Related Research Articles

The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side : the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal. The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first.
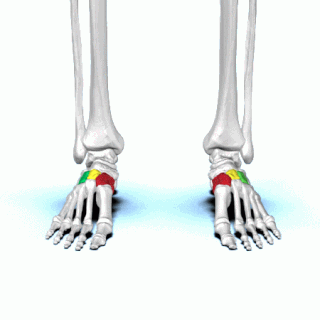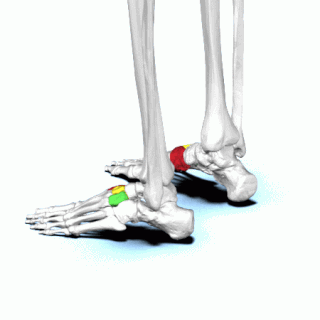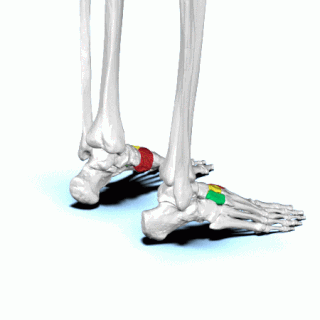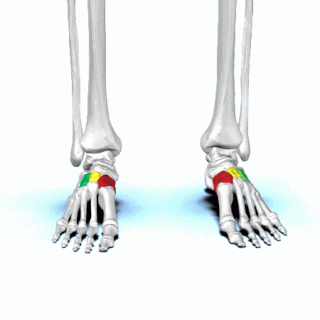
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot:

The hock, or gambrel, is the joint between the tarsal bones and tibia of a digitigrade or unguligrade quadrupedal mammal, such as a horse, cat, or dog. This joint may include articulations between tarsal bones and the fibula in some species, while in others the fibula has been greatly reduced and is only found as a vestigial remnant fused to the distal portion of the tibia. It is the anatomical homologue of the ankle of the human foot. While homologous joints occur in other tetrapods, the term is generally restricted to mammals, particularly long-legged domesticated species.
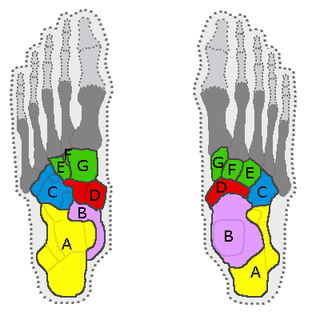
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot and hindfoot.
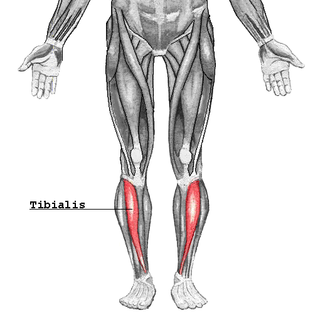
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle in humans that originates along the upper two-thirds of the lateral (outside) surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.

The Adductor hallucis arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve.

The cuneonavicular joint is a joint (articulation) in the human foot. It is formed between the navicular bone and the three cuneiform bones. The navicular and cuneiform bones are connected by dorsal and plantar ligaments.
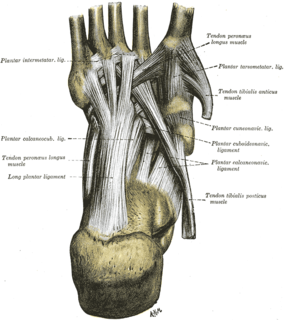
The cuboideonavicular joint is a joint (articulation) in the foot formed between the navicular bone and cuboid bone. The navicular bone is connected with the cuboid bone by the dorsal, plantar, and interosseous cuboideonavicular ligaments.
The intermetacarpal joints are in the hand formed between the metacarpal bones. The bases of the second, third, fourth and fifth metacarpal bones articulate with one another by small surfaces covered with cartilage. The metacarpal bones are connected together by dorsal, palmar, and interosseous ligaments.
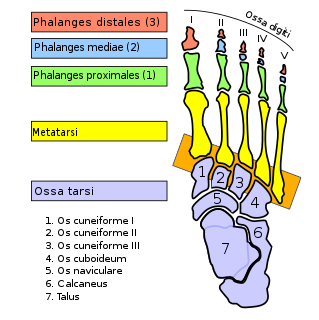
The tarsometatarsal joints are arthrodial joints in the foot. The tarsometatarsal joints involve the first, second and third cuneiform bones, the cuboid bone and the metatarsal bones. The eponym of Lisfranc joint is 18th-19th century surgeon and gynecologist, Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin.

The intermetatarsal joints are the articulations between the base of metatarsal bones.

The intercuneiform joints are the joints the cuneiform bones.

The intercarpal joints can be subdivided into three sets of joints : Those of the proximal row of carpal bones, those of the distal row of carpal bones, and those of the two rows with each other.
The arcuate artery of the foot arises from dorsalis pedis slightly anterior to the lateral tarsal artery, specifically over the naviculocuneiform joint; it passes lateralward, over the bases of the lateral four metatarsal bones, beneath the tendons of the extensor digitorum brevis, its direction being influenced by its point of origin; and it terminates in the lateral tarsal artery. It communicates with the plantar arteries through the perforating arteries of the foot.

The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand

The fourth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is smaller in size than the third metatarsal bone and is the third longest of the five metatarsal bones. The fourth metatarsal is analogous to the fourth metacarpal bone in the hand

The third metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is the second longest metatarsal. The longest being the second metatarsal. The third metatarsal is analogous to the third metacarpal bone in the hand

The second metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is the longest of the metatarsal bones, being prolonged backward and held firmly into the recess formed by the three cuneiform bones. The second metatarsal forms joints with the second proximal phalanx through the metatarsophalangeal joint, the cuneiform bones, third metatarsal and occasionally the first metatarsal bone.

The skeletal system of the horse has three major functions in the body. It protects vital organs, provides framework, and supports soft parts of the body. Horses typically have 205 bones. The pelvic limb typically contains 19 bones, while the thoracic limb contains 20 bones.

The dorsal tarsometatarsal ligaments are ligaments located in the foot. They are strong, flat bands that stretch from the tarsal bones to the metatarsals.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)