
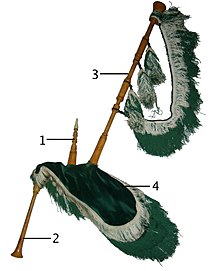


The gaita asturiana is a type of bagpipe native to the autonomous communities of Principality of Asturias and Cantabria on the northern coast of Spain.




The gaita asturiana is a type of bagpipe native to the autonomous communities of Principality of Asturias and Cantabria on the northern coast of Spain.
The first evidence for the existence of the gaita asturiana dates back to the 13th century, as a piper can be seen carved into the capital of the church of Santa María de Villaviciosa. Further evidence includes an illumination of a rabbit playing the gaita in the 14th century text Llibru la regla colorada. An early carving of a wild boar playing the pipes may be seen at the Cathedral of Oviedo.
Traditionally the gaita asturiana had only the two pipes: the chanter and the drone, the same as the gaita gallega. The traditional tuning of the chanter was in C5 (an octave above the piano's Middle C). Traditionally the C of the gaita was between concert C and C#, known as C brillante ("C brilliant"), though examples are also found in D (rare) and B (more frequent, used to accompany male "tonada" singers). Some times it was also possible to see tiny chanters tuned above D. The drone is tuned to the tonic of the chanter, but two octaves lower. However, in the modern day some makers add a tenor drone (ronquín) tuned one octave below the chanter, the same as the ronqueta of the gaita gallega.
Currently, the gaita asturiana is constructed in a wider array of keys and types, anywhere from A to as high as E♭. Also, refinement of the chanter construction has made it possible to play as high as the tonic in the third octave. Further, the ability to hit chromatic notes has increased, turning the chanter from a completely diatonic instrument to a nearly fully chromatic one. The addition of auxiliary holes has also increased. As a further sign of modernisation, keys have been added to some variants to extend range and chromatic ability.
In the history of the gaita, there have been numerous notable players. It is necessary to begin with the legendary Gaiteru Llibardón, author of the first recording of the gaita. Throughout the 20th century there have been other famous gaiteros, such as José Remis Vega (aka Capilla and El Gaiteru Margolles) and his son José Remis Ovalle, a reference for today's gaita interpretations.
José Ángel Hevia Velasco, known professionally as Hevia (born 1967 in Villaviciosa, Asturias). Hevia is known for helping invent a special brand of MIDI electronic bagpipes, which he is often seen playing live. He commonly performs with his sister, Maria José, on drums. In 1992 he was awarded first prize for solo bagpipes at the Festival Interceltique de Lorient, Brittany.
La Reina del Truébano is an Asturian gaitero band that has performed in several continents. [1]

Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, Northern Africa, Western Asia, around the Persian Gulf and northern parts of South Asia.

The uilleann pipes, also known as Union pipes and sometimes called Irish pipes, are the characteristic national bagpipe of Ireland. Their current name is a partial translation of the Irish language terms píobaí uilleann, from their method of inflation. There is no historical record of the name or use of the term uilleann pipes before the 20th century. It was an invention of Grattan Flood and the name stuck. People mistook the term 'union' to refer to the 1800 Act of Union; however, this is incorrect as Breandán Breathnach points out that a poem published in 1796 uses the term 'union'.

The great Highland bagpipe is a type of bagpipe native to Scotland, and the Scottish analogue to the great Irish warpipes. It has acquired widespread recognition through its usage in the British military and in pipe bands throughout the world.

The Scottish smallpipe is a bellows-blown bagpipe re-developed by Colin Ross and many others, adapted from an earlier design of the instrument. There are surviving bellows-blown examples of similar historical instruments as well as the mouth-blown Montgomery smallpipes, dated 1757, which are held in the National Museum of Scotland. Some instruments are being built as direct copies of historical examples, but few modern instruments are directly modelled on older examples; the modern instrument is typically larger and lower-pitched. The innovations leading to the modern instrument, in particular the design of the reeds, were largely taken from the Northumbrian smallpipes.

The border pipes are a type of bagpipe related to the Scottish Great Highland Bagpipe. It is perhaps confusable with the Scottish smallpipe, although it is a quite different and much older instrument. Although most modern Border pipes are closely modelled on similar historic instruments, the modern Scottish smallpipes are a modern reinvention, inspired by historic instruments but largely based on Northumbrian smallpipes in their construction.

The Galician gaita is the traditional instrument of Galicia and northern Portugal.

The Northumbrian smallpipes are bellows-blown bagpipes from Northeastern England, where they have been an important factor in the local musical culture for more than 250 years. The family of the Duke of Northumberland have had an official piper for over 250 years. The Northumbrian Pipers' Society was founded in 1928, to encourage the playing of the instrument and its music; Although there were so few players at times during the last century that some feared the tradition would die out, there are many players and makers of the instrument nowadays, and the Society has played a large role in this revival. In more recent times the Mayor of Gateshead and the Lord Mayor of Newcastle have both established a tradition of appointing official Northumbrian pipers.
Northwest Iberian folk music is a traditional highly distinctive folk style, located along Spain's north-west Atlantic coast, mostly Galicia and Asturias, that has some similarities with the neighbouring area of Cantabria. The music is characterized by the use of bagpipes.

José Ángel Hevia Velasco, known professionally as Hevia, is an Asturian bagpiper – specifically, an Asturian gaita player. He commonly performs with his sister, María José, on drums. In 1992 he was awarded first prize for solo bagpipes at the Festival Interceltique de Lorient, Brittany.
The Hungarian duda is the traditional bagpipe of Hungary. It is an example of a group of bagpipes called Medio-Carparthian bagpipes.
The Brian Boru bagpipe was invented and patented in 1908 by Henry Starck, an instrument maker, in London, in consultation with William O'Duane. The name was chosen in honour of the Irish king Brian Boru (941–1014), though this bagpipe is not a recreation of any pipes that were played at the time of his reign.

Welsh bagpipes are a related instrument to one type of bagpipe, a chanter, which when played without the bag and drone is called a pibgorn. The generic term pibau which covers all woodwind instruments is also used in Welsh. They have been played, documented, represented and described in Wales since the fourteenth century. A piper in Welsh is called a pibydd or a pibgodwr.

The electronic bagpipes is an electronic musical instrument emulating the tone and/or playing style of the bagpipes. Most electronic bagpipe emulators feature a simulated chanter, which is used to play the melody. Some models also produce a harmonizing drone(s). Some variants employ a simulated bag, wherein the player's pressure on the bag activates a switch maintaining a constant tone. As with other electronic musical instruments, they must be plugged into an instrument amplifier and loudspeaker to hear the sound. Some electronic bagpipes are MIDI controllers that can be plugged into a synth module to create synthesized or sampled bagpipe sounds.

Asturians are a Romance ethnic group with Celtic roots, native to the autonomous community of Asturias, in the North-West of the Iberian Peninsula.

The gaita de boto is a type of bagpipe native to the Aragon region of northern Spain.

The gaita de saco is a type of bagpipe native to the provinces of Soria, La Rioja, Álava, and Burgos in north-central Spain. In the past, it may also have been played in Segovia and Ávila.
It is unclear whether Lincolnshire bagpipes refer to a specific type of pipes native to Lincolnshire, England, or to the popularity of a more general form of pipes in the region. Written records of bagpipes being associated with Lincolnshire date back to 1407, but it is difficult to find certain proof that any regional variation of the bagpipe existed which was peculiar to Lincolnshire. Despite the lack of evidence for a uniquely local instrument, it is clear that the bagpipe was enjoyed by the people of Lincolnshire.
The muiñeira is a traditional dance and musical genre of Galicia and some parts of Asturias (Spain). It is distinguished mainly by its expressive and lively tempo, played usually in 6
8, although some variants are performed in other time signatures. There are also variant types of muiñeira which remain in the tempo of 6
8 but which displace the accent in different ways. Muiñeira is associated with traditional choreographic schemes and the associated instrumentation is a form of bagpipe known as a gaita. It is subject to highly varied interpretation in differing local traditions. According to "Galicia-The Spanish Cousins", an article on Roots World, muiñeira is the Galician "equivalent" of a jig, which is consistent with the time signature of 6
8. The word "muiñeira" means literally both millstone and a mill landlady. Galician music is classified as part of Celtic music.

The term „Marktsackpfeife" commonly refers to a type of bagpipe which has been developed in East Germany at the beginning of 1980s for the specific purpose to be played at faires and markets as a modern interpretation of a certain type of Medieval bapipes. Depictions of such bagpipes are found in Medieval sources and are characterized by specific features like wide flaring bells atop the chanter and drones, apparent conical shape of the chanter and reportedly substantial volume of their sound. Since no actual chanters of this type of bagpipe have survived and/or have been recovered so far, the MSP has to be classified as a purely modern musical instrument having a historically informed exterior. MSP chanters typically use double reeds made of plastic or Arundo donax cane and drones usually work with single reeds made of same materials. Chanter bores are conical with a pronounced flare at the end as they transition into the bell.
La gaita asturiana. Xornaes d'estudiu. *, some texts in Asturian and some others in Spanish, comprising the longer one, a conference about the History of Asturian bagpipe, the evolution and changes suffered by the Galician one, and some confusion and conflicts in the border area.