
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

The Noctilucales are an order of marine dinoflagellates. They differ from most others in that the mature cell is diploid and its nucleus does not show a dinokaryotic organization. They show gametic meiosis.
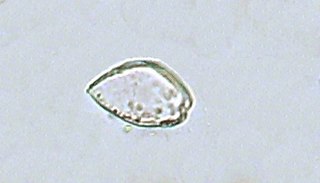
The Prorocentrales are a small order of dinoflagellates. They are distinguished by having their two flagella inserted apically, rather than ventrally as in other groups. One flagellum extends forward and the other circles its base, and there are no flagellar grooves. This arrangement is called desmokont, in contrast to the dinokont arrangement found in other groups. Accordingly, the Prorocentrales may be called desmoflagellates, and in some classifications were treated as a separate class Desmophyceae.
The Syndiniales are an order of early branching dinoflagellates, found as parasites of crustaceans, fish, algae, cnidarians, and protists. The trophic form is often multinucleate, and ultimately divides to form motile spores, which have two flagella in typical dinoflagellate arrangement. They lack a theca and chloroplasts, and unlike all other orders, the nucleus is never a dinokaryon. A well-studied example is Amoebophrya, which is a parasite of other dinoflagellates and may play a part in ending red tides. Several MALV groups have been assigned to Syndiniales; recent studies, however, show paraphyly of MALVs suggesting that only those groups that branch as sister to dinokaryotes belong to Syndiniales.

Bicosoecida (ICZN) or Bicosoecales/Bicoecea (ICBN) is an order of Bikosea, a small group of unicellular flagellates, included among the stramenopiles. Informally known as bicosoecids, they are a small group of unicellular flagellates. The cells are free-living, with no chloroplasts, and in some genera are encased in a lorica.

Peridinium is a genus of motile, marine and freshwater dinoflagellates. Their morphology is considered typical of the armoured dinoflagellates, and their form is commonly used in diagrams of a dinoflagellate's structure. Peridinium can range from 30 to 70 μm in diameter, and has very thick thecal plates.

Testate amoebae are a polyphyletic group of unicellular amoeboid protists, which differ from naked amoebae in the presence of a test that partially encloses the cell, with an aperture from which the pseudopodia emerge, that provides the amoeba with shelter from predators and environmental conditions.

The Gymnodiniales are an order of dinoflagellates, of the class Dinophyceae. Members of the order are known as gymnodinioid or gymnodinoid. They are athecate, or lacking an armored exterior, and as a result are relatively difficult to study because specimens are easily damaged. Many species are part of the marine plankton and are of interest primarily due to being found in algal blooms. As a group the gymnodinioids have been described as "likely one of the least known groups of the open ocean phytoplankton."

Dinophyceae is a class of dinoflagellates.
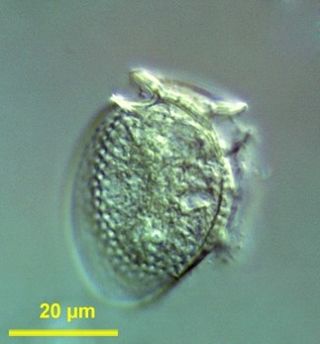
Dinophysis is a genus of dinoflagellates common in tropical, temperate, coastal and oceanic waters. It was first described in 1839 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.
Calcareous dinoflagellate cysts or calcareous dinocysts are dinoflagellate cysts produced by a group of peridinoid dinoflagellates, called calcareous dinoflagellates.

Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich was an American micropaleontologist who was a professor of geology at the University of California, Los Angeles, a United States Geological Survey (USGS) biostratigrapher, and a scientific illustrator whose micropaleontology specialty was research on Cretaceous foraminifera.
Alfred R. Loeblich Jr (1914–1994) was an American micropaleontologist. He was married to Helen Niña Tappan Loeblich and the two co-authored a number of important works on the Foraminifera and related organisms.
Centrodinium is genus of dinoflagellates in the order Gonyaulacales.
Peridiniaceae is a family of dinoflagellates belonging to the order Peridiniales.









