
Aragua State is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. It is located in the north-central region of Venezuela. It has plains and jungles and Caribbean beaches. The most popular are Cata and Choroni. It has Venezuela's first national park which is called Henri Pittier. The capital is Maracay, other important cities include Turmero and El Limón.

Maracay is a city in north-central Venezuela, near the Caribbean coast, and is the capital and most important city of the state of Aragua. Most of it falls under the jurisdiction of Girardot Municipality. The population of Maracay and its surroundings in the 2011 census was 955,362. In Venezuela, Maracay is known as "Ciudad Jardín".

Municipalities of Venezuela are subdivisions of the States of Venezuela. There are 335 municipalities dividing the 23 states and the Capital District.
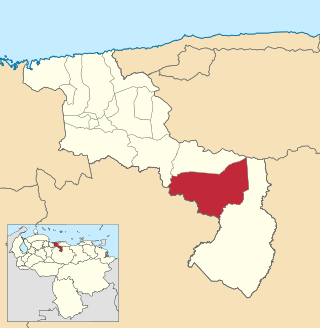
The Camatagua Municipality is one of the 18 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Aragua and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 16,627. The town of Camatagua is the shire town of the Camatagua Municipality.

The Mario Briceño Iragorry Municipality is one of the 18 municipalities (municipios) that make up the Venezuelan state of Aragua and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 99,852. The town of El Limón is the shire town of the Mario Briceño Iragorry Municipality. The municipality is named for the writer Mario Briceño Iragorry.
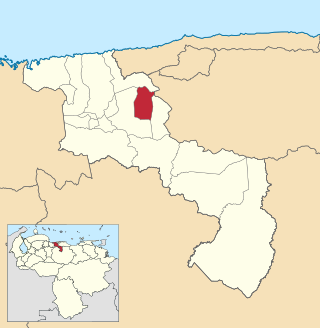
The José Rafael Revenga Municipality is one of the 18 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Aragua and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 48,800. The town of El Consejo is the shire town of the José Rafael Revenga Municipality. The municipality is named for José Rafael Revenga.
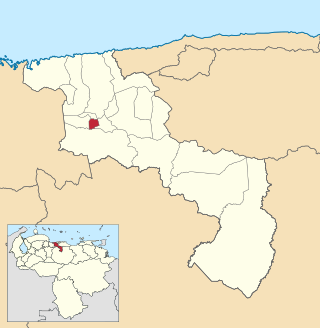
The José Angel Lamas Municipality is one of the 18 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Aragua and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 32,981. The town of Santa Cruz is the municipal seat of the José Angel Lamas Municipality. The municipality is named for the Venezuelan composer José Ángel Lamas.

Sucre Municipality is one of the 18 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Aragua and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 114,509. The town of Cagua is the shire town of the Sucre Municipality.

Páez is one of the 21 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Miranda and, according to a 2007 population estimate by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 39,097. The town of Río Chico is the municipal seat of the Páez Municipality.

The Pedro Zaraza Municipality is one of the 15 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the central Venezuelan state of Guárico and, according to a 2007 population estimate by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 60,595. The town of Zaraza is the shire town of the Pedro Zaraza Municipality.

The Río Negro Municipality is one of the seven municipalities (municipios) that makes up the southern Venezuelan state of Amazonas and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 2,300. The town of San Carlos de Río Negro is the shire town of the Río Negro Municipality.

The Atures Municipality is one of the seven municipalities (municipios) that makes up the southern Venezuelan state of Amazonas and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 104,228. The city of Puerto Ayacucho is the shire town of the Atures Municipality.
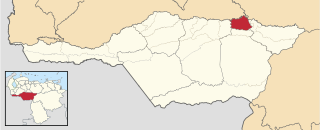
The Biruaca Municipality is one of the seven municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Apure and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 54,323. The town of Biruaca is the municipal seat of the Biruaca Municipality.

The Muñoz Municipality is one of the seven municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Apure and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 27,542. The town of Bruzual is the municipal seat of the Muñoz Municipality. The municipality is named for Major General José Cornelio Muñoz, leader of a division of independence forces during the Venezuelan War of Independence.

Páez is one of the seven municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Apure and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 100,125. The town of Guasdualito is the municipal seat of the Páez Municipality.

The Pedro Camejo Municipality is one of the seven municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Apure and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 28,966. The town of San Juan de Payara is the municipal seat of the Pedro Camejo Municipality. The municipality is named after Afro-Venezuelan independence hero Pedro Camejo.

The Rómulo Gallegos Municipality is one of the seven municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Apure and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 24,418. The town of Elorza is the shire town of the Rómulo Gallegos Municipality.

The Francisco Linares Alcántara Municipality is one of the 18 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the Venezuelan state of Aragua and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 123,122. The town of Santa Rita is the shire town of the Francisco Linares Alcántara Municipality.

The Fernando de Peñalver Municipality is one of the 21 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the eastern Venezuelan state of Anzoátegui and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 33,437. The town of Puerto Píritu is the shire town of the Fernando de Peñalver Municipality.

Francisco de Miranda is one of the 21 municipalities (municipios) that makes up the eastern Venezuelan state of Anzoátegui and, according to the 2011 census by the National Institute of Statistics of Venezuela, the municipality has a population of 43,173. The town of Pariaguán is the shire town of the Francisco de Miranda Municipality.
























