
Kassel is a city on the Fulda River in northern Hesse, in central Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Kassel and the district of the same name, and had 201,048 inhabitants in December 2020. The former capital of the state of Hesse-Kassel, it has many palaces and parks, including the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Kassel is also known for the documenta exhibitions of contemporary art. Kassel has a public university with 25,000 students (2018) and a multicultural population.

Göttingen is a district in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Northeim and Goslar, and by the states of Thuringia and Hesse. The capital is the university city of Göttingen.

Kassel is one of the three Regierungsbezirke of Hesse, Germany, located in the north of the state. It was created in 1866 when Prussia annexed the Electorate of Hesse, forming part of the new Province of Hesse-Nassau. It was enlarged following the incorporation of the former Free State of Waldeck in 1929. From 1944 to 1945 it formed its own province: Kurhessen. After World War II it became part of Greater Hesse within the American Occupation Zone, the precursor to the modern state of Hesse. In its modern form it consists of 138 municipalities.

Kassel district is a district in the north of Hesse, Germany. Neighboring districts are Northeim, Göttingen, Werra-Meißner, Schwalm-Eder, Waldeck-Frankenberg, Höxter. The independent city of Kassel is nearly completely surrounded by the district.

The Hoher Meißner is a mountain massif with a height of 753.6 m and is located in the Meißner-Kaufunger Wald nature park in Hesse, Germany.

The Kaufungen Forest is a range of steep, wooded hills straddling the border between the states of Hesse and Lower Saxony in central Germany. It takes its name from the town Kaufungen.

Guxhagen is a municipality in Schwalm-Eder district in northern Hesse, Germany.

Bad Emstal is a municipality in the district of Kassel, in Hesse, Germany. It is situated 19 km southwest of Kassel, Germany.
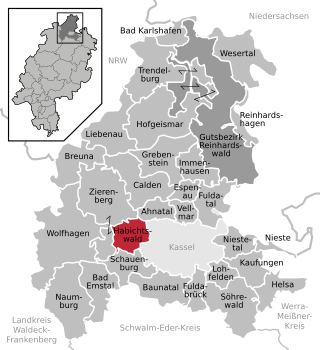
Habichtswald is a municipality in the district of Kassel, in Hesse, Germany. It is located 12 kilometers west of Kassel.
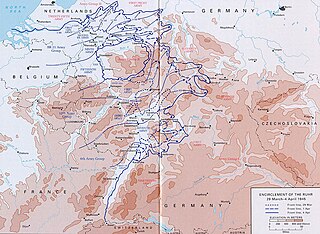
The Battle of Kassel was a four-day struggle between the U.S. Army and the German Army in April 1945 for Kassel, a medium-sized city 140 kilometers northeast of Frankfurt am Main, which also is the second-largest city in Hesse. The battle resulted as the U.S. Third Army pushed northeast from the region of Frankfurt and Mainz. The battle opened on April 1, 1945 and ended with an American victory three days later. Opposing the Third Army's 80th Infantry Division were an infantry replacement battalion, some heavy tanks, and anti-aircraft guns. Although the Germans gave battle at Kassel, their army was on the brink of collapse as the Western Allies and the Red Army made deep inroads into Germany. The defense of Kassel did not materially impede the Allied advance, and, one month after the battle ended, Germany was forced to capitulate.

Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe is a landscape park in Kassel, Germany. The area of the park is 2.4 square kilometres, making it the largest European hillside park, and second largest park on a hill slope in the world. Construction of the Bergpark, or "mountain park", began in 1689 at the behest of the Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel and took about 150 years. The park is open to the public today. Since 2013, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its monumental Baroque architecture and its unique fountains and water features.

The West Hesse Highlands, also known as the West Hessian Lowlands and Highlands, are a heavily forested region of the Central Uplands in Germany. These highlands lie mainly within the state of Hesse, between that part of the Rhenish Massif right of the Rhine in the west, the Weser Uplands to the north, the Hessian Central Uplands to the east and the Wetterau to the south.

The West Hesse Depression is part of the West Hesse Highlands and Lowlands region in the north of the German state of Hesse. Like the East Hesse Depression, it is a series of separate depressions that form a natural corridor and have been an important historical trade route.

The Reinhardswald is a range of hills up to 472.2 m above sea level (NN) and covering an area of over 200 km² in the Weser Uplands in the district of Kassel, Hesse (Germany). Of this, 183 km² are part of the unincorporated area known as Gutsbezirk Reinhardswald.
The Kiffing is a range of hills, relatively small in area and up to 344.1 m above sea level (NN), in the district of Kassel in the German state of Hesse.

The Alheimer is a hill in Hesse, Germany.

Hoher Dörnberg is a high hill in Hesse, Germany. It is 579 metres (1900 ft) high. It is located in the Habichtswald around 11 km (7 mi) northwest of the city of Kassel in Kassel district.

Heiligenberg is a mountain of Hesse, Germany. It is located between Altendorf to the north and Heimarshausen to the south of the Naumburgh township in the district of Kassel. It lies in the East Waldeck Border Lowlands of the West Hesse Highlands, and is covered with a mixed deciduous and evergreen forest. It lies within the Habichtswald Nature Park. The Elbe, a northern tributary of the Eder, runs east past the mountain.

The Langenberg, also colloquially called the Langenberge (plural) due to its several and widely spaced hilltops, is a hill range of the German Central Uplands which covers an area of over 22 km² and reaches a height of 556.7 m above sea level (NHN) at the Schwengeberg. It is a natural region in the Habichtswald Highlands in the counties of Kassel and Schwalm-Eder-Kreis in North Hesse.


















