Related Research Articles

In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate.

Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) is one of the four recognized syndromes of shellfish poisoning, which share some common features and are primarily associated with bivalve mollusks. These shellfish are filter feeders and accumulate neurotoxins, chiefly saxitoxin, produced by microscopic algae, such as dinoflagellates, diatoms, and cyanobacteria. Dinoflagellates of the genus Alexandrium are the most numerous and widespread saxitoxin producers and are responsible for PSP blooms in subarctic, temperate, and tropical locations. The majority of toxic blooms have been caused by the morphospecies Alexandrium catenella, Alexandrium tamarense, Gonyaulax catenella and Alexandrium fundyense, which together comprise the A. tamarense species complex. In Asia, PSP is mostly associated with the occurrence of the species Pyrodinium bahamense.
Cocalodes is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1897. The name is an alteration of the salticid genus Cocalus.
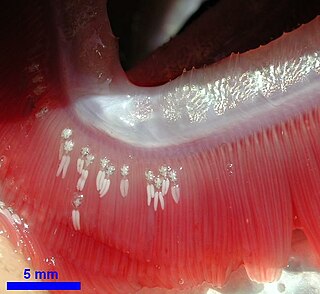
Ergasilus is a genus of copepod crustaceans occurring in both the ocean and fresh water, often called gill lice. The females are parasitic upon the gills of fishes. Being copepods, gill lice have a single median eye on their head. The second antennae are modified into prehensile pincers. Male gill lice are free-living.

Erieopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid found in Silurian to Devonian-aged marine strata of Europe and North America. The genus contains eight species from the Silurian to the Devonian, recovered from both North America and Europe.

Paguristes is a genus of hermit crab in the family Diogenidae. It includes the following species :
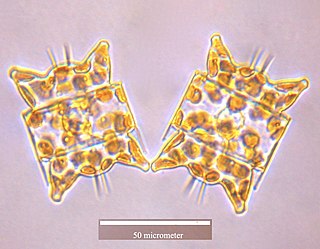
Eupodiscaceae is a diatom family (Bacillariophyceae) present both in marine and freshwater habitats Odontella is the only genera in this family with typical marine species. However, Round et al. (1990) placed Odontella in Triceratiaceae (Schutt) Lemmermann, order Triceratiales Round and Crawford, subclass Biddulphiophycidae Round and Crawford. The taxonomic status of this family is unclear and disputed.
Pachylaelaps is a genus of mites in the family Pachylaelapidae. There are more than 50 described species in Pachylaelaps.

Panopeus is a genus of crabs, containing these extant species:

Artomyces is a genus of coral fungi in the family Auriscalpiaceae. It was circumscribed by Walter Jülich in 1982, who set Artomyces pyxidatus as the type species.
Microphallus turgidus is a widespread and locally common flatworm parasite in New Zealand lakes and streams. Multilocus allozyme genotype data show that Microphallus turgidus is a single outbred species with high levels of gene flow among South Island populations. Microphallus turgidus is commonly found in the abdominal muscles of grass shrimp.
Raymondaspis is a genus of trilobites in the family Styginidae. It was described by Pribyl in 1949, and contains the species R. reticulatus and R. turgidus from the Whiterockian of Canada, R. vespertina from the Ordovician and Whiterockian of the United States and Norway, and a new species, R. grandigena, which existed during the Middle Ordovician of what is now Sweden. R. grandigena was described in 2012 by Martin Stein and Jan Bergström.
Xystosomus is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae, containing the following species:

Pao is a genus of mostly freshwater pufferfish with one species also occurring in brackish water. They are found in Southeast Asia. Until 2013, its species were generally placed in Tetraodon.
Pao turgidus is a species of freshwater pufferfish native to the Mekong basin. It may also occur in the Chao Phraya basin in Thailand. This species grows to a length of 18.5 centimetres (7.3 in) SL.

Phlogacanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Acanthaceae and tribe Andrographideae. Its distribution includes India through to Indo-China, southern China and Sulawesi.

Trixagus is a genus of small false click beetles in the family Throscidae. There are more than 30 described species in Trixagus.

Diastrophus is a genus of gall wasps in the family Cynipidae. There are at least eight described species in Diastrophus.
Pseudomus is a genus of hidden snout weevils in the beetle family Curculionidae. There are more than 20 described species in Pseudomus.
Heligmosomoides is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Heligosomidae.
References
- ↑ Biolib.cz - Freocorus turgidus. Retrieved on 8 September 2014.