The CarterCopter is an experimental compound autogyro developed by Carter Aviation Technologies in the United States to demonstrate slowed rotor technology. On 17 June 2005, the CarterCopter became the first rotorcraft to achieve mu-1 (μ=1), an equal ratio of airspeed to rotor tip speed, but crashed on the next flight and has been inoperable since. It is being replaced by the Carter Personal Air Vehicle.

A jet pack, rocket belt, rocket pack or flight pack is a device worn as a backpack which uses jets to propel the wearer through the air. The concept has been present in science fiction for almost a century and the first working experimental devices were demonstrated in the 1960s.

The Hiller YH-32 Hornet was an American ultralight helicopter built by Hiller Aircraft in the early 1950s. It was a small and unique design because it was powered by two Hiller 8RJ2B ramjet engines mounted on the rotor blade tips which weigh 13 lb (5.9 kg) each and deliver an equivalent of 45 hp (34 kW) for a total of 90 hp (67 kW). Versions of the HJ-1 Hornet were built for the United States Army and the United States Navy in the early 1950s.
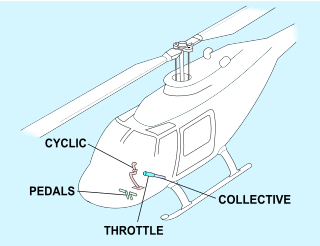
Helicopter flight controls are used to achieve and maintain controlled aerodynamic helicopter flight. Changes to the aircraft flight control system transmit mechanically to the rotor, producing aerodynamic effects on the rotor blades that make the helicopter move in a desired way. To tilt forward and back (pitch) or sideways (roll) requires that the controls alter the angle of attack of the main rotor blades cyclically during rotation, creating differing amounts of lift at different points in the cycle. To increase or decrease overall lift requires that the controls alter the angle of attack for all blades collectively by equal amounts at the same time, resulting in ascent, descent, acceleration and deceleration.

The SoloTrek XFV was a single-person VTOL aircraft. It was first flown in December 2001 by Millennium Jet Inc, a private company run by Michael Moshier. Millennium Jet subsequently changed its name to Trek Aerospace Inc. The SoloTrek pilot maintained a standing position and was propelled by two ducted fans located above and on either side of the user, leading some to class it as a type of backpack helicopter. It ran for around 2 hours on gasoline fuel. According to Michael Moshier, its inventor and designer, SoloTrek was capable of hovering for up to two hours, flying at 100 km/h and travelling more than 200 km.

On a helicopter, the main rotor or rotor system is the combination of several rotary wings with a control system, that generates the aerodynamic lift force that supports the weight of the helicopter, and the thrust that counteracts aerodynamic drag in forward flight. Each main rotor is mounted on a vertical mast over the top of the helicopter, as opposed to a helicopter tail rotor, which connects through a combination of drive shaft(s) and gearboxes along the tail boom. The blade pitch is typically controlled by the pilot using the helicopter flight controls. Helicopters are one example of rotary-wing aircraft (rotorcraft). The name is derived from the Greek words helix, helik-, meaning spiral; and pteron meaning wing.

A tip jet is a jet nozzle at the tip of some helicopter rotor blades, used to spin the rotor, much like a Catherine wheel firework. Tip jets replace the normal shaft drive and have the advantage of placing no torque on the airframe, thus not requiring the presence of a tail rotor. Some simple monocopters are composed of nothing but a single blade with a tip rocket.

A quadcopter, also called quadrocopter, or quadrotor is a type of helicopter or multicopter that has four rotors.

A gyrodyne is a type of VTOL aircraft with a helicopter rotor-like system that is driven by its engine for takeoff and landing only, and includes one or more conventional propeller or jet engines to provide forward thrust during cruising flight. During forward flight the rotor is unpowered and free-spinning, like an autogyro, and lift is provided by a combination of the rotor and conventional wings. The gyrodyne is one of a number of similar concepts which attempt to combine helicopter-like low-speed performance with conventional fixed-wing high-speeds, including tiltrotors and tiltwings.

A rotorcraft or rotary-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotary wings or rotor blades, which generate lift by rotating around a vertical mast. Several rotor blades mounted on a single mast are referred to as a rotor. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines a rotorcraft as "supported in flight by the reactions of the air on one or more rotors".

A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of short take-off and landing (STOL) or short take-off and vertical landing (STOVL) aircraft cannot perform without a runway.
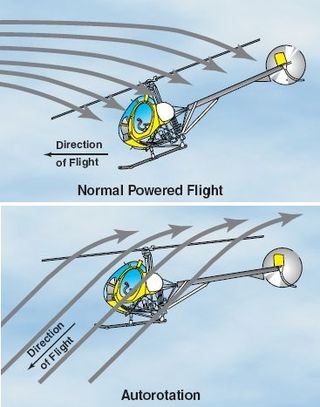
Autorotation is a state of flight in which the main rotor system of a helicopter or other rotary-wing aircraft turns by the action of air moving up through the rotor, as with an autogyro, rather than engine power driving the rotor. The term autorotation dates to a period of early helicopter development between 1915 and 1920, and refers to the rotors turning without the engine. It is analogous to the gliding flight of a fixed-wing aircraft. Some trees have seeds that have evolved wing-like structures that enable the seed to spin to the ground in autorotation, which helps the seeds to disseminate over a wider area.

The McDonnell XV-1 is an experimental Convertiplane developed by McDonnell Aircraft for a joint research program between the United States Air Force and the United States Army to explore technologies to develop an aircraft that could take off and land like a helicopter but fly at faster airspeeds, similar to a conventional airplane. The XV-1 would reach a speed of 200 mph, faster than any previous rotorcraft, but the program was terminated due to the tip-jet noise and complexity of the technology which gave only a modest gain in performance.

The Gyrodyne RON Rotorcycle was a tiny, single-seat helicopter designed under contract for the United States Navy. in the mid-1950s. It later was redesigned for a U.S. Marine Corps requirement for a small personal helicopter that would fulfill an array of roles, including observation, liaison, small unit tactical maneuvers, and which could be dropped to downed airmen behind enemy lines to facilitate their escape.

The Martin Jetpack was a single-person aircraft under development. Despite its name, it did not use a jet pack as such, but ducted fans for lift. Martin Aircraft Company of New Zealand developed it, and unveiled it at the Experimental Aircraft Association's 2008 AirVenture in Oshkosh, Wisconsin, US. The US Federal Aviation Administration classified it as an experimental ultralight airplane.

The Hiller ROE Rotorcycle was a single-seat ultralight helicopter designed in 1953 for a military requirement. A total of 12 were produced for the United States Marine Corps. And in 1954, the Hiller Helicopters was selected by the US Navy's Bureau of Aeronautics to build this design of a one-man, foldable, self-rescue and observation helicopter. It featured a two-blade rotor system. Its original empty weight was 290 lb (132 kg).

The Solution F/Chretien Helicopter is a coaxial electric helicopter prototype designed and built by Pascal Chretien for the Solution F company in France. The aircraft is intended to be a demonstration and exploration of several key electrical power technologies for use in future hybrid helicopters. The helicopter is the first all electric helicopter to hover out of ground effect and set a Guinness World Record on August 12, 2011. It received an IDTechEx Electric Vehicles Land Sea & Air award in 2012. The prototype is on permanent display at the Musée de l'air et de l'espace in Paris le Bourget, France
Jetpack Aviation is a California-based company that produces jetpacks and other personal aircraft.

The Hoppi-Copter was a functional backpack helicopter developed by the American company Hoppi-Copters Inc. founded by Horace T. Pentecost in the 1940s. The original Hoppi-Copter consisted of two contra-rotating rotors on a pole attached to a motorized backpack. Although it was capable of flight, it was extremely hard to control.

The Hiller XH-44 Hiller-Copter is an American experimental helicopter designed by Stanley Hiller.


















