
Lingzhi, Ganoderma sichuanense, also known as reishi or Ganoderma lingzhi is a polypore fungus native to East Asia belonging to the genus Ganoderma.

Thymidine kinase is an enzyme, a phosphotransferase : 2'-deoxythymidine kinase, ATP-thymidine 5'-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.21. It can be found in most living cells. It is present in two forms in mammalian cells, TK1 and TK2. Certain viruses also have genetic information for expression of viral thymidine kinases. Thymidine kinase catalyzes the reaction:
An angiogenesis inhibitor is a substance that inhibits the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). Some angiogenesis inhibitors are endogenous and a normal part of the body's control and others are obtained exogenously through pharmaceutical drugs or diet.
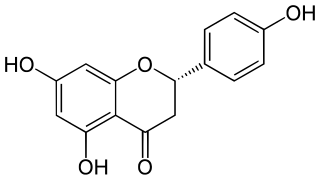
Naringenin is a flavorless, colorless flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, and is found in a variety of fruits and herbs.

Mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) also known as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Mdm2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MDM2 gene. Mdm2 is an important negative regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor. Mdm2 protein functions both as an E3 ubiquitin ligase that recognizes the N-terminal trans-activation domain (TAD) of the p53 tumor suppressor and as an inhibitor of p53 transcriptional activation.
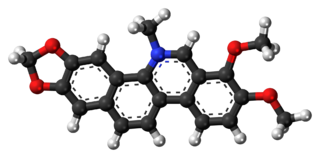
Chelerythrine is a benzophenanthridine alkaloid present in the plant Chelidonium majus. It is a potent, selective, and cell-permeable protein kinase C inhibitor in vitro. And an efficacious antagonist of G-protein-coupled CB1 receptors. This molecule also exhibits anticancer qualities and it has served as a base for many potential novel drugs against cancer. Structurally, this molecule has two distinct conformations, one being a positively charged iminium form, and the other being an uncharged form, a pseudo-base.
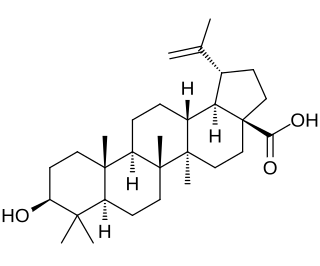
Betulinic acid is a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenoid which has antiretroviral, antimalarial, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a more recently discovered potential as an anticancer agent, by inhibition of topoisomerase. It is found in the bark of several species of plants, principally the white birch from which it gets its name, but also the ber tree, selfheal, the tropical carnivorous plants Triphyophyllum peltatum and Ancistrocladus heyneanus, Diospyros leucomelas, a member of the persimmon family, Tetracera boiviniana, the jambul, flowering quince, rosemary, and Pulsatilla chinensis.

Ganoderma applanatum is a bracket fungus with a cosmopolitan distribution.

Ursolic acid, is a pentacyclic triterpenoid identified in the epicuticular waxes of apples as early as 1920 and widely found in the peels of fruits, as well as in herbs and spices like rosemary and thyme.

Ganoderma is a genus of polypore fungi in the family Ganodermataceae that includes about 80 species, many from tropical regions. They have a high genetic diversity and are used in traditional Asian medicines. Ganoderma can be differentiated from other polypores because they have a double-walled basidiospore. They may be called shelf mushrooms or bracket fungi.

Emodin (6-methyl-1,3,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone) is a chemical compound, of the anthraquinone family, that can be isolated from rhubarb, buckthorn, and Japanese knotweed. Emodin is particularly abundant in the roots of the Chinese rhubarb, knotweed and knotgrass as well as Hawaii ‘au‘auko‘i cassia seeds or coffee weed. It is specifically isolated from Rheum palmatum L. It is also produced by many species of fungi, including members of the genera Aspergillus, Pyrenochaeta, and Pestalotiopsis, inter alia. The common name is derived from Rheum emodi, a taxonomic synonym of Rheum australe, and synonyms include emodol, frangula emodin, rheum emodin, 3-methyl-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone, Schüttgelb (Schuttgelb), and Persian Berry Lake.

Honokiol is a lignan isolated from the bark, seed cones, and leaves of trees belonging to the genus Magnolia. It has been identified as one of the chemical compounds in some traditional eastern herbal medicines along with magnolol, 4-O-methylhonokiol, and obovatol.

Ganoderma tsugae, also known as hemlock varnish shelf, is a flat polypore mushroom of the genus Ganoderma.

Tetrandrine, a bis-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, is a calcium channel blocker. It is isolated from the plant Stephania tetrandra, and other Chinese and Japanese herbs.

Cerevisterol (5α-ergosta-7,22-diene-3β,5,6β-triol) is a sterol. Originally described in the 1930s from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, it has since been found in several other fungi and, recently, in deep water coral. Cerevisterol has some in vitro bioactive properties, including cytotoxicity to some mammalian cell lines.
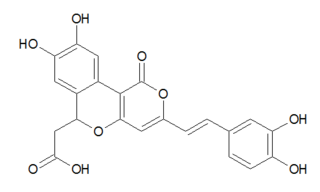
Phellibaumins are hispidin derivatives made by the fungus Phellinus. Five such derivatives have been identified, known as Phellibaumin A through E. Phellibaumins A and B are classified as pyranones, while Phellibaumins C, D, and E are classified as styrylpyranones.
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol and ergosterol synthesis inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, immunosuppressants and fungicides.

Ganoderma microsporum is a species of Ganoderma mushroom native to Taiwan that grows on willow trees. The specific epithet microsporum refers to the small size of its spores, measuring 6–8.5 by 4.5–5 μm, which is smaller than the spores of all other known types of Ganoderma.

Fungal immunomodulatory proteins (FIPs) are a type of functional compound found in various species of fungi. FIPs are part of the immunoglobulin (ig) family, which are structurally similar to human antibodies, and can interact with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), causing these cells to secrete different types of hormones and regulate cellular activity.

















