
Octopodiformes is a superorder of the subclass Coleoidea, comprising the octopuses and the vampire squid. All living members of Octopodiformes have eight arms, either lacking the two tentacles of squid or modifying the tentacles into thin filaments. Octopodiformes is often considered the crown group of octopuses and vampire squids, including all descendants of their common ancestor. Some authors use the term Vampyropoda for the same general category, though others use "Vampyropoda" to refer to the total group. Another term is Octobranchia, referring to cephalopods without prominent tentacles.

Bathypolypus is a genus of octopuses in the monotypic family Bathypolypodidae.
Thaumeledone is a genus of octopuses in the family Octopodidae found in deep waters in the Southern Hemisphere.

Scaeurgus is a genus of octopuses in the family Octopodidae. The species of this genus are characterized by inhabiting the upper bathyal benthic zone from temperate and tropical latitudes in all major oceans.
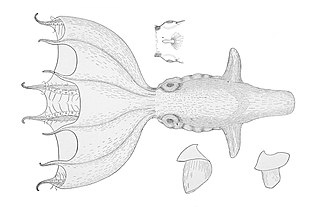
Stauroteuthis syrtensis, also known as the glowing sucker octopus or bioluminescent octopus, is a species of small pelagic octopus found at great depths in the north Atlantic Ocean. It is one of a very small number of octopuses to exhibit bioluminescence.

Cirroteuthis muelleri, also known as the big-finned jellyhead, was the first cirrate octopus species to be scientifically described. It is closely related to the genus Cirrothauma within the family Cirroteuthidae. At present the genus contains a single recognized species restricted to the Arctic Ocean and northern basins of the Atlantic and Pacific, but other species may be present in the southern hemisphere.

Eledone moschata, the musky octopus, is a species of octopus belonging to the family Octopodidae.

Muusoctopus levis is a species of octopus in the family Enteroctopodidae. It was first described by William Evans Hoyle in 1885 in an article in the Annals and Magazine of Natural History detailing the new species of octopus found on HMS Challenger as part of the Challenger expedition; the type specimen was retrieved from the Southern Ocean. The species is found in subantarctic waters in the Southern Ocean, particularly surrounding Heard Island and Kerguelen Island, but specimens comparable to M. levis have also been found at the Antarctic Peninsula.
Thaumeledone gunteri is a species of small, benthic, deep-sea octopus found in the bathyal zone in the Southern Ocean near South Georgia.
Stauroteuthis gilchristi is a species of small pelagic octopus found at great depths in the south Atlantic Ocean. It is believed to be one of a very small number of octopuses to exhibit bioluminescence, like its sister taxon Stauroteuthis syrtensis.

Megaleledonidae is a family of octopuses in the superfamily Octopodoidea. It was formerly placed in the family Octopodidae sensu lato as the subfamily Megaleledoninae but more recent studies have raised this taxon as a valid family. Megaleledonidae contains about 43 species in 12 genera.
Sasakiopus is a genus of octopus containing only one species, Sasakiopus salebrosus, the rough octopus. It is part of the family Enteroctopodidae. Genetic analysis appeared to show that S. salebrosus is the sister taxon of the genera Benthoctopus and Vulcanoctopus, although the former is now considered a synonym of Bathypolypus, the only genus in the family Bathypolypodidae, and the latter as a synonym of Muusoctopus.
Richard E. Young is a teuthologist. He is an Emeritus Professor of Oceanography at the University of Hawaii's School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology.

Cirrothauma magna, also known as the big-eye jellyhead, is a species of deep-sea cirrate octopus that has been found in the Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific oceans. It is known from four damaged specimens. Their shells are somewhat saddle-shaped. C. magna is the sister taxon of Cirrothauma murrayi, but can be readily distinguished by having large and well developed eyes.

Grimpoteuthis discoveryi is a small species of octopus known from more than 50 specimens. It was described in 2003, but specimens have been found as early as 1910. The type species was found at 49°35'N, 14°01'W.
Grimpoteuthis innominata, commonly known as the small jellyhead, is a species of small, pelagic octopus described by Steve O'Shea in 1999 from two specimens, however several further specimens have since been identified. The genus Enigmateuthis was described to contain this species when described, but Martin Collins placed the species in the genus Grimpoteuthis due to uncertainty regarding the type specimen of Grimpoteuthis.
Opisthoteuthis calypso or calypso flapjack octopus is a species of genus Opisthoteuthis, which are known as the cirrate octopuses. Octopuses in this genus are known as the flapjack octopuses and can be found in a variety of oceans across the world.
Opisthoteuthis bruuni is a species of finned cirrate octopus found along the western coast of South America. Their tissue is almost jelly-like, and they have short, round bodies.

Opisthoteuthis depressa, also known as the Japanese flapjack octopus, is an octopus found in waters near Japan.

Bathypolypus sponsalis, commonly called the globose octopus, is a deep sea cephalopod that can be found in both the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It possesses many morphological traits adapted to a deep sea environment, including large eggs, reduced gills, no ink sac, and subgelatinous tissues. A distinguishing factor are the relatively large reproductive organs. Their diet consists of predominantly crustaceans and molluscs, but they sometimes consume fish as well. Bathypolypus sponsalis usually dies quickly after reproduction and only spawns once in their lifetime. Sexually mature females have a mantle length of at least 34 mm and sexually mature males have a mantle length of about 24 mm. Juveniles are white and transition to dark brown then to dark purple once maturity is reached.











