Related Research Articles

21 Aquilae is a solitary variable star in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. It has the variable star designation V1288 Aql; 21 Aquilae is its Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a dim, blue-white hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of about 5.1. The star is located at a distance of around 680 light-years from Earth, give or take a 20 light-year margin of error. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of –5 km/s.
RV Caeli, also known as HD 28552, is a solitary, red hued variable star located in the southern constellation Caelum, the chisel. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.4, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. The object is located relatively far at a distance of 1,340 light years based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, but is rapidly receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 98 km/s.
HD 92589 is a double star in the constellation Antlia. The system has a combined apparent magnitude of 6.39, placing it near the limit of naked eye visibility. The system is located about 590 light years away based on its parallax shift and has a heliocentric radial velocity of 11 km/s. This indicates that it is drifting away from the Solar System.
HD 30442 is a solitary star in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 5.47 and is estimated to be 403 light years away from the Solar System. The object has a heliocentric radial velocity of −37 km/s, indicating that it is drifting closer.
HD 63399 is an orange hued star located in the southern constellation Puppis, the poop deck. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.45, placing it near the limit for naked eye visibility. Based on parallax measurements from Gaia DR3, the object is estimated to be 445 light years distant. It appears to be receding with a spectroscopic radial velocity of 28.5 km/s. At its current distance, HD 63399 is diminished by 0.29 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
HD 126209, also known as HR 5389, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Apus. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.06, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is estimated to be 560 light years distant. It appears to be approaching the Solar System with a fairly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of −8.1 km/s. De Mederios et al. (2014) found the radial velocity to be variable, making it a probable spectroscopic binary. Eggen (1993) lists it as a member of the old disk population.
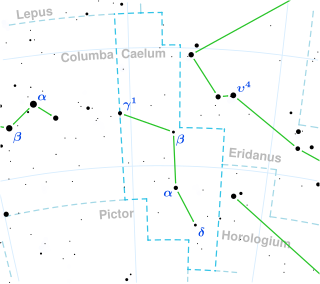
HD 39901 is an orange hued star located in the constellation Columba. It is also called HR 2069, which is the star's Bright Star Catalog designation. Eggen (1989) lists it as a member of the old disk population.

HD 121228 is a blue supergiant star located in the constellation Centaurus. The star is noted for its close visual proximity to the planetary nebula SuWt 2.
HD 49268 is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation Volans. It has an apparent magnitude of +6.49, placing it near the limit of naked eye visibility. Parallax measurements place the object at a distance of 456 light years; it is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 20.6 km/s.

Iota Mensae is a single star about 880 light years away in the faint constellation Mensa. It has a very slightly variable apparent magnitude of 6.0, making it visible with the naked eye under good skies.
HD 155448 is a quintuple star system consisting of 5 young B-type stars. With an apparent magnitude of 8.72, it is too dim to be visible with the naked eye.
HD 200044 is a solitary star in the equatorial constellation Delphinus. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.7, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. The object is located 598 light years away, but is approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −15.07 km/s.

HD 174387 is a solitary star in the southern constellation Telescopium. With an apparent magnitude of 5.49, it is faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under dark skies. Parallax measurements put the object at a distance of 810 light years and it is currently approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −28.1 km/s.

SY Equulei, also known as HD 203664, is a single variable star located in the equatorial constellation Equuleus. It has an average apparent magnitude of about 8.5, varying by a few hundredths of a magnitude, making it readily visible in binoculars and small telescopes, but not to the naked eye. The star is relatively far away at a distance of 8,000 light years and is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 48 km/s. At that distance, SY Equulei is dimmed by 0.19 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.
HD 37289, also known as HR 1916, is a solitary, orange hued star located in the northern circumpolar constellation Camelopardalis. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.61, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is estimated to be 308 light years distant. It appears to be approaching the Sun, having a heliocentric radial velocity of −20.7 km/s.

CW Octantis, also known as HD 148542, is a solitary, white hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.03, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements from Gaia DR3 place the object at a distance of 629 light years. It appears to be receding from the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of 7.1 km/s.
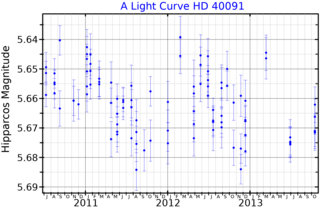
HD 40091, also known as HR 2082, is a solitary star located in the southern constellation Columba, the dove. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.54, making it faintly visible to the naked eye under ideal conditions. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is estimated to be 501 light years distant. However, it is rapidly receding with a high heliocentric radial velocity of 114 km/s.

PW Telescopii, also known as HD 183806 or simply PW Tel, is a solitary variable star located in the southern constellation Telescopium. It has an average apparent magnitude of 5.58, making it faintly visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia satellite, the star is estimated to be 395 light years distant. It appears to be approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −10 km/s. The value is somewhat constrained, having an uncertainty of 26%. At its current distance, PW Tel's brightness is diminished by 0.05 magnitudes due to interstellar dust.

HD 198716, also known as HR 7987 or 33 G. Microscopii, is a solitary star located in the southern constellation Microscopium. Eggen (1993) lists it as a member of the Milky Way's old disk population.
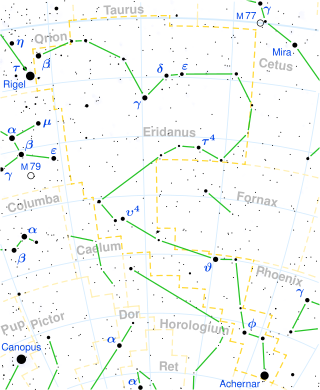
HD 27563, also known by the Bayer designation d Eridani, is a single star in Eridanus, in the direction of the Orion–Eridanus Superbubble, that is faintly visible to the naked eye at a magnitude of about 5.84. Cowley (1972) classifies this star as spectral type B5III, but Houk and Swift (1999) catalog it as B7II.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv: 2208.00211 . Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 . S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (March 2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27–L30. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H. ISSN 0004-6361.
- 1 2 3 Houk, N.; Cowley, A. P. (1975). University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. Volume I. Declinations −90° to −53°. Bibcode:1975mcts.book.....H.
- 1 2 Johnson, H. L.; Mitchell, R. I.; Iriarte, B.; Wisniewski, W. Z. (1966). "UBVRIJKL Photometry of the Bright Stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. 4: 99–110. Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- 1 2 Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv: 1606.08053 . Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. eISSN 1562-6873. ISSN 1063-7737. S2CID 119231169.
- 1 2 Kervella, Pierre; Arenou, Frédéric; Thévenin, Frédéric (2022). "Stellar and substellar companions from Gaia EDR3". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 657: A7. arXiv: 2109.10912 . Bibcode:2022A&A...657A...7K. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202142146 . eISSN 1432-0746. ISSN 0004-6361.
- 1 2 3 4 Stassun, Keivan G.; et al. (9 September 2019). "The Revised TESS Input Catalog and Candidate Target List". The Astronomical Journal. 158 (4): 138. arXiv: 1905.10694 . Bibcode:2019AJ....158..138S. doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/ab3467 . eISSN 1538-3881.
- 1 2 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365 . Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 . Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Anders, F.; et al. (February 2022). "Photo-astrometric distances, extinctions, and astrophysical parameters for Gaia EDR3 stars brighter than G = 18.5". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 658: A91. arXiv: 2111.01860 . Bibcode:2022A&A...658A..91A. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202142369 . eISSN 1432-0746. ISSN 0004-6361.
- 1 2 Hauck, B.; Curchod, A. (December 1980). "Properties of AM stars in the Geneva photometric system". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 92: 289–295. Bibcode:1980A&A....92..289H. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ↑ Gould, Benjamin Apthorp (1878). "Uranometria Argentina : brillantez y posicion de las estrellas fijas, hasta la septima magnitud, comprendidas dentro de cien grados del polo austral : con atlas". Resultados del Observatorio Nacional Argentino. 1. Bibcode:1879RNAO....1.....G.
- ↑ "HR 3544". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ↑ Renson, P.; Manfroid, J. (19 March 2009). "Catalogue of Ap, HgMn and Am stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 498 (3): 961–966. Bibcode:2009A&A...498..961R. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/200810788 . eISSN 1432-0746. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ↑ Hensberge, H.; Manfroid, J.; Schneider, H.; Maitzen, H. M.; Catalano, F. A.; Renson, P.; Weiss, W. W.; Floquet, M. (1984). "The frequency of Ap-stars with long rotation periods". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 132: 291. Bibcode:1984A&A...132..291H.
- ↑ Samus', N. N; Kazarovets, E. V; Durlevich, O. V; Kireeva, N. N; Pastukhova, E. N (2017). "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1". Astronomy Reports. 61 (1): 80. Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. S2CID 125853869.