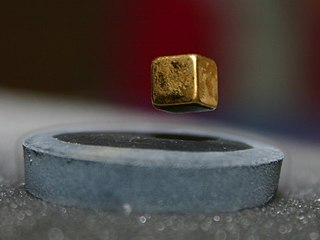A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor "unrolled", thus, instead of producing a torque (rotation), it produces a linear force along its length. However, linear motors are not necessarily straight. Characteristically, a linear motor's active section has ends, whereas more conventional motors are arranged as a continuous loop.

Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from two Latin words: pro, meaning before or forward; and pellere, meaning to drive. A propulsion system consists of a source of mechanical power, and a propulsor.

A hovercraft, also known as an air-cushion vehicle or ACV, is an amphibious craft capable of travelling over land, water, mud, ice, and various other surfaces.

Transrapid is a German-developed high-speed monorail train using magnetic levitation. Planning for the system started in the late 1960s, with a test facility in Emsland, Germany inaugurated in 1983. In 1991, technical readiness for application was approved by the Deutsche Bundesbahn in cooperation with renowned universities.

A linear induction motor (LIM) is an alternating current (AC), asynchronous linear motor that works by the same general principles as other induction motors but is typically designed to directly produce motion in a straight line. Characteristically, linear induction motors have a finite primary or secondary length, which generates end-effects, whereas a conventional induction motor is arranged in an endless loop.

Electrodynamic suspension (EDS) is a form of magnetic levitation in which there are conductors which are exposed to time-varying magnetic fields. This induces eddy currents in the conductors that creates a repulsive magnetic field which holds the two objects apart.
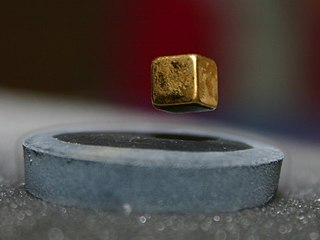
Levitation is the process by which an object is held aloft in a stable position, without mechanical support via any physical contact.

A hoverboard is a fictional levitating board used for personal transportation, first described in science-fiction, and made famous by the appearance of a skateboard-like hoverboard in the film Back to the Future Part II. Many attempts have been made to invent a functioning hoverboard.

Maglev is a system of rail transport whose rolling stock is levitated by electromagnets rather than rolled on wheels, eliminating rolling resistance.

A hover car is a personal vehicle that flies at a constant altitude of up to a few meters (yards) above the ground and used for personal transportation in the same way a modern automobile is employed. The concept usually appears in science fiction.

The Aérotrain was an experimental Tracked Air Cushion Vehicle (TACV), or hovertrain, developed in France from 1965 to 1977 under the engineering leadership of Jean Bertin (1917–1975) – and intended to bring the French rail network to the cutting edge of land-based public transportation.

Electromagnetic suspension (EMS) is the magnetic levitation of an object achieved by constantly altering the strength of a magnetic field produced by electromagnets using a feedback loop. In most cases the levitation effect is mostly due to permanent magnets as they have no power dissipation, with electromagnets only used to stabilise the effect.

The SCMaglev is a magnetic levitation (maglev) railway system developed by Central Japan Railway Company and the Railway Technical Research Institute.

Linimo, formally the Aichi Rapid Transit Tobu Kyuryo Line is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya. While primarily built to serve the Expo 2005 fair site, the line has since operated to serve the local community.

StarTram is a proposed space launch system propelled by maglev technology. The initial Generation 1 facility is proposed to launch cargo only from a mountain peak at an altitude of 3 to 7 kilometres using an evacuated tube remaining at local surface level. Annual orbital lift was estimated at approximately 150,000 tons. More advanced technology is required for a Generation 2 system for passengers, with a longer track instead gradually curving up at its end to the thinner air at 22 kilometres (72,000 ft) altitude, supported by magnetic levitation, reducing g-forces when each capsule transitions from the vacuum tube to the atmosphere. A SPESIF 2010 presentation stated that Generation 1 could be completed by the year 2020 or later if funding began in 2010, and Generation 2 by 2030 or later.
ROMAG was a personal rapid transit (PRT) system produced by the American company Rohr, Inc. It featured a linear induction motor that was arranged to provide both traction and suspension in a magnetic levitation system.

Tracked Hovercraft was an experimental high-speed train developed in the United Kingdom during the 1960s. It combined two British inventions, the hovercraft and linear induction motor, in an effort to produce a train system that would provide 250 mph (400 km/h) inter-city service with lowered capital costs compared to other high-speed solutions. Substantially similar to the French Aérotrain and other hovertrain systems of the 1960s, Tracked Hovercraft suffered a similar fate to these projects when it was cancelled as a part of wide budget cuts in 1973.

A hovertrain is a type of high-speed train that replaces conventional steel wheels with hovercraft lift pads, and the conventional railway bed with a paved road-like surface, known as the track or guideway. The concept aims to eliminate rolling resistance and allow very high performance, while also simplifying the infrastructure needed to lay new lines. Hovertrain is a generic term, and the vehicles are more commonly referred to by their project names where they were developed. In the UK they are known as tracked hovercraft, in the US they are tracked air-cushion vehicles. The first hovertrain was developed by Jean Bertin in the early 1960s in France, where they were marketed as the Aérotrain before being abandoned by the French government.

Otis Hovair Transit Systems is a type of hovertrain used in low-speed people mover applications. Traditional people mover systems used wheeled vehicles propelled by electric motors or cable traction, the Hovair replaces the wheels with a hovercraft lift pad. The aim is to reduce guideway complexity and vehicle maintenance. Another benefit is the system's ability to move in all directions, including sideways. The Hovair is the only hovertrain system to be used in commercial service.

Magnetic levitation (maglev) or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. Magnetic force is used to counteract the effects of the gravitational force and any other forces.