
Q-ships, also known as Q-boats, decoy vessels, special service ships, or mystery ships, were heavily armed merchant ships with concealed weaponry, designed to lure submarines into making surface attacks. This gave Q-ships the chance to open fire and sink them.

ORP Orzeł was an Orzeł class submarine of the Polish Navy that served during World War II.

In warfare, ramming is a technique used in air, sea, and land combat. The term originated from battering ram, a siege engine used to bring down fortifications by hitting it with the force of the ram's momentum, and ultimately from male sheep. Thus, in warfare, ramming refers to hitting a target by running oneself into the target.

HMS Graph was a German Type VIIC U-boat captured and recommissioned by the British Royal Navy during World War II.

HMS Swordfish (61S) was a first-batch S-class submarine built for the Royal Navy during the 1930s. Commissioned in 1932, she was given the pennant number 61S and was assigned to the 2nd Submarine Flotilla.

HMS Wild Swan was an Admiralty modified W-class destroyer built for the Royal Navy. She was one of four destroyers ordered in 1918 from Swan Hunter and Wigham Richardson, Wallsend-on-Tyne under the 14th Order for Destroyers of the Emergency War Program of 1917–18. She was the second Royal Navy ship to carry the name, after the sloop HMS Wild Swan in 1876. Like her sisters, she was completed too late to see action in the First World War.

HMCS Huron was a Tribal-class destroyer that served in the Royal Canadian Navy in the Second World War and the Korean War. She was the first ship to bear this name, entering service in 1943. She was named for the Huron people. During the Second World War the vessel saw service in Operation Neptune in the Bay of Biscay and along the French coast in support of the invasion of Normandy and escorted convoys to the Soviet Union. Following the war, the ship was placed in reserve. The destroyer was activated in 1950 as a training ship, but with the onset of the Korean War, was modernized and deployed twice to Korea. Following the war, Huron reverted to a training ship and took part in Cold War-era North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) naval exercises until being paid off for the final time in 1963 and broken up for scrap in 1965.

HMS Simoom was a third-batch S-class submarine built for the Royal Navy during World War II. She was laid down on 14 July 1941 and launched on 12 October 1942.
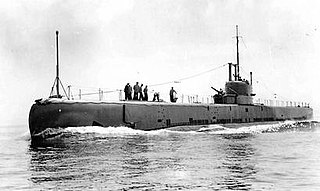
HMS Narwhal (N45) was one of the six ship class of Grampus-class mine-laying submarine of the Royal Navy. She was built by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow and launched 29 August 1935. She served in the Second World War in home waters. She was lost in the North Sea on 23 July 1940, probably sunk by German aircraft.

HMS P222 was a third-batch S-class submarine built for the Royal Navy during World War II. Commissioned in 1942, the boat had an uneventful first war patrol in the Alboran Sea. She intercepted the Vichy French merchant ship SS Mitidja in July, then provided protection for an Allied convoy to Malta in Operation Pedestal the next month. The navy intended that she was to be sighted on the surface by enemy aircraft to discourage potential attacks by surface warships. Though P222 did not encounter enemy forces, the convoy arrived at its destination on 15 August after sustaining severe losses. She then reconnoitred along the coast of Algeria in advance of Operation Torch, and was attacked by a French patrol ship, but sustained no damage.

Naval trawlers are vessels built along the lines of a fishing trawler but fitted out for naval purposes; they were widely used during the First and Second World Wars. Some, known in the Royal Navy as "Admiralty trawlers", were purpose-built to naval specifications; others were adapted from civilian use. Fishing trawlers were particularly suited for many naval requirements because they were robust vessels designed to work heavy trawls in all types of weather, and had large clear working decks. A minesweeper could be created by replacing the trawl with a mine sweep. Adding depth charge racks on the deck, ASDIC sonar below, and a 3-inch (76 mm) or 4-inch (102 mm) gun in the bow equipped the trawler for anti-submarine duties.
HMT Bedfordshire (FY141) was an armed naval trawler in the service of the Royal Naval Patrol Service during World War II. Transferred to the East Coast of the United States to assist the United States Navy with anti-submarine patrols, she was staffed by a British and Canadian crew. Bedfordshire was sunk by the German submarine U-558 on 11 May 1942 off the coast of Ocracoke Island in the Outer Banks of North Carolina, with the loss of all hands.

HMS Exmoor was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. She was a member of the first subgroup of the class, and saw service in the Second World War, before being sunk by German E-boats in 1941.
HM Trawler Arab was a trawler launched in 1936. At the outbreak of World War II, she became a naval trawler serving in the Royal Naval Patrol Service. Lieutenant Richard Been Stannard won the Victoria Cross (VC) while serving as her commander during the Namsos campaign in 1940. The Admiralty returned her to her owners in 1945 and she remained in commercial service until she was scrapped at Ghent in 1963.

HMS Puffin (L52), was a Kingfisher-class sloop of the British Royal Navy, built in the 1930s, that saw service during World War II. The ship was laid down on 12 June 1935 by Alexander Stephens and Sons, based at Linthouse in Glasgow, launched on 5 May 1936, and commissioned on 6 August 1936.

SS Espagne was a Belgian cargo ship that was torpedoed by the Imperial German Navy submarine SM UC-71 in the English Channel off St Catherine's Point, Isle of Wight, England, while she was travelling from Le Havre, France to Newport, Wales.
The following index is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Wikipedia's articles on recreational dive sites. The level of coverage may vary:

HMS Puckeridge was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy and first and so far only warship to bear the Name. The vessel was ordered on 4 September 1939 as part of the 1939 wartime emergency program. She was laid down on 1 January 1940 at the J. Samuel White yard, East Cowes, on the Isle of Wight, launched on 6 March 1941 and commissioned on 30 July 1941.














