| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Volans [2] |
| Right ascension | 08h 40m 17.985s [3] |
| Declination | −64° 50′ 16.84″ [3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.58–8.66 [4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A7VkA0mA0 λ Boo [5] |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 8.81±0.02 [6] |
| Apparent magnitude (J) | 8.065±0.020 [6] |
| Apparent magnitude (H) | 8.021±0.067 [6] |
| Apparent magnitude (K) | 7.944±0.040 [6] |
| Variable type | α2 CVn [4] or Ellipsoidal and δ Sct [7] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −9.719 [3] mas/yr Dec.: 11.732 [3] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.1018±0.0150 mas [3] |
| Distance | 1,550 ± 10 ly (476 ± 3 pc) |
| Details | |
| primary | |
| Mass | 2.1 [8] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.3 [8] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.6 [5] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,900 [8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −1.0 [5] dex |
| secondary | |
| Mass | 2.0 [8] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.2 [8] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.6 [5] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,600 [8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −1.0 [5] dex |
| Age | 800 [7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| HD 74423, CD−64°342, SAO 250298, TYC 8934-1662-1, TIC 355151781 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
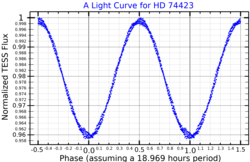
HD 74423 is a heartbeat binary star and one component pulsates on only one hemisphere. This is caused by tidal interaction with its partner. [7] The star is located in the Volans constellation.
HD 74423 is slightly variable in brightness. It fluctuates between magnitudes 8.58 and 8.66 every 19 hours. [4] The exact variability type is unclear. It was initially found in a search for α2 Canum Venaticorum variables and assumed to be one, but has since been considered to be a δ Scuti variable. [7] The spectrum shows unusually strong absorption lines of some iron peak elements, a characteristic of λ Boötis stars. Both components are thought to show the chemical peculiarity. [7]