Hamburger Flugzeugbau (HFB) was an aircraft manufacturer, located primarily in the Finkenwerder quarter of Hamburg, Germany. Established in 1933 as an offshoot of Blohm & Voss shipbuilders, it later became an operating division within its parent company and was known as Abteilung Flugzeugbau der Schiffswerft Blohm & Voss from 1937 until it ceased operation at the end of World War II. In the postwar period it was revived as an independent company under its original name and subsequently joined several consortia before being merged to form MBB. It participates in the present day Airbus and European aerospace programs.

The Junkers Ju 287 was an aerodynamic testbed built in Nazi Germany to develop the technology required for a multi-engine jet bomber. It was powered by four Junkers Jumo 004 engines, featured a revolutionary forward-swept wing, and apart from the wing was assembled largely from components scavenged from other aircraft. It was one of the first jet propelled aircraft built with fixed landing gear.

The Hamburger Flugzeugbau Ha 137 was a German ground-attack aircraft of the 1930s. It was Blohm & Voss' entry into the contest to equip the re-forming Luftwaffe with its first purpose-built dive bomber. Although the contest would eventually be won by the Junkers Ju 87, the Ha 137 demonstrated that B&V's Hamburger Flugzeugbau, not even two years old at this point, had a truly capable design team of its own. One Ha 137 single-seat prototype competed against the Henschel Hs 123 at Rechlin.
The Tupolev Tu-98 was a prototype swept wing jet bomber developed by Tupolev for the Soviet Union.

The IAI Westwind is a business jet initially produced by Aero Commander as the 1121 Jet Commander. Powered by twin GE CJ610 turbojets, it first flew on January 27, 1963 and received its type certification on November 4, 1964, before the first delivery. The program was bought by Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI) in 1968, which stretched it slightly into the 1123 Westwind, and then re-engined it with Garrett TFE731 turbofans into the1124 Westwind. The 16,800–23,500 lb (7.6–10.7 t) MTOW aircraft can carry up to 8 or 10 passengers, and 442 were produced until 1987.

The Piaggio PD.808 was an Italian business jet built by Piaggio. It was designed as a joint venture between Piaggio and Douglas Aircraft Company of Long Beach, California, United States.

The General Electric CJ610 is a non-afterburning turbojet engine derived from the military J85, and is used on a number of civilian business jets. The model has logged over 16.5 million hours of operation. Civilian versions have powered business jets such as the Learjet 23 and the Hamburger Flugzeugbau HFB 320 Hansa Jet. The engines are also used in the flyable Messerschmitt Me 262 reproductions built by the Me 262 Project in the United States.
Hans Wocke was a German airplane designer.

The Messerschmitt P.1101 was a single-seat, single-jet fighter project of World War II, developed in response to the 15 July 1944 Emergency Fighter Program which sought a second generation of jet fighters for the Third Reich. A characteristic feature of the P.1101 prototype was that the sweep angle of the wings could be changed before flight, a feature further developed in later variable-sweep aircraft such as the Bell X-5 and Grumman XF10F Jaguar.

The Blohm & Voss Ha 142 was a German four-engined long-distance monoplane, developed to meet a Luft Hansa requirement for its transatlantic airmail service. The first of several prototypes flew on 11 October 1938 and they saw some service in other roles during the Second World War.

The Learjet 24 is an American six-to-eight-seat twin-engine, high-speed business jet, which was manufactured by Learjet as the successor to the Learjet 23.
The Sukhoi Su-15 was a prototype Soviet all-weather interceptor which never reached production. The name was later reused for an entirely different 1960s interceptor, see Sukhoi Su-15.
The Dassault M.D.320 Hirondelle was a French 14-seat utility transport aircraft of the 1960s, designed and built by Dassault Aviation, in prototype form only.

The Viper Aircraft ViperJet is a small homebuilt jet aircraft by Viper Aircraft Corporation. It is a conventional, low-wing monoplane with swept wings and tail and two seats in tandem under a bubble canopy. The jet intakes are located at the sides of the fuselage and the tricycle undercarriage is retractable. Construction throughout is of composite materials.

The EM-10 Bielik is a low cost Polish military training aircraft prototype, built by Margański & Mysłowski Zakłady Lotnicze, first flown on 4 June 2003. The single engine aircraft has a composite fuselage with a light alloy aft section and the pressurized cockpit is fitted with ejection seats.
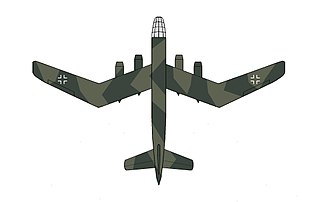
The Blohm & Voss Bv P 188 was a long-range, heavy jet bomber design project by the Blohm & Voss aircraft manufacturing division during the last years of the Third Reich. It featured a novel W-wing planform with variable incidence.

The Gerhard Neumann Museum is an aviation museum located in the German village of Niederalteich in Bavaria. The museum chronicles the work of German aero engine designer, Gerhard Neumann, in particular the General Electric J79 turbojet and Lockheed F-104 Starfighter which this engine powered. Many aerospace exhibits are on display including fixed-wing aircraft and aircraft engines.
The Hamburger Flugzeugbau 209 was a postwar design project for a twin-turboprop medium-range transport.
The Hamburger Flugzeugbau 314 was a postwar design project for a twin-turbojet medium-range transport.

The AJI T-610 Super Pinto was a trainer aircraft developed by American Jet Industries (AJI) as a modified version of the Temco TT Pinto.


















