
The hammerhead sharks are a group of sharks that form the family Sphyrnidae, so named for the unusual and distinctive structure of their heads, which are flattened and laterally extended into a "hammer" shape called a cephalofoil. Most hammerhead species are placed in the genus Sphyrna, while the winghead shark is placed in its own genus, Eusphyra. Many, but not necessarily mutually exclusive, functions have been postulated for the cephalofoil, including sensory reception, manoeuvering, and prey manipulation. Research has shown that the cephalofoil gives the shark improved binocular vision and depth perception.

The great white shark, also known as the great white, white shark or white pointer, is a species of large mackerel shark which can be found in the coastal surface waters of all the major oceans. It is notable for its size, with larger female individuals growing to 6.1 m (20 ft) in length and 1,905–2,268 kg (4,200–5,000 lb) in weight at maturity. However, most are smaller; males measure 3.4 to 4.0 m, and females measure 4.6 to 4.9 m on average. According to a 2014 study, the lifespan of great white sharks is estimated to be as long as 70 years or more, well above previous estimates, making it one of the longest lived cartilaginous fishes currently known. According to the same study, male great white sharks take 26 years to reach sexual maturity, while the females take 33 years to be ready to produce offspring. Great white sharks can swim at speeds of 25 km/hr (16 mph) for short bursts and to depths of 1,200 m (3,900 ft).

Requiem sharks are sharks of the family Carcharhinidae in the order Carcharhiniformes. They are migratory, live-bearing sharks of warm seas and includes such species as the tiger shark, the spinner shark, the blacknose shark, the blacktip shark, the grey reef shark, the blacktip reef shark, the silky shark, the dusky shark, the blue shark, the copper shark and the oceanic whitetip shark.

The megamouth shark is a species of deepwater shark. It is rarely seen by humans and is the smallest of the three extant filter-feeding sharks alongside the whale shark and basking shark. Since its discovery in 1976, few megamouth sharks have been seen, with fewer than 100 specimens being observed or caught. Like the other two planktivorous sharks, it swims with its enormous mouth wide open, filtering water for plankton and jellyfish. It is distinctive for its large head with rubbery lips. It is so unlike any other type of shark that it is usually considered to be the sole extant species in the distinct family Megachasmidae, though suggestion has been made that it may belong in the family Cetorhinidae, of which the basking shark is currently the sole extant member.

Glyphis is a genus in the family Carcharhinidae, commonly known as the river sharks. This genus was thought to contain five different species, but recent studies on molecular data revealed that the species Glyphis gangeticus has an irregular distribution in the Indo-West Pacific region. This genus contains only four extant species. Further species could easily remain undiscovered, due to the secretive habits of Glyphis sharks. Their precise geographic range is uncertain, but the known species are documented in parts of South Asia, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, and Australia. Of the four currently described species, the Ganges shark is restricted to freshwater, while the northern river shark and the speartooth shark are found in coastal marine waters, as well. While the bull shark is sometimes called both the river shark and the Ganges shark, it should not be confused with the river sharks of the genus Glyphis. The River sharks of the genus Glyphis remain very poorly known to science. They are facing a critically endangered status since river sharks are so poorly studied, and people know very little about their population and life history. One of the primary threats to River Sharks is habitat degradation which includes: human development, pollution, and fishing. The river shark is known to be one of the most rare sharks in the world. They have been found in nine different tidal areas, which consists of muddy waters with a low salinity. Their placement in connection to coastal marine waters indicate that they are usually born around October.

The Ganges shark is a critically endangered species of requiem shark found in the Ganges River and the Brahmaputra River of Bangladesh and India. It is often confused with the more common bull shark, which also inhabits the Ganges River and is sometimes incorrectly referred to as the Ganges shark. Unlike bull sharks, which need to migrate to salt water to reproduce, species in the genus Glyphis are true river sharks. The genus is currently considered to contain three recent species; genetic evidence has shown that both the Borneo river shark and Irrawaddy river shark should be regarded as synonyms of the Ganges shark, expanding the range of the species to Pakistan, Myanmar, Borneo, and Java. The species remains poorly known and very rare.

Calvert Cliffs State Park is a public recreation area in Lusby, Calvert County, Maryland, that protects a portion of cliffs that extend for 24 miles along the eastern flank of the Calvert Peninsula on the west side of Chesapeake Bay from Chesapeake Beach southward to Drum Point. The state park is known for the abundance of mainly Middle Miocene sub-epoch fossils that can be found on the shoreline.

Sand sharks, also known as sand tiger sharks, grey nurse sharks or ragged tooth sharks, are mackerel sharks of the family Odontaspididae. They are found worldwide in temperate and tropical waters. The three species are in two genera.
John Andrew Frank "Jack" Garrick was a New Zealand ichthyologist. He specialized in elasmobranchs and published many books and articles about shark and ray biology. In 1982, he published a thorough taxonomy on sharks of the genus Carcharhinus, where he identified the smoothtooth blacktip shark as a new species. He is the species authority for several types of sharks, including the New Zealand lanternshark. Garrick was a zoology professor at Victoria University of Wellington, appointed to a personal chair in 1971.

The speartooth shark is an extremely rare species of river shark, belonging to the family Carcharhinidae. It inhabits coastal marine waters and tidal reaches of large tropical rivers in northern Australia and New Guinea. Despite being a member of the river shark genus, it is also found in near-shore marine waters, favoring highly turbid environments over a wide range of salinities. This robustly built, gray-colored shark is characterized by a short and broad snout, tiny eyes, a relatively large second dorsal fin, and a black blotch beneath each pectoral fin near the tip. Another identifying trait is its teeth, which are large, triangular, and serrated in the upper jaw and narrow, spear-like, and serrated only near the tips in the lower jaw. Adults grow to about 2.6 m (8.5 ft) long.
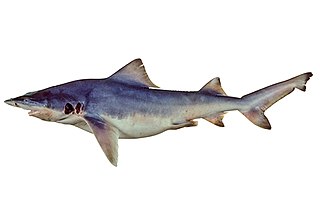
The northern river shark or New Guinea river shark is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae, found in scattered tidal rivers and associated coastal waters in northern Australia and in Papua New Guinea. This species inhabits areas with poor visibility, soft bottoms, and large tides, with immature sharks ranging into fresh and brackish water. It is similar to other river sharks in having a stocky grey body with a high back, tiny eyes, and broad fins. It measures up to 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long.

Isurus is a genus of mackerel sharks in the family Lamnidae, commonly known as the mako sharks.
The Temblor Formation is a geologic formation in California. It preserves fossils dating back from the Late Oligocene to the Middle Miocene of the Neogene period. It is notable for the famous Sharktooth Hill deposit.
The Jewett Sand Formation is a geologic formation in California, USA. It preserves fossils dating back to the Miocene Epoch of the Neogene period.

Isurus planus, also known as the hooked-tooth mako shark or hooked mako shark, is an extinct lamnid that lived during the Miocene epoch from 23 to 5 million years ago. I. planus can be found only in marine deposits on the Pacific Rim, especially the west coast of the United States. Teeth belonging to I. planus can reach lengths of 2.0 in (5.0 cm), and are often found in the Temblor Formation of Bakersfield, California.

Cosmopolitodus is an extinct genus of sharks. Its only species is currently Cosmopolitodus hastalis, the broad-tooth mako. It is an extinct mackerel shark that lived between thirty to one million years ago during the Oligocene to the Early Pleistocene epochs. Its teeth can reach lengths up to 3.5 in (7.5 cm) and are found worldwide. It is believed to be an ancestor to the great white shark, a fact supported by the transitional species Carcharodon hubbelli, and most likely would have been one of the major predators in its ecosystem; preying upon small whales and other mammals.

Carcharomodus escheri, commonly nicknamed the serrated mako shark or Escher's mako shark, is an extinct lamnid that lived during the Miocene. It has been formerly thought to have been the transitional between the broad-toothed "mako" Cosmopolitodus hastalis and the modern great white, but is now considered to be an evolutionary dead-end with the discovery of Carcharodon hubbelli. Fossil examples have been found along northern Atlantic coastlines and in parts of Western and Central Europe.

Alopias palatasi commonly referred to as the serrated giant thresher, is an extinct species of giant thresher shark that lived approximately 20.44 to 13.7 million years ago during the Miocene epoch, and is known for its uniquely serrated teeth. It is only known from such isolated teeth, which are large and can measure up to an excess of 4 centimetres (2 in), equating to a size rivaling the great white shark, but are rare and found in deposits in the East Coast of the United States and Malta. Teeth of A. palatasi are strikingly similar to those of the giant thresher Alopias grandis, and the former has been considered as a variant of the latter in the past. Scientists hypothesized that A. palatasi may have had attained lengths comparable with the great white shark and a body outline similar to it.














