
Galinthias is an African genus of praying mantises ; it is the type genus for the new family Galinthiadidae.

Mantidae is one of the largest families in the order of praying mantises, based on the type species Mantis religiosa; however, most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family in the order, and many references still use the term "mantid" to refer to any mantis. Technically, however, "mantid" refers only to members of the family Mantidae, and not the 14 remaining families of mantises. Some of the most recent classifications have promoted a number of the mantid subfamilies to the rank of family, e.g. Iridopterygidae, Sibyllidae, Tarachodidae, Thespidae, and Toxoderidae, while other classifications have reduced the number of subfamilies without elevating to higher rank.

Empusidae is a family of plant-mimicking mantises, consisting of 10 genera, holding almost 30 species. Unlike many other mantis families, the Empusidae are a monophyletic lineage. Empusidae mantises are ambush predators, with mouthparts adapted to feeding on other insects and small animals. The majority of Empusidae species are distributed throughout Africa, but they are also found in Southeast Asia and in the southern parts of Europe.
Idolomorpha is a genus of mantises in the family Empusidae.

Hymenopodinae is a subfamily of the mantis family Hymenopodidae.

Flower mantises are those species of praying mantises that mimic flowers. Their coloration is an example of aggressive mimicry, a form of camouflage in which a predator's colours and patterns lure prey. The flower mantises are not a natural group with a single ancestor, but most of the species are in the family Hymenopodidae. Their behaviours vary, but typically involve climbing a plant, and then staying still until a prey insect comes within range. Many species of flower mantises are popular as pets.

Gongylus is a genus of praying mantises in the family Empusidae. Characterized by extremely slender limbs with large appendages, at least one species is kept as a pet by hobbyists. Males of the species are capable of flight.
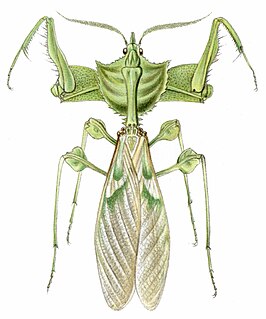
Idolomantis is a genus of praying mantises in the family Empusidae. It is represented by a single species, Idolomantis diabolica, commonly known as the devil's flower mantis or giant devil's flower mantis. It is one of the largest species of praying mantises, and is possibly the largest that mimics flowers

Rhombodera is a genus of praying mantises native to Asia and possessing common names such as shield mantis, hood mantis, and leaf mantis because of their extended, leaf-like thoraxes.

Chlidonoptera is an African genus of praying mantis in the family Hymenopodidae and tribe Hymenopodini.
Titanodula formosana is a species of praying mantis in the subfamily Hierodulinae. T. formosana is found in Taiwan, Malaysia and the Sunda islands.
Rhombodera javana is a species of praying mantises in the family Mantidae, found in China and the island of Java in Indonesia.
Rhombodera papuana is a species of praying mantises in the family Mantidae. It is found on the island of New Guinea.
Rhombodera sjostedti is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae, found on the Tenimbar Islands of Indonesia.

Empusa fasciata is a species of praying mantis in the genus Empusa in the order Mantodea.

Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They have triangular heads with bulging eyes supported on flexible necks. Their elongated bodies may or may not have wings, but all Mantodea have forelegs that are greatly enlarged and adapted for catching and gripping prey; their upright posture, while remaining stationary with forearms folded, has led to the common name praying mantis.

Helvia is a genus of praying mantises in the family Hymenopodidae found in Southeast Asia. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species, Helvia cardinalis.

Galinthiadidae is a family of 24 African mantis species in four genera.
Thespinae is a subfamily of mantids in the family Thespidae. There are 16 genera and at least 40 described species: found in Australasia, Central and South America.

Haaniinae is a subfamily of mantids, now placed in the new (2019) family Haaniidae; species can found in Asia.















