Related Research Articles

Flamenco is an art form based on the various folkloric music traditions of southern Spain, developed within the gitano subculture of the region of Andalusia, and also having historical presence in Extremadura and Murcia. In a wider sense, the term is used to refer to a variety of both contemporary and traditional musical styles typical of southern Spain. Flamenco is closely associated to the gitanos of the Romani ethnicity who have contributed significantly to its origination and professionalization. However, its style is uniquely Andalusian and flamenco artists have historically included Spaniards of both gitano and non-gitano heritage.

Lleida is a city in the west of Catalonia. It is the capital and largest town in Segrià county, the Ponent region and the province of Lleida. Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It had 140,797 inhabitants as of 2022.

Ferrocarrils de la Generalitat de Catalunya, or FGC, is a railway company which operates several unconnected lines in Catalonia, Spain.
Alegrías is a flamenco palo or musical form, which has a rhythm consisting of 12 beats. It is similar to Soleares. Its beat emphasis is as follows: 1 2 [3] 4 5 [6] 7 [8] 9 [10] 11 [12]. Alegrías originated in Cádiz. Alegrías belongs to the group of palos called Cantiñas and it is usually played in a lively rhythm. The livelier speeds are chosen for dancing, while quieter rhythms are preferred for the song alone.

Manresa is the capital of Bages county, located in the central region of Catalonia, Spain.

A palo or cante is the name given in flamenco for the different traditional musical forms.
Martinetes are a flamenco palo belonging to the group of the tonás or cantes a palo seco. As the rest of the songs in this group, it is sung with no accompaniment. In some dance shows for the stage, though, it is accompanied by percussion played with the compás of siguiriya. The percussion instruments chosen for this are frequently a hammer and anvil, to evocate the origins of this palo, attributed to Gypsy smiths. It is not probable, though, that they were real work songs: they demand too much effort and faculties to be sung while carrying out a heavy task like that of a smith. They were more probably sung in family gatherings.

Sant Feliu de Codines is a municipality in the comarca of Vallès Oriental, Catalonia, Spain. It is located in the north-west corner of the comarca, on the border with comarca of Moianès to the north, and the comarca of Vallès Occidental to the west.

Plaça d'Espanya is one of Barcelona's most important squares, built on the occasion of the 1929 Barcelona International Exposition, held at the foot of Montjuïc, in the Sants-Montjuïc district.

Rail transport in Catalonia operates on three rail gauges and services are operated by a variety of public operators:

Soleares is one of the most basic forms or palos of Flamenco music, probably originating among the Calé Romani people of Cádiz or Seville in Andalusia, the most southern region of Spain. It is usually accompanied by one guitar only, in phrygian mode "por arriba" ; "Bulerías por soleá" is usually played "por medio". Soleares is sometimes called "mother of palos" although it is not the oldest one and not even related to every other palo
The Catalonian independence referendums of 2009–2010 have been carried out by civil society and the implications of public institutions for their organizations are persecuted by the Spanish State. But several city councils and comarcal councils have approved motions in favor of this referendum to be called a civil organization, supporting them in this way without violating the laws.

Fira Mediterrània of Manresa (Catalonia-Spain) is a performing arts fair rooted in Mediterranean tradition. It has two main areas of focus: popular culture and world music. It has been held every year since 1998 and has become a setting for exchange professionals that sell and buy productions.

Catalunya en Miniatura is miniature park inaugurated in 1983 in Torrelles de Llobregat, 17 km from Barcelona. The park is 60,000 square meters, 35,000 of them devoted to the scale models, it is one of the largest miniature parks in the world, and the largest of the 14 miniature building exhibitions present in Europe. It displays 147 models of palaces, churches, bridges and other buildings from Catalonia and Mallorca and it includes all the major works by the renowned architect Antoni Gaudí.

FiraTàrrega is the international market for performing arts that takes place every year in Tàrrega during the second weekend in September. Founded in 1981, it is a great shop window of what is going on in performing arts, with special emphasis on street arts, visual and unconventional shows. As a meeting place and an international point of reference for debate, the main objective of FiraTàrrega is to boost the performing arts market, opening the door to the internationalisation of the companies. Other more specific objectives are the accompaniment and promotion of creations by emergent artists, encouraging training, focused on artistic creation and culture management and on generating strategic alliances to develop transnational street art circuits or productions.
Marrecs de Salt is a group of castellers from Salt, Girona (Catalonia), founded in 1995. They are also to be considered as the local group in Girona, together with their university counterpart: Xoriguers de la UdG. They are one of the seven active groups in the province of Girona, and since the dissolution of Castellers de l'Albera, also the oldest. Their best human tower is the 5 in 8 and their best performance was on 27 October 2013 for the performance of Sant Narcís in the city of Girona, were they completed the 4 in 8, the 2 in 8 with double base, the 3 in 8 and the pillar of 6. Their shirt is blue standing for the river Ter, which flows through both Salt and Girona, as well as other regions of the province.

Valentí Serra i Fornell, is a Spanish Capuchin and priest, whose religious name is Valentí Serra de Manresa.
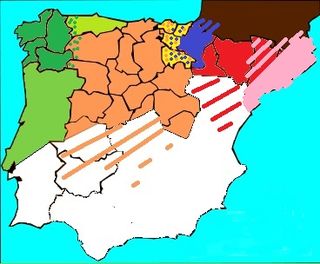
Spanish Romanesque designates the Romanesque art developed in the Hispanic-Christian kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula in the 11th and 12th centuries. Its stylistic features are essentially common to the European Romanesque although it developed particular characteristics in the different regions of the peninsula. There is no Romanesque art in the southern half of the peninsula because it remained under Muslim rule (Al-Andalus). The examples of Romanesque buildings in the central area of the peninsula are sparse and of the latest period, with virtually no presence south of the Ebro and the Tagus. Most Romanesque buildings can be found in the northern third of the peninsula. Romanesque art was introduced into the peninsula from east to west, so scholars have usually defined regional characteristics accordingly: the "eastern kingdoms" comprising the Pyrenean areas, Catalan Romanesque, Aragonese Romanesque and Navarrese Romanesque, and the "western kingdoms" comprising Castilian-Leonese Romanesque, Asturian Romanesque, Galician Romanesque and Portuguese Romanesque.

Lluís Puig i Gordi is an art director, dancer, musician, folklorist and Spanish politician from Catalonia. He was Minister of Culture of Catalonia, the department in charge of the libraries, language and heritage preservation, historical commemorations... He succeeded Santi Vila on 5 July 2017.
References
- ↑ Peña, Paco (1976). Toques Flamencos. London: Musical New Services. p. 10.
