
Xenosauridae is a family of anguimorph lizards whose only living representative is the genus Xenosaurus, which is native to Central America. Xenosauridae also includes the extinct genera Exostinus and Restes. Also known as knob-scaled lizards, they have rounded, bumpy scales and osteoderms. Most living species prefer humid, rocky habitats, although they are widespread within their native regions, with some inhabiting semi-arid scrub environments. They are carnivorous or insectivorous, and give birth to live young.

The Varanidae are a family of lizards in the superfamily Varanoidea and order Anguimorpha. The family, a group of carnivorous and frugivorous lizards, includes the living genus Varanus and a number of extinct genera more closely related to Varanus than to the earless monitor lizard (Lanthanotus). Varanus includes the Komodo dragon, crocodile monitor, savannah monitor, the goannas of Australia and Southeast Asia, and various other species with a similarly distinctive appearance. Their closest living relatives are the earless monitor lizard and Chinese crocodile lizard. The oldest members of the family are known from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia.

Alxasaurus is a genus of therizinosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the Early Cretaceous Bayin-Gobi Formation of Inner Mongolia.
Ovoo gurvel is an extinct varanid lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It is one of the smallest and earliest monitor lizards. It was described in 2008. Ovoo possesses a pair of small bones in its skull that are not seen in any other lizard.

Telmasaurus is an extinct genus of varanoid lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Fossils have been found from the Djadokha and Barun Goyot Formations that date between the early and middle Campanian stage from approximately 80 to 75 million years ago. The type species Telmasaurus grangeri was named in 1943.
Gobekko is an extinct genus of gecko or gecko-like lizard from the Late Cretaceous Djadokhta Formation of the Gobi Desert in Mongolia. Gobekko is either a basal member of Gekkota, the group that includes geckos and the legless pygopodid lizards, or a stem-gekkotan outside Gekkota but within the larger group Gekkonomorpha. It is the fourth oldest known member of Gekkonomorpha after Hoburogekko, a gecko from the Early Cretaceous of Mongolia, AMNH FR21444, an unnamed specimen also from the Early Cretaceous of Mongolia, and Cretaceogekko, a gecko preserved in amber from the Early Cretaceous of Burma.
Hoburogekko is an extinct genus of stem-group gecko that includes a single species, Hoburogekko suchanovi, from the Early Cretaceous Dzunbain Formation of Mongolia. It is known from two fossil specimens, one preserving the front part of the skull and the other preserving part of the lower jaw. Hoburogekko is one of four known Mesozoic geckos or gecko-like lizards, the others being Cretaceogekko from the Early Cretaceous of Burma, AMNH FR21444, an undescribed specimen from a slightly older deposit in Mongolia, and Gobekko from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Hoburogekko is the third oldest known gecko behind AMNH FR21444 and Cretaceogekko.

Scincogekkonomorpha is a proposed clade of lizards that includes scleroglossans and all lizards more closely related to scleroglossans than to iguanians. These "stem" scleroglossans include extinct lizards from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous such as Bavarisaurus, Eichstaettisaurus, Liushusaurus, and Scandensia. Scincogekkonomorpha was named in 1961 and is now occasionally used as a stem-based taxon in contrast to the node-based taxon Scleroglossa. According to phylogenies based on morphological characteristics, Scincogekkonomorpha is the sister taxon of Iguania and together they make up crown group Squamata, the smallest clade including all living snakes and lizards. The grouping has not been recovered as monophyletic in recent molecular studies, with Iguania generally found deeply nested within Squamata.
Myrmecodaptria is an extinct genus of scleroglossan lizard from the Late Cretaceous Djadokhta Formation in Ukhaa Tolgod, Mongolia. The type and only species, Myrmecodaptria microphagosa, was named in 2000 by paleontologists Gao Keqin and Mark Norell. Myrmecodaptria is known from a single holotype skull and lower jaws. It is distinguished from all other lizards by its extremely elongated skull. The eyes are placed close to the snout, which is short and rounded. The top of the skull is covered in bony knobs called osteoderms. The parietal bone at the back of the skull is elongated and about as long as the frontal bones, which are the usually the longest bones along the top of the skull in lizards. The squamosal bone at the back of the skull reaches forward to connect with the jugal bone behind the eye, forming a thin arch between the temporal fenestrae. Myrmecodaptria also has fewer and more widely spaced teeth in its jaws than do most other lizards.
Priscagamidae is an extinct family of iguanian lizards known from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia and China and the Eocene of India, spanning a range from 83.6 to 48.6 million years ago. Probably the earliest priscagamids on indeterminate genera were found in Aptian-Albian sediments in "Hobur", Mongolia. It includes the genera Heterodontagama, Mimeosaurus, Phrynosomimus, Priscagama, and possibly Pleurodontagama. The first fossils of priscagamids were found in the Djadochta and Khermeen Tsav formations of Mongolia. More recently they have been found in the Cambay Formation in India, leading to the naming of Heterodontagama in 2013. Priscagamidae was originally described as a subfamily of Agamidae called Priscagaminae in 1984, but it was reclassified as a distinct family in 1989. Most phylogenetic analyses still find a close relationship between Priscagamidae and Agamidae, although a 2015 study found it to be basal to all other iguanian clades, warranting its removal from Iguania and placement in a larger clade called Iguanomorpha.
Saichangurvel is an extinct genus of iguanian lizards from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It is a member of a clade called Gobiguania, an exclusively Late Cretaceous group of iguanian lizards that was likely endemic to the Gobi Desert. The type species, Saichangurvel davidsoni, was named by paleontologists Jack Conrad and Mark Norell of the American Museum of Natural History in 2007. It is known from a single nearly complete and fully articulated skeleton called IGM 3/858, which was found eroding from a block of sandstone during a thunderstorm at a fossil locality called Ukhaa Tolgod. IGM 3/858 comes from the Djadochta Formation, which is between 75 and 71 million years in age. Just as it is today, the Gobi was a desert during the Cretaceous. IGM 3/858 may have died in a collapsing sand dune, the rapid burial preserving its skeleton in pristine condition.
Xihaina is an extinct genus of iguanian lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Inner Mongolia, China. The type species Xihaina aquilonia was named in 1995 from the Djadochta Formation and is known from a partial skeleton that preserves parts of the skull, most of the vertebral column, the pelvis, and the right hind limb. The incomplete nature of this specimen makes the classification of Xihaina difficult; it has never been incorporated into a phylogenetic analysis, but it shares similarities with a group of Late Cretaceous Mongolian lizards called Gobiguania, particularly the gobiguanian genera Anchaurosaurus and Polrussia. The fact that many skeletal elements are missing yet the rest of the skeleton is articulated suggests the individual may have been partially eaten by a predator or scavenger and then rapidly buried soon after.
Polrussia is an extinct genus of iguanian lizards dating to the Late Cretaceous epoch, found in what is now Mongolia. It belongs to a group of extinct iguanians called Gobiguania that was endemic to the Gobi Desert during the Late Cretaceous. The type species Polrussia mongoliensis was named in 1991 on the basis of a skull found in the Barun Goyot Formation. The genus name refers to the Polish and Russian paleontologists who worked together to find and describe the material. Polrussia has a short skull, slightly pointed and flattened snout, and large eye sockets. The teeth each have one cusp, as opposed to the multiple cusps seen in some other gobiguanians. The skull is only 1.2 centimetres (0.47 in) long, making Polrussia one of the smallest gobiguanians.

Igua is an extinct genus of iguanian lizards belonging to a group called Gobiguania that was endemic to the Gobi Desert during the Late Cretaceous. The type species Igua minuta was named in 1991 on the basis of a skull from the Barun Goyot Formation in Mongolia. The skull itself is very small, only 14 millimetres (0.55 in) long, and may have belonged to a juvenile given that it possesses a large fontanelle and that many of the bones are unfused. The snout-vent length of the individual is estimated to have been 55 to 65 millimetres. Igua differs from related gobiguanians like Polrussia in having a more rounded skull. It is similar in appearance to the living genera Liolaemus and Tropidurus. The teeth are tricuspid and pleurodont, meaning they are attached to inner surfaces of the jaws.
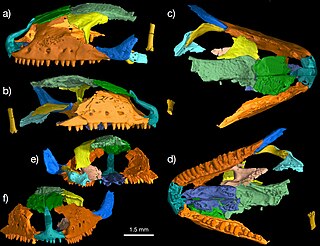
Paramacellodidae is an extinct family of lizards that first appeared in the Middle Jurassic around 170 million years ago (Ma) and became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous around 66 Ma. It was one of the earliest groups of lizards to have undergone an evolutionary radiation, with members found across the supercontinent Laurasia. The phylogenetic relationships and constituent species of Paramacellodidae are uncertain. Many studies regard them to be scincomorphs, a large group that includes skinks and their closest extinct relatives, and possibly also to Cordyoidea, a group that includes spinytail lizards and relatives. Like modern skinks, paramacelloidids had rectangular bony plates called osteoderms covering most of their bodies, including their backs, undersides, and tails. They also had short and robust limbs. Paramacellodids are distinguished from other lizards by the combination two traits in their dentition, the teeth are labiolingually expanded at their bases, and the tooth apices are lingually concave.
Barbatteiidae is an extinct family of lizards, endemic to the paleoisland Hațeg Island in the Tethys Ocean during the final stages of the Cretaceous, In what is now Romania. It contains two monotypic genera, Barbatteius and Oardasaurus, alongside some indeterminate material. It appears to be closely related to modern teiids and the Early Cretaceous lizard genus Meyasaurus
Meyasaurus is an extinct genus of Teiid lizard known from the Barremian of Spain and the Isle of Wight, UK. Four species are known from Spain, from the La Huérguina, Camarillas, and La Pedrera de Rúbies Formations while an indeterminate taxon is known from the Wessex Formation of Isle of Wight. It is a possible close relative of Barbatteius and other members of Barbatteiidae.

Ardeosauridae is an extinct family of lizards known from the Late Jurassic of Germany and North America and Early Cretaceous of Mongolia, with other potential species elsewhere from Europe and Asia over the same time period.
Pseudosaurillus is a genus of extinct lizard from the Early Cretaceous of southern England. The type and only species is Pseudosaurillus becklesi, named in 1967 by R. Hoffstetter limited jaw and tooth material from the Berriasian Lulworth Formation. A large amount of material that was additionally referred to Saurillus by Hoffstetter was reassigned to Pseudosaurillus in 1983 by Estes, but this has since been reclassified within its own genus Parasaurillus by Susan E. Evans and Belinda Searle in 2002. The taxon was found in the Mammal Bed near the base of the formation alongside the other lizards Becklesius, Dorsetisaurus, Durotrigia, Paramacellodus, Parasaurillus, Parviraptor and Saurillus. Like Becklesius, Pseudosaurillus may be a member of the family Paramacellodidae.

Ondogurvel is a genus of alvarezsaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) Barun Goyot Formation in southern Mongolia. The type and only species is O. alifanovi, known from a partial skeleton consisting of fragments of two last dorsal vertebrae, three anterior sacral vertebrae, right ilium, left and right pubis and ischium, articulated right tibia, fibula, metatarsals II and IV, and phalanges IV-1 and IV-2, right carpometacarpus, left and right manual phalanx II-1, right femur, left pedal phalanx II-1, and fragments of unidentified phalanges.








