
The history of the petroleum industry in the United States goes back to the early 19th century, although the indigenous peoples, like many ancient societies, have used petroleum seeps since prehistoric times; where found, these seeps signaled the growth of the industry from the earliest discoveries to the more recent.

Mobil is a petroleum brand owned and operated by American oil and gas corporation ExxonMobil. The brand was formerly owned and operated by an oil and gas corporation of the same name, which itself merged with Exxon to form ExxonMobil in 1999.

Esso is a trading name for ExxonMobil. Originally, the name was primarily used by its predecessor Standard Oil of New Jersey after the breakup of the original Standard Oil company in 1911. The company adopted the name "Esso", to which the other Standard Oil companies would later object.
OMV is an Austrian multinational integrated oil, gas and petrochemical company which is headquartered in Vienna, Austria. The company is listed on the Vienna Stock Exchange. In the 2021 Forbes Global 2000, OMV Group was ranked as the 413th -largest public company in the world.

APA Corporation is the holding company for Apache Corporation, an American company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration. It is organized in Delaware and headquartered in Houston. The company is ranked 431st on the Fortune 500.
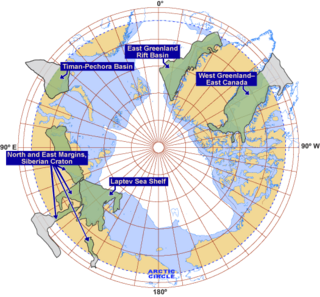
Exploration for petroleum in the Arctic is expensive and challenging both technically and logistically. In the offshore, sea ice can be a major factor. There have been many discoveries of oil and gas in the several Arctic basins that have seen extensive exploration over past decades but distance from existing infrastructure has often deterred development. Development and production operations in the Arctic offshore as a result of exploration have been limited, with the exception of the Barents and Norwegian seas. In Alaska, exploration subsequent to the discovery of the Prudhoe Bay oilfield has focussed on the onshore and shallow coastal waters.

XTO Energy Inc. is an American energy company and subsidiary of ExxonMobil principally operating in North America. Acquired by ExxonMobil in 2010 and based out of Spring, Texas, it is involved with the production, processing, transportation, and development of oil and natural gas resources. The company specializes in developing shale gas via unconventional means like hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling.

Canada's early petroleum discoveries took place near population centres or along lines of penetration into the frontier.
The National Oil Corporation is the national oil company of Libya. It dominates Libya's oil industry, along with a number of smaller subsidiaries, which combined account for around 70% the country's oil output. Of NOC's subsidiaries, the largest oil producer is the Waha Oil Company (WOC), followed by the Arabian Gulf Oil Company (Agoco), Zueitina Oil Company (ZOC), and Sirte Oil Company (SOC).
The Makó gas field is a large natural gas field next to Makó, in southeastern Hungary.
Petroleum industry in Guyana is rapidly evolving. Guyana has emerged as one of the newest petroleum producing regions in the world, achieving its first commercial grade crude oil draw in December 2019. Crude oil is sent abroad for refining.

ExxonMobil Corporation is an American multinational oil and gas corporation and the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil. The company, which took its present name in 1999 per the merger of Exxon and Mobil, is vertically integrated across the entire oil and gas industry, and within it is also a chemicals division which produces plastic, synthetic rubber, and other chemical products. ExxonMobil is headquartered near the Houston suburb of Spring, Texas, though officially incorporated in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The company is the largest oil and gas company based in the US, America's third largest by revenue among all industries, and the eighth largest in the world.

Offshore drilling for oil and gas on the Atlantic coast of the United States took place from 1947 to the early 1980s. Oil companies drilled five wells in Atlantic Florida state waters and 51 exploratory wells on federal leases on the outer continental shelf of the Atlantic coast. None of the wells were completed as producing wells. All the leases have now reverted to the government.

The oil and gas industry in New Zealand explores and develops oil and gas fields, and produces and distributes petroleum products and natural gas.

The East-Prinovozemelsky field is a gigantic undeveloped Arctic oil and gas field located in the South Kara basin of the continental shelf of Russia, in the South Kara Sea between the Yamal Peninsula and Novaya Zemlya island. It is the continuation of the continental West Siberian hydrocarbon province.
Shale gas is an unconventional natural gas produced from shale, a type of sedimentary rock. Shale gas has become an increasingly important source of natural gas in the United States over the past decade, and interest has spread to potential gas shales in Canada, Europe, Asia, and Australia. One analyst expects shale gas to supply as much as half the natural gas production in North America by 2020.

The Vaca Muerta Formation, commonly known as Vaca Muerta, is a geologic formation of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous age, located in the Neuquén Basin in northern Patagonia, Argentina. It is well known as the host rock for major deposits of shale oil and shale gas.
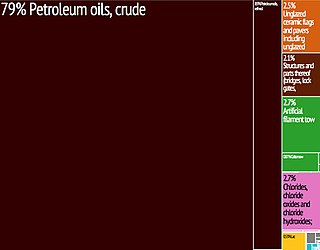
Chad maintains sizable reserves of crude oil which, alongside agriculture, makes up the largest share of the landlocked former French colony's export revenue. Producing around 100,000 barrels of oil a day, most of Chad's crude comes from its reserves in the Doba Basin in southern Chad where oil was discovered in the early 1970s by foreign drillers. There is an estimated one billion barrels of oil in Chad, most of it being exploited by hundreds of rigs operated by Western companies such as ExxonMobil and Shell. However, many challenges exist to Chad's petroleum industry including but not limited to corruption, internal conflict, and geography. Since Chad is landlocked, most of Chad's oil exports are transported out of the country by a pipeline that leads to the Cameroonian port city of Kribi. This pipeline, owned by a consortium, has come under fire due to allegations of exploitation by international corruption watchdogs, and Chadian politicians. In addition, environmentalists have voiced their concerns over the pipeline's impact on the natural environment, citing several spills.
ExxonMobil, an American multinational oil and gas corporation presently based out of Texas, has had one of the longest histories of any company in its industry. A direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, the company traces its roots as far back as 1866 to the founding of the Vacuum Oil Company, which would become part of ExxonMobil through its own merger with Mobil during the 1930s. The present name of the company comes from a 1999 merger of Standard Oil's New Jersey and New York successors, which adopted the names Exxon and Mobil respectively throughout the middle of the 20th century. Because of Standard Oil of New Jersey's ownership over all Standard Oil assets at the time of the 1911 breakup, ExxonMobil is seen by some as the definitive continuation of Standard Oil today.
Australia is a major petroleum producer and importer, with a number of petroleum companies involved in upstream and downstream operations. Western Australia is the largest contributor to Australia's production of most petroleum products.












