
Lake Nicaragua or Cocibolca or Granada is a freshwater lake in Nicaragua. Of tectonic origin and with an area of 8,264 km2 (3,191 sq mi), it is the largest lake in Central America, the 19th largest lake in the world and the tenth largest in the Americas, slightly smaller than Lake Titicaca. With an elevation of 32.7 metres (107 ft) above sea level, the lake reaches a depth of 26 metres (85 ft). It is intermittently joined by the Tipitapa River to Lake Managua.

The Nicaragua Canal, formally the Nicaraguan Canal and Development Project was a proposed shipping route through Nicaragua to connect the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. Scientists were concerned about the project's environmental impact, as Lake Nicaragua is Central America's key freshwater reservoir while the project's viability was questioned by shipping experts and engineers.

Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests and woodlands for associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management plays an essential role in the creation and modification of habitats and affects ecosystem services provisioning.

Illegal logging is the harvest, transportation, purchase, or sale of timber in violation of laws. The harvesting procedure itself may be illegal, including using corrupt means to gain access to forests; extraction without permission, or from a protected area; the cutting down of protected species; or the extraction of timber in excess of agreed limits. Illegal logging is a driving force for a number of environmental issues such as deforestation, soil erosion and biodiversity loss which can drive larger-scale environmental crises such as climate change and other forms of environmental degradation.

The Forest Stewardship Council GmbH (FSC) is an international non-profit, multistakeholder organization established in 1993 that promotes responsible management of the world's forests via timber certification. This organization uses a market-based approach to transnational environmental policy.

Certified wood and paper products come from responsibly managed forests – as defined by a particular standard. With third-party forest certification, an independent standards setting organization (SSO) develops standards for good forest management, and independent auditing companies issue certificates to forest operations that comply with those standards.
Kleercut is the name of a former campaign conducted by Greenpeace, the Natural Resources Defense Council, and others towards Kimberly-Clark. It lasted from 2004 to 2009. Kimberly-Clark is the world’s largest manufacturer of tissue products, most notably the Kleenex brand. According to its annual environmental report, the company purchases over 3.1 million metric tonnes of virgin fiber from logging companies annually. The Kleercut campaign claims that this fiber is derived from wood pulp from old growth forests. Kimberly-Clark claims that the forests in question are largely cut for timber. The Kleercut campaign claims that Kimberly-Clark support the clearcutting of such forests in Canada and the United States, including forests habitat for wolverine and threatened wildlife the woodland caribou. Kimberly-Clark has responded that many of its supplies are certified by the Sustainable Forestry Initiative or the Canadian Standards Association.

The Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) is an international, non-profit, non-governmental organization which promotes sustainable forest management through independent third party certification. It is considered the certification system of choice for small forest owners.

Sustainable forest management (SFM) is the management of forests according to the principles of sustainable development. Sustainable forest management has to keep the balance between three main pillars: ecological, economic and socio-cultural. Sustainable forestry can seem contradicting to some individuals as the act of logging trees is not sustainable. However, the goal of sustainable forestry is to allow for a balance to be found between ethical forestry and maintaining biodiversity through the means of maintaining natural patterns of disturbance and regeneration. The forestry industry mitigates climate change by boosting carbon storage in growing trees and soils and improving the sustainable supply of renewable raw materials via sustainable forest management. Successfully achieving sustainable forest management will provide integrated benefits to all, ranging from safeguarding local livelihoods to protecting biodiversity and ecosystems provided by forests, reducing rural poverty and mitigating some of the effects of climate change. Forest conservation is essential to stop climate change.

The Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) is a sustainability organization operating in the U.S. and Canada that works across four pillars: standards, conservation, community, and education. SFI was founded in 1994 by the American Forest & Paper Association (AF&PA). SFI is the world's largest single forest certification standard by area. SFI is headquartered in Ottawa and Washington, D.C.

Deforestation is a major threat to biodiversity and ecosystems in Costa Rica. The country has a rich biodiversity with some 12,000 species of plants, 1,239 species of butterflies, 838 species of birds, 440 species of reptiles and amphibians, and 232 species of mammals, which have been under threat from the effects of deforestation. Agricultural development, cattle ranching, and logging have caused major deforestation as more land is cleared for these activities. Despite government efforts to mitigate deforestation, it continues to cause harm to the environment of Costa Rica by impacting flooding, soil erosion, desertification, and loss of biodiversity.
Impact investing refers to investments "made into companies, organizations, and funds with the intention to generate a measurable, beneficial social or environmental impact alongside a financial return". At its core, impact investing is about an alignment of an investor's beliefs and values with the allocation of capital to address social and/or environmental issues.
Proteak is a forestry company that cultivates teak trees on plantations located on reclaimed ranch lands in the dry tropical regions of Mexico and Latin America. Based out of Mexico City, Mexico, Proteak has satellite offices in Wimberley, Texas and Tepic, Mexico. At their manufacturing facilities, Proteak produces a range of teak products including: cutting boards, butcher blocks, decking, flooring and lumber.
Environmental certification is a form of environmental regulation and development where a company can voluntarily choose to comply with predefined processes or objectives set forth by the certification service. Most certification services have a logo which can be applied to products certified under their standards. This is seen as a form of corporate social responsibility allowing companies to address their obligation to minimise the harmful impacts to the environment by voluntarily following a set of externally set and measured objectives.

OroVerde – Die Tropenwaldstiftung is a non-profit environmental organisation working on the preservation of tropical forests. For this purpose, international projects are initiated, supported and realized in cooperation with local partner organisations. In Germany, environmental education projects are promoted and materials for teachers and pupils are created.
Forest conservation is the practice of planning and maintaining forested areas for the benefit and sustainability of future generations. Forest conservation involves the upkeep of the natural resources within a forest that are beneficial for both humans and the ecosystem. Forests provide wildlife with a suitable habitat for living along with filtering groundwater and preventing runoff.
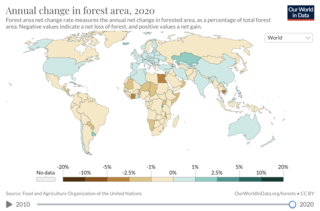
Deforestation is a primary contributor to climate change, and climate change affects forests.
HK Nicaragua Canal Development Investment Co., Ltd. also known as HKND was a private infrastructure development firm that is registered in Hong Kong. HKND was founded in 2012 with the purpose to develop the Nicaragua Canal as a wider and deeper alternative to the Panama Canal. HK Nicaragua Canal Development Investment is owned or controlled by the Chinese businessman Wang Jing. In 2014 it was announced that an IPO is being prepared to provide financing for the project but following financial difficulties, HKND finally closed its offices in April 2018.
Winner of the U.S. Department of State's 2014 Award for Corporate Excellence, founded in 2010 by Troy Wiseman and Camille Rebelo, EcoPlanet Bamboo has pioneered the industrialization of bamboo as an alternative fiber for timber manufacturing industries. To date the Company has 37,250 acres of bamboo farms under ownership, in Central American, Western and Southern Africa, with larger scale plantations underway.














