The history of the telescope can be traced to before the invention of the earliest known telescope, which appeared in 1608 in the Netherlands, when a patent was submitted by Hans Lippershey, an eyeglass maker. Although Lippershey did not receive his patent, news of the invention soon spread across Europe. The design of these early refracting telescopes consisted of a convex objective lens and a concave eyepiece. Galileo improved on this design the following year and applied it to astronomy. In 1611, Johannes Kepler described how a far more useful telescope could be made with a convex objective lens and a convex eyepiece lens. By 1655, astronomers such as Christiaan Huygens were building powerful but unwieldy Keplerian telescopes with compound eyepieces.

James Gregory was a Scottish mathematician and astronomer. His surname is sometimes spelt as Gregorie, the original Scottish spelling. He described an early practical design for the reflecting telescope – the Gregorian telescope – and made advances in trigonometry, discovering infinite series representations for several trigonometric functions.

A reflecting telescope is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Many variant forms are in use and some employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptric telescope.
Laurent Cassegrain was a Catholic priest who is notable as the probable inventor of the Cassegrain reflector, a folded two-mirror reflecting telescope design.

The Newtonian telescope, also called the Newtonian reflector or just a Newtonian, is a type of reflecting telescope invented by the English scientist Sir Isaac Newton, using a concave primary mirror and a flat diagonal secondary mirror. Newton's first reflecting telescope was completed in 1668 and is the earliest known functional reflecting telescope. The Newtonian telescope's simple design has made it very popular with amateur telescope makers.

The William Herschel Telescope (WHT) is a 4.20-metre (165 in) optical/near-infrared reflecting telescope located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The telescope, which is named after William Herschel, the discoverer of the planet Uranus, is part of the Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes. It is funded by research councils from the United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Spain.

A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930.

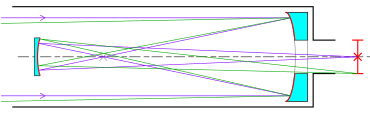
The Giant Magellan Telescope is a 25.4-meter, ground-based, extremely large telescope under construction at Las Campanas Observatory in Chile's Atacama Desert. Commissioning is anticipated in the late 2020s. Once complete, the Giant Magellan will be the largest Gregorian telescope ever built observing in optical and mid-infrared light. The telescope uses seven of the world’s largest mirrors to form a light collecting area of 368 square meters.

Transition Region and Coronal Explorer was a NASA heliophysics and solar observatory designed to investigate the connections between fine-scale magnetic fields and the associated plasma structures on the Sun by providing high resolution images and observation of the solar photosphere, the transition region, and the solar corona. A main focus of the TRACE instrument is the fine structure of coronal loops low in the solar atmosphere. TRACE is the third spacecraft in the Small Explorer program, launched on 2 April 1998, and obtained its last science image on 21 June 2010, at 23:56 UTC.

A catadioptric optical system is one where refraction and reflection are combined in an optical system, usually via lenses (dioptrics) and curved mirrors (catoptrics). Catadioptric combinations are used in focusing systems such as searchlights, headlamps, early lighthouse focusing systems, optical telescopes, microscopes, and telephoto lenses. Other optical systems that use lenses and mirrors are also referred to as "catadioptric", such as surveillance catadioptric sensors.

The Maksutov is a catadioptric telescope design that combines a spherical mirror with a weakly negative meniscus lens in a design that takes advantage of all the surfaces being nearly "spherically symmetrical". The negative lens is usually full diameter and placed at the entrance pupil of the telescope. The design corrects the problems of off-axis aberrations such as coma found in reflecting telescopes while also correcting chromatic aberration. It was patented in 1941 by Soviet optician Dmitri Dmitrievich Maksutov. Maksutov based his design on the idea behind the Schmidt camera of using the spherical errors of a negative lens to correct the opposite errors in a spherical primary mirror. The design is most commonly seen in a Cassegrain variation, with an integrated secondary, that can use all-spherical elements, thereby simplifying fabrication. Maksutov telescopes have been sold on the amateur market since the 1950s.
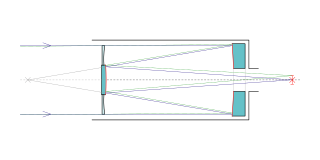
The Schmidt–Cassegrain is a catadioptric telescope that combines a Cassegrain reflector's optical path with a Schmidt corrector plate to make a compact astronomical instrument that uses simple spherical surfaces.

The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system.

The Alice P. Lennon Telescope and its Thomas J. Bannan Astrophysics Facility, known together as the Vatican Advanced Technology Telescope (VATT), is a Gregorian telescope observing in the optical and infrared situated on Mount Graham in southeast Arizona, United States. Measuring 1.83 m wide, the telescope achieved its first light in 1993.
The following timeline lists the significant events in the invention and development of the telescope.

An extremely large telescope (ELT) is an astronomical observatory featuring an optical telescope with an aperture for its primary mirror from 20 metres up to 100 metres across, when discussing reflecting telescopes of optical wavelengths including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and near infrared wavelengths. Among many planned capabilities, extremely large telescopes are planned to increase the chance of finding Earth-like planets around other stars. Telescopes for radio wavelengths can be much bigger physically, such as the 300 metres aperture fixed focus radio telescope of the Arecibo Observatory. Freely steerable radio telescopes with diameters up to 100 metres have been in operation since the 1970s.

The first reflecting telescope built by Sir Isaac Newton in 1668 is a landmark in the history of telescopes, being the first known successful reflecting telescope. It was the prototype for a design that later came to be called the Newtonian telescope. There were some early prototypes and also modern replicas of this design.

The James Gregory Telescope was constructed in 1962 by the University of St Andrews. It is of a Schmidt-Cassegrain design and is fitted with a CCD camera. The telescope has very large field of view, compared even to regular 'wide field' designs, and can view 5 square degrees.
Sheep Hill Observatory is an Astronomical observatory located in Morris County, New Jersey. It features an 18-inch (457mm) Newtonian reflecting telescope and is open to the public on the 3rd Friday evening of each month, weather permitting. It is also made available to Schools, Scouting Groups and other educational groups upon request.