
The Federal Reserve System is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises. Over the years, events such as the Great Depression in the 1930s and the Great Recession during the 2000s have led to the expansion of the roles and responsibilities of the Federal Reserve System.
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed. The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, the compounding frequency, and the length of time over which it is lent, deposited, or borrowed.

The monetary policy of the United States is the set of policies which the Federal Reserve follows to achieve its twin objectives of high employment and stable inflation.

In macroeconomics, money supply refers to the total volume of money held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circulation and demand deposits. Money supply data is recorded and published, usually by the national statistical agency or the central bank of the country. Empirical money supply measures are usually named M1, M2, M3, etc., according to how wide a definition of money they embrace. The precise definitions vary from country to country, in part depending on national financial institutional traditions.

Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability. Further purposes of a monetary policy may be to contribute to economic stability or to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies. Today most central banks in developed countries conduct their monetary policy within an inflation targeting framework, whereas the monetary policies of most developing countries' central banks target some kind of a fixed exchange rate system. A third monetary policy strategy, targeting the money supply, was widely followed during the 1980s, but has diminished in popularity since then, though it is still the official strategy in a number of emerging economies.

The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) is Australia's central bank and banknote issuing authority. It has had this role since 14 January 1960, when the Reserve Bank Act 1959 removed the central banking functions from the Commonwealth Bank.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is a committee within the Federal Reserve System that is charged under United States law with overseeing the nation's open market operations. This Federal Reserve committee makes key decisions about interest rates and the growth of the United States money supply. Under the terms of the original Federal Reserve Act, each of the Federal Reserve banks was authorized to buy and sell in the open market bonds and short term obligations of the United States Government, bank acceptances, cable transfers, and bills of exchange. Hence, the reserve banks were at times bidding against each other in the open market. In 1922, an informal committee was established to execute purchases and sales. The Banking Act of 1933 formed an official FOMC.

Ian John Macfarlane is an Australian economist, and central banker. After an early career as an economist in Melbourne, Sydney, Oxford and Paris, he joined the Reserve Bank of Australia in 1979 and rose to become Governor from 1996 to 2006. After retiring from the Reserve Bank, he became a company director, economic consultant and author of two books.
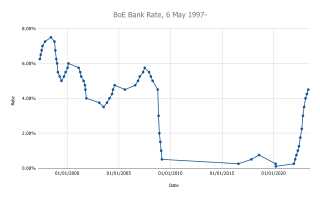
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a committee of the Bank of England, which meets for three and a half days, eight times a year, to decide the official interest rate in the United Kingdom.
In macroeconomics, inflation targeting is a monetary policy where a central bank follows an explicit target for the inflation rate for the medium-term and announces this inflation target to the public. The assumption is that the best that monetary policy can do to support long-term growth of the economy is to maintain price stability, and price stability is achieved by controlling inflation. The central bank uses interest rates as its main short-term monetary instrument.

The Bank of Canada is a Crown corporation and Canada's central bank. Chartered in 1934 under the Bank of Canada Act, it is responsible for formulating Canada's monetary policy, and for the promotion of a safe and sound financial system within Canada. The Bank of Canada is the sole issuing authority of Canadian banknotes, provides banking services and money management for the government, and loans money to Canadian financial institutions. The contract to produce the banknotes has been held by the Canadian Bank Note Company since 1935.
The official cash rate (OCR) is the term used in Australia and New Zealand for the bank rate and is the rate of interest which the central bank charges on overnight loans between commercial banks. This allows the Reserve Bank of Australia and the Reserve Bank of New Zealand to adjust the interest rates that apply in each country's economy. The OCR cannot be changed by transactions between financial institutions as this does not change the supply of money, only its location. Only transfers between the central bank and an institution can affect the OCR.

Quantitative easing (QE) is a monetary policy action where a central bank purchases predetermined amounts of government bonds or other financial assets in order to stimulate economic activity. Quantitative easing is a novel form of monetary policy that came into wide application after the 2007–2008 financial crisis. It is used to mitigate an economic recession when inflation is very low or negative, making standard monetary policy ineffective. Quantitative tightening (QT) does the opposite, where for monetary policy reasons, a central bank sells off some portion of its holdings of government bonds or other financial assets.

The Greenspan put was a monetary policy response to financial crises that Alan Greenspan, former chair of the Federal Reserve, exercised beginning with the crash of 1987. Successful in addressing various crises, it became controversial as it led to periods of extreme speculation led by Wall Street investment banks overusing the put's repurchase agreements and creating successive asset price bubbles. The banks so overused Greenspan's tools that their compromised solvency in the 2007–2008 financial crisis required Fed chair Ben Bernanke to use direct quantitative easing. The term Yellen put was used to refer to Fed chair Janet Yellen's policy of perpetual monetary looseness.

James Brian Bullard is the former chief executive officer and 12th president of the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, a position he held from 2008 until August 14, 2023. In July 2023, he was named dean of the Mitchell E. Daniels Jr. School of Business at Purdue University.
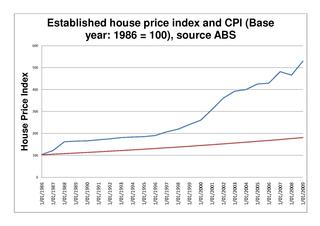
The Australian property bubble is the economic theory that the Australian property market has become or is becoming significantly overpriced and due for a significant downturn. Since the early 2010s, various commentators, including one Treasury official, have claimed the Australian property market is in a significant bubble.
The early 1990s recession saw a period of economic downturn affect much of the world in the late 1980s and early 1990s. The economy of Australia suffered its worst recession since the Great Depression.

Philip Lowe is an Australian economist and former Governor of the Reserve Bank of Australia, from September 2016 to September 2023. He was also deputy governor under Glenn Stevens from February 2012 to September 2016.

Christopher J. Waller is an American economist who has been a member of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors since 2020. A nominee of then-President Donald Trump, he was confirmed by the Senate in December 2020, to serve through January 2030.
Guy Debelle is an Australian economist who is the former Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of Australia, having been appointed in 2016.












