
HAT-P-1b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the Sun-like star HAT-P-1, also known as ADS 16402 B. HAT-P-1 is the dimmer component of the ADS 16402 binary star system. It is located roughly 521 light years away from Earth in the constellation Lacerta. HAT-P-1b is among the least dense of any of the known extrasolar planets.
HD 147506 is a magnitude 8.7 F8 dwarf star that is somewhat larger and hotter than the Sun. The star is approximately 419 light years from Earth and is positioned near the keystone of Hercules. It is estimated to be 2 to 3 billion years old. There is one known transiting extrasolar planet.

HAT-P-2b is an extrasolar planet detected by the HATNet Project in May 2007. It orbits a class F star HAT-P-2,, located about 420 light-years away in the constellation Hercules.
The Hungarian Automated Telescope Network (HATNet) project is a network of six small fully automated "HAT" telescopes. The scientific goal of the project is to detect and characterize extrasolar planets using the transit method. This network is used also to find and follow bright variable stars. The network is maintained by the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian.

XO-3b is an exoplanet with about 11.79 times the mass of Jupiter, and it orbits its parent star in about 3.2 days. The radius of this object is 1.217 times that of Jupiter. Astronomers announced their discovery on May 30, 2007, at the American Astronomical Society in Honolulu, Hawaii. Its discovery is attributed to the combined effort of amateur and professional astronomers working together on the XO Project using a telescope located on the Haleakala summit in Hawaii.

HAT-P-4b is a confirmed extrasolar planet orbiting the star HAT-P-4 over 1000 light years away in Boötes constellation. It was discovered by transit on October 2, 2007, which looks for slight dimming of stars caused by planets that passed in front of them. It is the fourth planet discovered by the HATNet Project. It is also called BD+36 2593b, TYC 2569-01599-1b, 2MASS J15195792+3613467b, SAO 64638b.

WASP-6b is an extrasolar planet approximately 600 light years away in the constellation Aquarius. It was discovered in 2008, by the WASP survey, by astronomical transit across its parent star WASP-6. This planet orbits only 4% that of Earth-Sun distance. The planet has mass half that of Jupiter, but its insolation has forced a thermal expansion of its radius over that of Jupiter. The planet is an inflated Hot Jupiter. Starspots on the host star WASP-6 helped to refine the measurements of the mass and the radius of the planet.
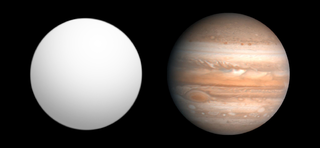
WASP-7b is an extrasolar planet discovered in 2008. This 5-day period planet is slightly smaller than Jupiter, roughly the same mass and more dense.
WASP-11/HAT-P-10 is a binary star. It is a primary main-sequence orange dwarf star. Secondary is M-dwarf with a projected separation of 42 AU. The system is located about 424 light-years away in the constellation Aries.

WASP-14b is an extrasolar planet discovered in 2008 by SuperWASP using the transit method. Follow-up radial velocity measurements showed that the mass of WASP-14b is almost eight times larger than that of Jupiter. The radius found by the transit observations show that it has a radius 25% larger than Jupiter. This makes WASP-14b one of the densest exoplanets known. Its radius best fits the model of Jonathan Fortney.

HAT-P-9b, formally named Alef, is an exoplanet approximately 1500 light years away in the constellation Auriga. This planet was found by the transit method on June 26, 2008. It has a mass 78% that of Jupiter and a radius 140% that of Jupiter. As with most transiting planets, this planet is a hot Jupiter, meaning this Jupiter-like planet orbits extremely close to its parent star, taking only 3.92 days to orbit.

HAT-P-8b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 720 light years away in the constellation of Pegasus, orbiting the 10th magnitude star GSC 02757-01152. This planet was discovered by transit on December 5, 2008. Despite the designation as HAT-P-8b, it is the 11th planet discovered by the HATNet Project. The mass of the planet is 50% more than Jupiter while the radius is also 50% more than Jupiter. The mass of this planet is exact since the inclination of the orbit is known, typical for transiting planets. This is a so-called “hot Jupiter” because this Jupiter-like gas giant planet orbits in a really close torch orbit around the star, making this planet extremely hot. The distance from the star is roughly 20 times smaller than that of Earth from the Sun, which places the planet roughly 8 times closer to its star than Mercury is from the Sun. The “year” on this planet lasts only 3 days, 1 hour, 49 minutes, and 54 seconds, compared with Earth's 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes, and 10 seconds in a sidereal year.
HAT-P-13, also known as GSC 03416-00543, is a G-type main sequence star approximately 800 light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. In 2009 it was discovered that this star is orbited by two massive planets, the innermost of which transits the star. This was the first known example of an extrasolar transiting planet with an additional planet in the same system.
HAT-P-13c is a substellar object orbiting the star HAT-P-13 located 698 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Ursa Major. A search for transits was negative, however only 72% of the possible transit configurations could be ruled out. With a mass at least 15.2 times that of Jupiter, it may be a massive planet or a small brown dwarf. The gravitational effect of this object on the inner transiting planet HAT-P-13b may allow a precise determination of the inner planet's internal structure.

HAT-P-14b, also known as WASP-27b, is an extrasolar planet located approximately 224.2 ± 0.6 parsecs (731.2 ± 2.0 ly) away in the constellation of Hercules, orbiting the 10th magnitude F-type main-sequence star HAT-P-14. This planet was discovered in 2010 by the HATNet Project using the transit method. It was independently detected by the SuperWASP project.
HAT-P-24b is an extrasolar planet discovered by the HATNet Project in 2010 orbiting the F8 dwarf star HAT-P-24. It is a hot Jupiter, with a mass three quarters that of Jupiter and a radius 20% larger.
HAT-P-17 is a K-type main-sequence star about 92.6 parsecs (302 ly) away. It has a mass of about 0.857 ± 0.039 M☉. It is the host of two planets, HAT-P-17b and HAT-P-17c, both discovered in 2010. A search for a binary companion star using adaptive optics at the MMT Observatory was negative. A candidate companion was detected by a spectroscopic search of high-resolution K band infrared spectra taken at the Keck observatory.
Kepler-13 or KOI-13 is a stellar triple star system consisting of Kepler-13A, around which an orbiting hot Jupiter exoplanet was discovered with the Kepler spacecraft in 2011, and Kepler-13B a common proper motion companion star which has an additional star orbiting it.
HD 146389, is a star with a yellow-white hue in the northern constellation of Hercules. The star was given the formal name Irena by the International Astronomical Union in January 2020. It is invisible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 9.4 The star is located at a distance of approximately 446 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −9 km/s. The star is known to host one exoplanet, designated WASP-38b or formally named 'Iztok'.
HAT-P-15 is a G-type main-sequence star about 630 light-years away. The star is older than Sun yet has a concentration of heavy elements roughly 190% of solar abundance. The star has no noticeable starspot activity.










