
The Yellow Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula, and can be considered the northwestern part of the East China Sea. It is one of four seas named after common colour terms, and its name is descriptive of the golden-yellow color of the silt-ridden water discharged from major rivers.

The Wadden Sea is an intertidal zone in the southeastern part of the North Sea. It lies between the coast of northwestern continental Europe and the range of low-lying Frisian Islands, forming a shallow body of water with tidal flats and wetlands. It has a high biological diversity and is an important area for both breeding and migrating birds. In 2009, the Dutch and German parts of the Wadden Sea were inscribed on UNESCO's World Heritage List and the Danish part was added in June 2014.

Long Island Sound is a marine sound and tidal estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It lies predominantly between the U.S. state of Connecticut to the north and Long Island in New York to the south. From west to east, the sound stretches 110 mi (180 km) from the East River in New York City, along the North Shore of Long Island, to Block Island Sound. A mix of freshwater from tributaries, and saltwater from the Atlantic Ocean, Long Island Sound is 21 mi (34 km) at its widest point and varies in depth from 65 to 230 feet.

A salt marsh, saltmarsh or salting, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is dominated by dense stands of salt-tolerant plants such as herbs, grasses, or low shrubs. These plants are terrestrial in origin and are essential to the stability of the salt marsh in trapping and binding sediments. Salt marshes play a large role in the aquatic food web and the delivery of nutrients to coastal waters. They also support terrestrial animals and provide coastal protection.

Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal flat ecosystems are as extensive globally as mangroves, covering at least 127,921 km2 (49,391 sq mi) of the Earth's surface. They are found in sheltered areas such as bays, bayous, lagoons, and estuaries; they are also seen in freshwater lakes and salty lakes alike, wherein many rivers and creeks end. Mudflats may be viewed geologically as exposed layers of bay mud, resulting from deposition of estuarine silts, clays and aquatic animal detritus. Most of the sediment within a mudflat is within the intertidal zone, and thus the flat is submerged and exposed approximately twice daily.

Coos Bay is an estuary where the Coos River enters the Pacific Ocean, the estuary is approximately 12 miles long and up to two miles wide. It is the largest estuary completely within Oregon state lines. The Coos Bay watershed covers an area of about 600 square miles and is located in northern Coos County, Oregon in the United States. The Coos River, which begins in the Oregon Coast Range, enters the bay from the east. From Coos River, the bay forms a sharp loop northward before arching back to the south and out to the Pacific Ocean. Haynes Inlet enters the top of this loop. South Slough branches off from the bay directly before its entrance into the Pacific Ocean. The bay was formed when sea levels rose over 20,000 years ago at the end of the Last Glacial Maximum, flooding the mouth of the Coos River. Coos Bay is Oregon's most important coastal industrial center and international shipping port, with close ties to San Francisco, the Columbia River, Puget Sound and other major ports of the Pacific rim.
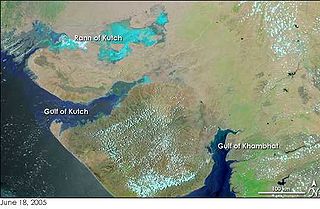
The Gulf of Kutch is located between the peninsula regions of Kutch and Saurashtra, bounded in the state of Gujarat that borders Pakistan. It opens towards the Arabian Sea facing the Gulf of Oman.

The Sundarbans National Park is a national park, tiger reserve and biosphere reserve in West Bengal, India. It is part of the Sundarbans on the Ganges Delta and adjacent to the Sundarban Reserve Forest in Bangladesh. It is located to south-west of the Bangladesh. The delta is densely covered by mangrove forests, and is one of the largest reserves for the Bengal tiger. It is also home to a variety of bird, reptile and invertebrate species, including the salt-water crocodile. The present Sundarban National Park was declared as the core area of Sundarban Tiger Reserve in 1973 and a wildlife sanctuary in 1977. On 4 May 1984 it was declared a national park. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site inscribed in 1987, and it has been designated as a Ramsar site since 2019. It is considered as a World Network of Biosphere Reserve from 1989.

Sundarbans is a mangrove area in the delta formed by the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna Rivers in the Bay of Bengal. Sundarban Reserve Forest (SRF) of Bangladesh is the largest mangrove forest in the world. It spans the area from the Baleswar River in Bangladesh's division of Khulna to the Hooghly River in India's state of West Bengal. It comprises closed and open mangrove forests, land used for agricultural purpose, mudflats and barren land, and is intersected by multiple tidal streams and channels. Sundarbans is home to the world's largest area of mangrove forests. Four protected areas in the Sundarbans are enlisted as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, viz. Sundarbans West (Bangladesh), Sundarbans South (Bangladesh), Sundarbans East (Bangladesh) and Sundarbans National Park (India).

Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangroves cannot withstand freezing temperatures. There are about 80 different species of mangroves, all of which grow in areas with low-oxygen soil, where slow-moving waters allow fine sediments to accumulate.

Elkhorn Slough is a 7-mile-long (11 km) tidal slough and estuary on Monterey Bay in Monterey County, California. It is California's second largest estuary and the United States' first estuarine sanctuary. The community of Moss Landing and the Moss Landing Power Plant are located at the mouth of the slough on the bay.

The Moreton Bay Marine Park was established in 1993 to protect ecologically significant habitats in Moreton Bay. The marine park extends from Caloundra south to the southern tip of South Stradbroke Island. The marine park's border extends up to the highest tidal mark and covers a total of 3,400 km2.

Suncheon Bay Ecological Park is a protected natural area near Suncheon, South Korea. It is a bay between Yeosu and Goheung peninsulas, located 8 km (5.0 mi) from the center of Suncheon, with 21.6 km2 (8.3 sq mi) of mudflats and 5.4 km2 (2.1 sq mi) of reed beds.

A marine habitat is a habitat that supports marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea. A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species. The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats.

Australia has approximately 11,500 km2 of mangroves, primarily on the northern and eastern coasts of the continent. Areas where mangroves occur include the intertidal zone of tropical, subtropical and protected temperate coastal rivers, estuaries, bays and marine shorelines. Less than 1% of Australia's total forest area is mangrove forest.
The Point Cook Coastal Park covers an area of 863 hectares and includes the Cheetham Wetlands. The park extends from the RAAF Williams Point Cook Base northeast along the coast to the Laverton creek which comprises its northern boundary. The park is approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) from Melbourne, Australia in a southwesterly direction along Port Phillip Bay. The park is adjoined by the Point Cook Marine Sanctuary, which extends around the point to the south and the east. The northwestern boundary to the park is residential housing.

Koggala Lagoon is a coastal body of water located in Galle District, Southern Sri Lanka. It is situated near the town of Koggala and adjacent to the southern coast, about 110 km (68 mi) south of Colombo. The lagoon is embellished with eight ecologically rich small islands.

Climate change in Delaware encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Delaware.

Käina Bay is almost isolated and very shallow approximately 9 km2 (3.5 sq mi) marine area between the Estonian islands Hiiumaa and Kassari, which is connected to the surrounding Väinameri and adjacent Vaemla Bay via three tiny channels - Orjaku channel, Orjaku sill and Vaemla channel. The maximum depth of Käina Bay is about 1 meter. Käina Bay is separated from the Väinameri Sea by Kassari Island, Õunaku Bay and Jausa Bay by a dyke road. There are many thickets of reeds and islets (23). In the southern part of the bay there is mineral curative mud.



















