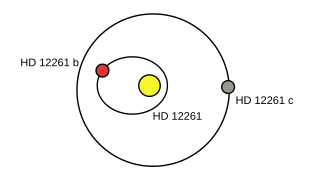
HD 12661 is a G-type main sequence star in the northern constellation of Aries. The star is slightly larger and more massive than the Sun, with an estimated age of seven billion years. It has two known extrasolar planets.
HD 168443 is an ordinary yellow-hued star in the Serpens Cauda segment of the equatorial constellation of Serpens. It is known to have two substellar companions. With an apparent visual magnitude of 6.92, the star lies just below the nominal lower brightness limit of visibility to the normal human eye. This system is located at a distance of 127 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −48.7 km/s.
HD 114783 is a star with two exoplanetary companions in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. With an apparent visual magnitude of 7.56 it is too faint to be visible with the unaided eye, but is an easy target for binoculars. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of 68.7 light years from the Sun, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −12 km/s.
HD 217107 is a yellow subgiant star approximately 65 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pisces. Its mass is very similar to the Sun's, although it is considerably older. Two planets have been discovered orbiting the star: one is extremely close and completes an orbit every seven days, while the other is much more distant, taking fourteen years to complete an orbit.
HD 38529 is a binary star approximately 138 light-years away in the constellation of Orion.
HD 142 is a wide binary star system in the southern constellation of Phoenix. The main component has a yellow-white hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.7. The system is located at a distance of 85.5 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +6 km/s.
HD 1237 is a binary star system approximately 57 light-years away in the constellation of Hydrus.
HD 40979 is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Auriga. The combined brightness of this group lies below the typical limit of visibility to the naked eye at an apparent visual magnitude of 6.74. It is located at a distance of approximately 108 light years from the Sun based on parallax. The system is receding with a radial velocity of +32 km/s. It has a relatively high rate of proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of 0.182″ per year.
HD 217107 b is an extrasolar planet approximately 65 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pisces. The planet was discovered orbiting the star HD 217107 approximately every seven days, classifying the planet as a hot Jupiter. Because of the planet's somewhat eccentric orbit, scientists were able to confirm another planet within the system.

HD 217107 c is an extrasolar planet approximately 64 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pisces. The planet was the second planet to be discovered orbiting the star HD 217107. HD 217107 c's existence was hypothesized in 1998 due to the eccentricity of the inner planet's orbit and confirmed in 2005 when radial velocity studies of the star indicated another, more distant and massive companion orbiting the star. The planet has an eccentric orbit lasting on order of a decade.

HD 12661 b is a giant exoplanet two and a half times the mass of Jupiter orbiting around the star HD 12661.
HD 92788 is a star in the equatorial constellation of Sextans. It has a yellow hue but is too dim to be visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 7.31. The star is located at a distance of 113 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −4.5 km/s. Two planets have been found in orbit around the star.
HD 40979 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star HD 40979, was detected from the Lick and Keck observatories and photometric observations at Fairborn Observatory reveal low-amplitude brightness variations in HD 40979. It is thought to be a large gas giant planet. It was discovered in 2002 by Debra Fischer.
HD 92788 b is an exoplanet located approximately 113 light-years away in the constellation of Sextans, orbiting the star HD 92788. The semimajor axis of this 3.68 Jupiter mass planet is 0.97 astronomical units, taking approximately 326 days to revolve.
HAT-P-8 is a magnitude 10 star located 750 light-years away in Pegasus. It is a F-type star about 28% more massive than the Sun. Two red dwarf companions have been detected around HAT-P-8. The first has a spectral type of M5V and has a mass of 0.22 M☉. The second is even less massive, at 0.18 M☉, and its spectral type is M6V.
HD 86226 is a G-type yellowish white star found in the constellation of Hydra.
HD 212771 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the G-type star HD 212771 approximately 364 light years away in the constellation Aquarius.

HD 114613 is a fifth magnitude yellow subgiant that lies 66.7 light-years away in the constellation of Centaurus. The star may be host to a long-period giant planet.
HD 219077 is a faint, yellow-hued star in the southern constellation of Tucana. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +6.12, which is near the lower limit on stars visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 34.25 mas as seen from Earth, it lies 95 light years from the Sun. HD 219077 is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −31.01, and has a relatively high proper motion.



