Telecommunications in Burkina Faso include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Telecommunications in Gabon include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
The following is an outline of communications technology in Morocco.
Telecommunications in Namibia include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.

Telefónica, S.A. is a Spanish multinational telecommunications company with registered office and headquarters located in two different places, both in Madrid, Spain. It is one of the largest telephone operators and mobile network providers in the world. It provides fixed and mobile telephony, broadband, and subscription television, operating in Europe and the Americas.

e&, formerly branded as Etisalat, is a UAE state-owned telecommunications company. It is the 16th largest mobile network operator in the world by number of subscribers.

TIM S.p.A. is an Italian telecommunications company with headquarters in Rome, Milan, and Naples, which provides fixed, public and mobile telephony, and DSL data services.

Fastweb is an Italian telecommunications company that provides fixed and mobile telephony, broadband Internet and IPTV services. It is also one of the prominent companies in Italy providing FTTH connections, and is a subsidiary of Fastweb + Vodafone and part of the Swiss telecommunications group Swisscom.
The telecommunications industry in China is dominated by three state-run businesses: China Telecom, China Unicom and China Mobile. The three companies were formed by restructuring launched in May 2008, directed by the Ministry of Information Industry (MII), National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the Minister of Finance. Since then, all three companies gained nationwide fixed-line and cellular mobile telecom licenses in China. In 2019, all three telecoms were issued 5G national licenses.

Maroc Telecom is the main telecommunications company in Morocco. Currently employing around 11,178 employees, it is the largest telecommunications network in the country with 8 regional delegations and 220 offices present across Morocco. The company is listed on both the Casablanca Stock Exchange and Euronext Paris.

Wind Telecomunicazioni S.p.A., more commonly known as Wind, was an Italian telecommunications company of the VimpelCom Ltd. group, which offered mobile telephony services and, through Infostrada, also fixed-line telephony services, Internet and IPTV.

Bharti Airtel Limited is an Indian multinational telecommunications company based in New Delhi. It operates in 18 countries across South Asia and Africa, as well as the Channel Islands. Currently, Airtel provides 5G, 4G and LTE Advanced services throughout India. Currently offered services include fixed-line broadband, and voice services depending upon the country of operation. Airtel had also rolled out its Voice over LTE (VoLTE) technology across all Indian telecom circles. It is the second largest mobile network operator in India and the second largest mobile network operator in the world. Airtel was named India's 2nd most valuable brand in the first ever Brandz ranking by Millward Brown and WPP plc.

Emirates Integrated Telecommunications Company P.J.S.C., commercially rebranded as du (دو) in February 2007, is one of the two main telecom operators in the United Arab Emirates. du offers fixed line, mobile telephony, internet and digital television services across the UAE. It also provides carrier services, a data hub, internet exchange facilities and satellite service for broadcasters. It expanded its services in support of economic and social transformation of UAE and operates subsidiaries such as EITC Investment Holdings Limited, Edara, Smart Dubai Platform Project Company LLC and EITC Singapore PTE. LTD.
Sotelma is a private telecommunications company in Mali. The company is based in Bamako. Sotelma provides local telephony, international telephony, internet service and mobile telephone service, etc. Its mobile service subsidiary is Malitel. It is also the official registry of the .ml country code domain.

Neuf Cegetel was a French wireline telecommunications service provider and a mobile virtual network operator (MVNO). It offered various telecommunications services to consumers, enterprises and wholesale customers, ranking second in the country in annual revenues. It was legally established in 2005 following the completion of the merger between Neuf Telecom and Cegetel. As of June 2008, the company became a wholly owned subsidiary of SFR, and the brand disappeared commercially.
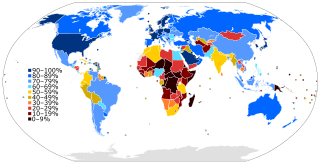
The Internet in Africa is limited by a lower penetration rate when compared to the rest of the world. Measurable parameters such as the number of ISP subscriptions, overall number of hosts, IXP-traffic, and overall available bandwidth are indicators that Africa is far behind the "digital divide". Moreover, Africa itself exhibits an inner digital divide, with most Internet activity and infrastructure concentrated in South Africa, Morocco, and Egypt, as well as smaller economies like Mauritius and the Seychelles. In general, only 43% of the African population has access to the Internet as of 2021. Only 0.4% of the African population has a fixed-broadband subscription. The majority of internet users use it through mobile broadband.

Iliad S.A. is a French telecommunications company. It is based in Paris and its operations comprise fixed and mobile telephony services, prepaid phone cards and Internet access providing and hosting services. The company was founded by Xavier Niel in 1990.
The mass media in Gabon is primarily monitored by the Gabon government. Although the main newspapers are associated with the government, there are private broadcasters, and private weekly newspapers that are mostly controlled by opposition parties.
Inwi is a telecommunications company in Morocco. One of the three major Internet service providers in the country, it is a subsidiary of the group SNI and the Kuwaiti group Zain.

Monaco Telecom is the primary telecommunications provider in the Principality of Monaco. Established in 1997, the company was formed following the government of Monaco's decision to privatize the previously state-owned Office Monégasque des Téléphones. Monaco Telecom provides various services including internet access and mobile phone services. It is a key entity in facilitating communication within Monaco and connecting the principality to global telecommunications networks. Additionally, the company operates a retail store which functions as a point of service and customer interaction.











