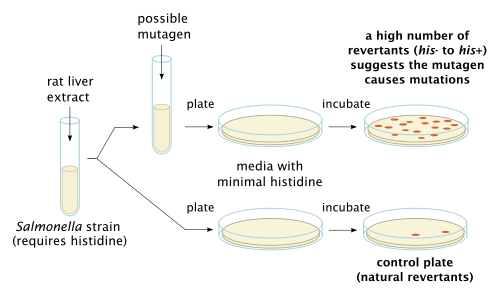
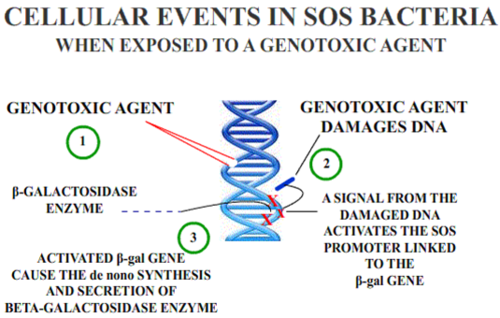
Genotoxic effects such as deletions, breaks and/or rearrangements can lead to cancer if the damage does not immediately lead to cell death. Regions sensitive to breakage, called fragile sites, may result from genotoxic agents (such as pesticides). Some chemicals have the ability to induce fragile sites in regions of the chromosome where oncogenes are present, which could lead to carcinogenic effects. In keeping with this finding, occupational exposure to some mixtures of pesticides are positively correlated with increased genotoxic damage in the exposed individuals. DNA damage is not uniform in its severity across populations because Individuals vary in their ability to activate or detoxify genotoxic substances, which leads to variability in the incidence of cancer among individuals. The difference in ability to detoxify certain compounds is due to individuals' inherited polymorphisms of genes involved in the metabolism of the chemical. Differences may also be attributed to individual variation in efficiency of DNA repair mechanisms. [9]
Genotoxins implicated in the four most common cancers worldwide
Major genotoxic agents responsible for the four most common cancers worldwide (lung, breast, colon and stomach) have been identified.
Lung cancer is the most frequent cancer in the world, both in terms of yearly cases (1.61 million cases; 12.7% of all cancer cases) and deaths (1.38 million deaths; 18.2% of all cancer deaths). [12] Tobacco smoke is the main cause of lung cancer. Risk estimates for lung cancer indicate that tobacco smoke is responsible for 90% of lung cancers in the United States. Tobacco smoke contains more than 5,300 identified chemicals. The most significant carcinogens in tobacco smoke have been determined by a "Margin of Exposure" approach. [13] By this approach, the tumorigenic compounds in tobacco smoke were, in order of importance, acrolein, formaldehyde, acrylonitrile, 1,3-butadiene, cadmium, acetaldehyde, ethylene oxide, and isoprene. In general, these compounds are genotoxic and cause DNA damage. As examples, DNA damaging effects have been reported for acrolein, [14] formaldehyde, [15] and acrylonitrile. [16]
Breast cancer is the second most frequent cancer worldwide on a yearly basis [(1.38 million cases, 10.9% of all cancer cases), and ranks 5th as cause of death (458,000, 6.1% of all cancer deaths)]. [12] Breast cancer risk is associated with persistently high blood levels of estrogen. [17] Estrogen likely contributes to breast carcinogenesis by the following three processes; (1) metabolic conversion of estrogen to genotoxic, mutagenic carcinogens, (2) stimulation of growth of tissues, and (3) repression of phase II detoxification enzymes that metabolize genotoxic reactive oxygen species, thus resulting in increased oxidative DNA damage. [18] [19] [20] The principal human estrogen, estradiol, can be metabolized to quinone derivatives that form DNA adducts. [21] These derivatives can cause the removal of bases from the phosphodiester backbone of DNA (e.g. depurination). This removal may be followed by inaccurate repair or replication of the apurinic site leading to mutation and eventually cancer.
Colorectal cancer is the third most frequent cancer worldwide [1.23 million cases (9.7% of all cancer cases), 608,000 deaths (8.0% of all cancer deaths)]. [12] In the United States, tobacco smoke may be responsible for up to 20% of colorectal cancers. [22] In addition, bile acids are implicated by substantial evidence as an important genotoxic factor in colon cancer. [23] In particular, the bile acid deoxycholic acid causes the production of DNA-damaging reactive oxygen species in human and rodent colon epithelial cells. [23]
Stomach cancer is the fourth most common cancer worldwide [990,000 cases (7.8% of all cancer cases), 738,000 deaths (9.7% of all cancer deaths )]. [12] Infection by Helicobacter pylori is the main causative factor in stomach cancer. Chronic inflammation due to H. pylori, if untreated, is often long-standing. H. pylori infection of gastric epithelial cells causes increased production of genotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS). [24] [25] ROS cause oxidative damage to DNA that includes the major base alteration 8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine. In a recent retrospective study it was found that use of a bile acid sequestrant was associated with a significant reduction in gastric cancer risk, suggesting that bile acids may be a contributory factor in stomach cancer. [26]
Genotoxic chemotherapy
Genotoxic chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with the use of one or more genotoxic drugs. The treatment is traditionally part of standardized regime. By utilizing the destructive properties of genotoxins treatments aims to induce DNA damage into cancer cells. Any damage done to a cancer is passed on to descendent cancer cells as proliferation continues. If this damage is severe enough, it will induce cells to undergo apoptosis. [27]
Risks
A drawback of treatment is that many genotoxic drugs are effective on cancerous cells and normal cells alike. Selectivity of a particular drug's action is based on the sensitivity of the cells themselves. So, while rapidly dividing cancer cells are particularly sensitive to many drug treatments, often normal functioning cells are affected. [27]
Another risk of treatment is that, in addition to being genotoxic, many of the drugs are also mutagenic and cytotoxic. So the effects of these drugs are not limited to just DNA damage. In addition, some of these drugs that are meant to treat cancers are also carcinogens themselves, raising the risk of secondary cancers, such as leukemia. [27]
Different treatments
This table depicts different genotoxic-based cancer treatments along with examples. [27]