prepared foods as jam, juice, pies, ice cream, milkshakes, and chocolates. Artificial strawberry flavorings and aromas are also widely used in products such as candy, soap, lip gloss, perfume, and many others.


















