
Basidiomycota is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: agarics, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and Cryptococcus, the human pathogenic yeast.

Gymnosporangium is a genus of heteroecious plant-pathogenic fungi which alternately infect members of the family Cupressaceae, primarily species in the genus Juniperus (junipers), and members of the family Rosaceae in the subfamily Amygdaloideae. The common name cedar-apple rusts has been used for these fungi. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi, there was 57 species in the genus. In 2023, Species Fungorum lists up to 74 species.

Rusts are fungal plant pathogens of the order Pucciniales causing plant fungal diseases.

The Trichocomaceae are a family of fungi in the order Eurotiales. Taxa are saprobes with aggressive colonization strategies, adaptable to extreme environmental conditions. Family members are cosmopolitan in distribution, ubiquitous in soil, and common associates of decaying plant and food material.

Sordariomycetes is a class of fungi in the subdivision Pezizomycotina (Ascomycota). It is the second-largest class of Ascomycota, with a worldwide distribution that mostly accommodates terrestrial based taxa, although several can also be found in aquatic habitats. Some are phytopathogens that can cause leaf, stem, and root diseases in a wide variety of hosts, while other genera can cause diseases in arthropods and mammals.

The Pucciniaceae are a family of rust fungi that cause plant diseases, mainly on cereals such as wheat. The family contains over 4900 species: many of them in the type genus Puccinia.

Gyalectales is an order of lichen-forming fungi in the class Lecanoromycetes. It contains 5 families, 15 genera and about 550 species.

The Entolomataceae are a family of fungi in the order Agaricales. The family contains eight genera and 2250 species, the majority of which are in Entoloma. Basidiocarps are typically agaricoid, but a minority are cyphelloid. secotioid, or gasteroid. All produce pink basidiospores that are variously angular (polyhedral), ridged, or nodulose. Species are mostly saprotrophic, though a few are parasitic on other fungi. The family occurs worldwide.

Gymnosporangium globosum is a fungal plant pathogen that causes cedar-hawthorn rust.

Gymnosporangium juniperi-virginianae is a plant pathogen that causes cedar-apple rust. In virtually any location where apples or crabapples (Malus) and Eastern red cedar coexist, cedar apple rust can be a destructive or disfiguring disease on both the apples and cedars. Apples, crabapples, and eastern red cedar are the most common hosts for this disease. Similar diseases can be found on Quince and hawthorn and many species of juniper can substitute for the eastern red cedars.

Pucciniomycotina is a subdivision of fungus within the division Basidiomycota. The subdivision contains 10 classes, 21 orders, and 38 families. Over 8400 species of Pucciniomycotina have been described - more than 8% of all described fungi. The subdivision is considered a sister group to Ustilaginomycotina and Agaricomycotina, which may share the basal lineage of Basidiomycota, although this is uncertain due to low support for placement between the three groups. The group was known as Urediniomycetes until 2006, when it was elevated from a class to a subdivision and named after the largest order in the group, Pucciniales.
The Cintractiellaceae are a monotypic, family of smut fungi, in the order Cintractiellales, but unplaced beyond that. The family contains one genera, Cintractiella with 4 species. The family was circumscribed by mycologist Kálmán Vánky in 2003.

The Chaconiaceae are a family of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales. The family contained 8 genera and 75 species in 2008. By 2020, there were 8 genera and 84 species.

The Coleosporiaceae are a family of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales. The family contains 6 genera and 131 species. It was updated in 2020, to 7 genera and 173 species.
The Mikronegeriaceae were a family of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales: now incorporated into the Zaghouaniaceae. The family contained 4 genera and 13 species.
The Pucciniosiraceae are a family of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales. The family contains 10 genera and 57 species.
Achrotelium is a genus of rust fungi in family Zaghouaniaceae. The genus, previously placed in the Chaconiaceae, contains five species that are found in the USA, Philippines, India, and Zimbabwe.

Botryorhiza is a genus of rust fungi in the family Zaghouaniaceae. The genus, previously placed in the Chaconiaceae, is monotypic, containing the single species Botryorhiza hippocrateae, which grows on Hippocratea plants in Brazil and the Caribbean.

The Zaghouaniaceae are a family of rust fungus genera, some of which have long been considered incertae sedis in the order Pucciniales, based on the type genus Zaghouania. The classification of fungal taxa based on only morphological characteristics has long been recognised as problematical, so this order was reviewed over a long-term study using three DNA loci and published in 2021.
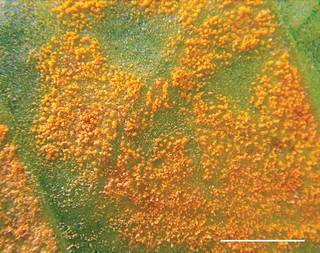
Hemileia is a genus of rust fungi, now placed in the family Zaghouaniaceae, but long considered incertae sedis in the order Pucciniales. This genus has a pan-tropical distribution and includes important crop plant pathogens, such as the causative organism of coffee leaf rust.














